|
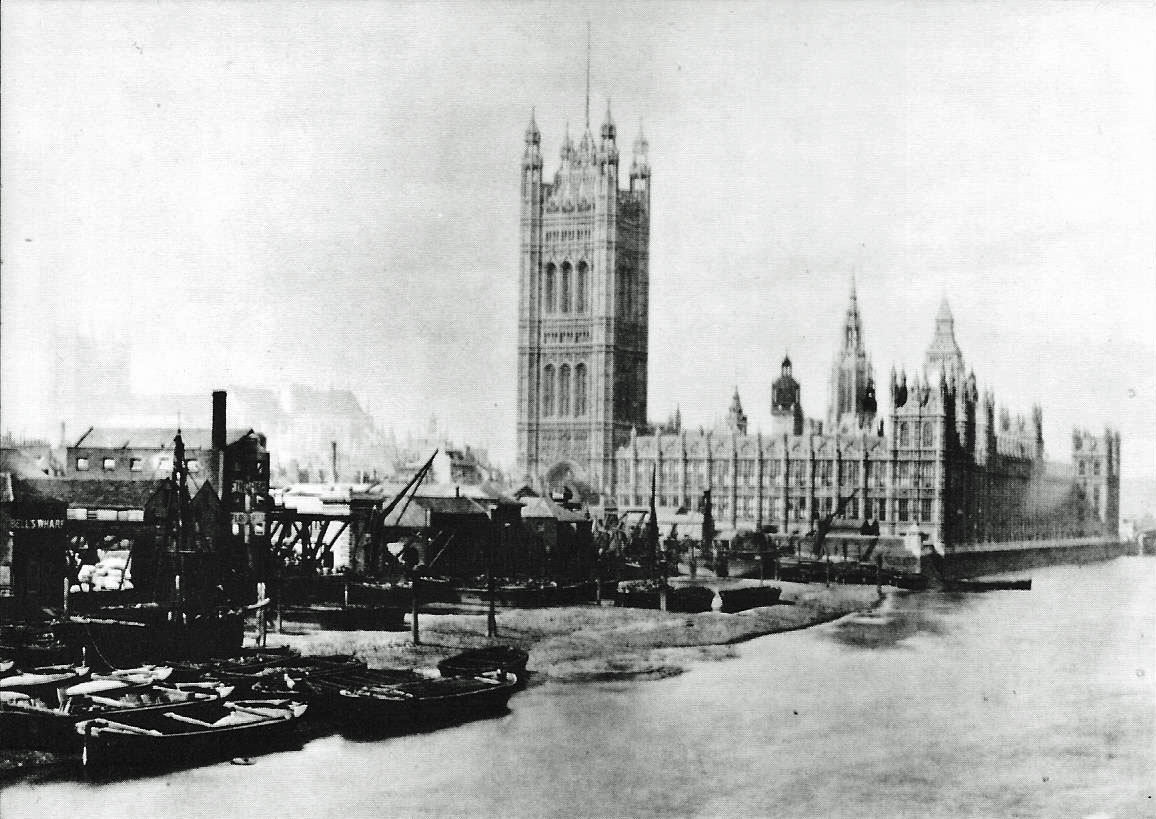
Thames Embankment
The Thames Embankment was built as part of the London Main Drainage (1859-1875) by the Metropolitan Board of Works, a pioneering Victorian civil engineering project which housed intercept sewers, roads and underground railways and embanked the River Thames. It consisted of the Victoria Embankment and Chelsea Embankment on the north side and the Albert Embankment on the south. Designed by the Chief Engineer Joseph Bazalgette, it modernised London's infrastructure, improving public health, mobility, and the image of the British capital. History There had been a long history of failed proposals to embank the Thames in central London. Embankments along the Thames were first proposed by Christopher Wren in the 1660s, then in 1824 former soldier and aide to George IV of the United Kingdom, George IV, Sir Frederick Trench (British Army officer), Frederick Trench suggested an embankment known as 'Trench's Terrace' from Blackfriars, London, Blackfriars to Charing Cross. Trench brought a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thames Embankment, London, England-LCCN2002696941
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn. The river rises at Thames Head in Gloucestershire and flows into the North Sea near Tilbury, Essex and Gravesend, Kent, via the Thames Estuary. From the west, it flows through Oxford (where it is sometimes called the Isis), Reading, Henley-on-Thames and Windsor. The Thames also drains the whole of Greater London. The lower reaches of the river are called the Tideway, derived from its long tidal reach up to Teddington Lock. Its tidal section includes most of its London stretch and has a rise and fall of . From Oxford to the estuary, the Thames drops by . Running through some of the drier parts of mainland Britain and heavily abstracted for drinking water, the Thames' discharge is low considering its length and breadth: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
London Sewerage System
The London sewer system is part of the water infrastructure serving London, England. The modern system was developed during the late 19th century, and as London has grown the system has been expanded. It is currently owned and operated by Thames Water and serves almost all of Greater London. History During the early 19th century the River Thames was an open sewer, with disastrous consequences for public health in London, including cholera epidemics. These were caused by enterotoxin-producing strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Although the contamination of the water supply was correctly diagnosed by John Snow (physician), Dr John Snow in 1849 as the method of communication, up to the outbreak of 1866 it was believed that Miasma theory, miasma, or bad air, was responsible. Proposals to modernise the sewerage system had been made in the early 1700s but the costs of such a project deterred progress. Further proposals followed in 1856, but were again neglected due to the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or as the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent home counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, opening on 10 January 1863 as the world's first underground passenger railway. The Metropolitan is now part of the Circle line (London Underground), Circle, District line, District, Hammersmith & City line, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric locomotive, electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines with of track. However, the Underground does not cover most southern parts of Greater London; there are only 33 Underground stations south of the River Thames. The system's List of London Underground stations, 272 stations collectively accommodate up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Circle Line (London Underground)
The Circle line is a spiral-shaped London Underground line, running from Hammersmith in the west to Edgware Road and then looping around central London back to Edgware Road. The railway is below ground in the central section and on the loop east of Paddington. Unlike London's deep-level lines, the Circle line tunnels are just below the surface and are of similar size to those on British main lines. Printed in yellow on the Tube map, the line serves 36 stations, including most of London's main line termini. Almost all of the route, and all the stations, are shared with one or more of the three other sub-surface lines, namely the District, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. On the Circle and Hammersmith & City lines combined, over 141 million passenger journeys were recorded in 2019. The first section became operational in 1863 when the Metropolitan Railway opened the world's first underground line between Paddington and with wooden carriages and steam locomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
