|
Thallide
Thallides are compounds containing anions composed of thallium. Thallium may occur as a monatomic ion (Tl5− in LiMg2Tl), as a Metal cluster compound, cluster of several atoms (e.g. Tl48−), or as a polyatomic structure Tlnn− in thallides. They are a subclass of trielides, which also includes gallides and Indide, indides. A more general classification is polar intermetallics, as clusters contain delocalized multicentre bonds. Thallides were discovered by Eduard Zintl in 1932. Mixed-anion compounds, Mixed anion compounds with thallides include Halide, halides (Bromide, bromides and Chloride, chlorides), Oxide, oxides, and tetrelates (silicate, germanate). Production Thallide compounds can be produced by melting metals together in a tantalum crucible under an inert argon atmosphere. However if arsenic is included in the mix, it can react with the crucible wall. A low temperature production route, is to dissolve an alkali metal in liquid ammonia, and use that to reduce a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