District Line
The District line is a London Underground line running from in the east and Edgware Road tube station (Circle, District and Hammersmith & City lines), Edgware Road in the west to in west London, where it splits into multiple branches. One branch runs to in south-west London and a short branch, with a limited service, only runs for one stop to . The main route continues west from Earl's Court to after which it divides again into two western branches, to Richmond station (London), Richmond and . Printed in green on the Tube map, the line serves 60 stations (more than any other Underground line) over . It is the only Underground line to use a bridge to traverse the River Thames, crossing on both the Wimbledon and Richmond branches. The track and stations between and are shared with the Hammersmith & City line, and between and and on the Edgware Road branch they are shared with the Circle line (London Underground), Circle line. Some of the stations between and are shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blackfriars Bridge
Blackfriars Bridge is a road and foot traffic bridge over the River Thames in London, between Waterloo Bridge and Blackfriars Railway Bridge, carrying the A201 road. The north end is in the City of London near the Inns of Court and Temple Church, along with Blackfriars station. The south end is in the London Borough of Southwark, near the Tate Modern art gallery and the Oxo Tower. Opened in the 1860s, it replaced an earlier bridge from the 1760s. History The first fixed crossing at Blackfriars was a long toll bridge designed in an Italianate style by Robert Mylne and constructed with nine semi-elliptical arches of Portland stone. Beating designs by John Gwynn and George Dance, it took nine years to build, opening to the public in 1769. It was the third bridge across the Thames in the then built-up area of London, supplementing the ancient London Bridge, which dated from several centuries earlier, and Westminster Bridge. It was originally named "William Pitt Bridge" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Palace Of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and is located in London, England. It is commonly called the Houses of Parliament after the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two legislative chambers which occupy the building. The palace is one of the centres of political life in the United Kingdom; "Westminster" has become a metonym for the UK Parliament and the British Government, and the Westminster system of government commemorates the name of the palace. The Elizabeth Tower of the palace, nicknamed Big Ben, is a landmark of London and the United Kingdom in general. The palace has been a Grade I listed building since 1970 and part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1987. The building was originally constructed in the eleventh century as a royal palace and was the primary residence of the kings of England until 1512, when a fire destroyed the royal apartments. The monarch moved to the adjacent Palace of Whitehall, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Victoria Tower Gardens
Victoria Tower Gardens is a public park along the north bank of the River Thames in London, adjacent to the Victoria Tower, at the south-western corner of the Palace of Westminster. The park, extends southwards from the Palace to Lambeth Bridge, between Millbank and the river. It forms part of the Thames Embankment. Victoria Tower Gardens is a Grade II* listed park created in two stages in 1879–81 and 1913–14. It is in a conservation area, is partly within the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Westminster, and is designated a zone of Monument Saturation. History The northern part of the gardens was acquired by the government under the Houses of Parliament Act 1867 in order to reduce the fire risk to the Palace of Westminster from the wharves there. There was disagreement about whether at least some of the land should be built on, but eventually the newspaper retailer William Henry Smith donated £1,000 towards laying it out as an open space and Parliament paid the remaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Millbank
Millbank is an area of central London in the City of Westminster. Millbank is located by the River Thames, east of Pimlico and south of Westminster. Millbank is known as the location of major government offices, Burberry headquarters, the Millbank Tower and prominent art institutions such as Tate Britain and the Chelsea College of Art and Design. History The area derives its name from a watermill owned by Westminster Abbey that once stood at a site close to present day College Green, London, College Green. John Norden, Norden's survey, taken during the reign of Elizabeth I in 1573, records the existence of such a mill although much of the area that comprises Millbank today, was referred to by Samuel Pepys and others as Tothill Fields. Described as a place of plague pits and a "low, marshy locality" suitable for shooting snipe in the nearby "bogs and quagmires". After Cromwell's victory at the Battle of Worcester in September 1651, some 4,000 defeated Royalists were imprisoned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cheyne Walk
Cheyne Walk is a historic road in Chelsea, London, England, in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. It runs parallel with the River Thames. Before the construction of Chelsea Embankment reduced the width of the Thames here, it fronted the river along its whole length. Location At its western end, Cheyne Walk meets Cremorne Road end-on at the junction with Lots Road. The Walk runs alongside the River Thames until Battersea Bridge where, for a short distance, it is replaced by Chelsea Embankment with part of its former alignment being occupied by Ropers Gardens. East of Old Church Street and Chelsea Old Church, the Walk runs along the north side of Albert Bridge Gardens and Chelsea Embankment Gardens parallel with Chelsea Embankment. At the north end of Albert Bridge, the Walk merges with Chelsea Embankment. The Walk ends at Royal Hospital Road. At the western end between Lots Road and Battersea Bridge is a collection of residential houseboats that have been ''in sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battersea Bridge
Battersea Bridge is a five-span arch bridge with cast-iron girders and granite piers crossing the River Thames in London, England. It is situated on a sharp bend in the river, and links Battersea south of the river with Chelsea to the north. The bridge replaced a ferry service that had operated near the site since at least the middle of the 16th century. The first Battersea Bridge was a toll bridge commissioned by John, Earl Spencer, who had recently acquired the rights to operate the ferry. Although a stone bridge was planned, difficulties in raising investment meant that a cheaper wooden bridge was built instead. Designed by Henry Holland, it was initially opened to pedestrians in November 1771, and to vehicle traffic in 1772. The bridge was inadequately designed and dangerous both to its users and to passing shipping, and boats often collided with it. To reduce the dangers to shipping, two piers were removed and the sections of the bridge above them were strengthened wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lamorna
Lamorna () is a village, valley and cove in west Cornwall, England, UK. It is on the Penwith peninsula approximately south of Penzance. Lamorna became popular with the artists of the Newlyn School, including Alfred Munnings, Laura Knight and Harold Knight, and is also known for former residents Derek and Jean Tangye who farmed land and wrote "The Minack Chronicles". Toponymy First recorded as ''Nansmorno'' (in 1305), than ''Nansmurnou'' (1309), ''Nansmorne'' (1319), ''Nansmornou'' (1339), ''Nansmorna'' (1387) and ''Namorna'' (1388). In Cornish ''Nans'' means valley, and the 2nd element is possibly ''mor'', which means sea. Geography Lamorna Cove is at the SE end of a north-west to south-east valley. The cove is delineated by Carn-du (Black Rock) on the eastern side and Lamorna Point on the western side. The valley is privately owned from The Wink (public house) down to the cove, which is reached by a narrow lane to the car park and quay. The small village, half a mile i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |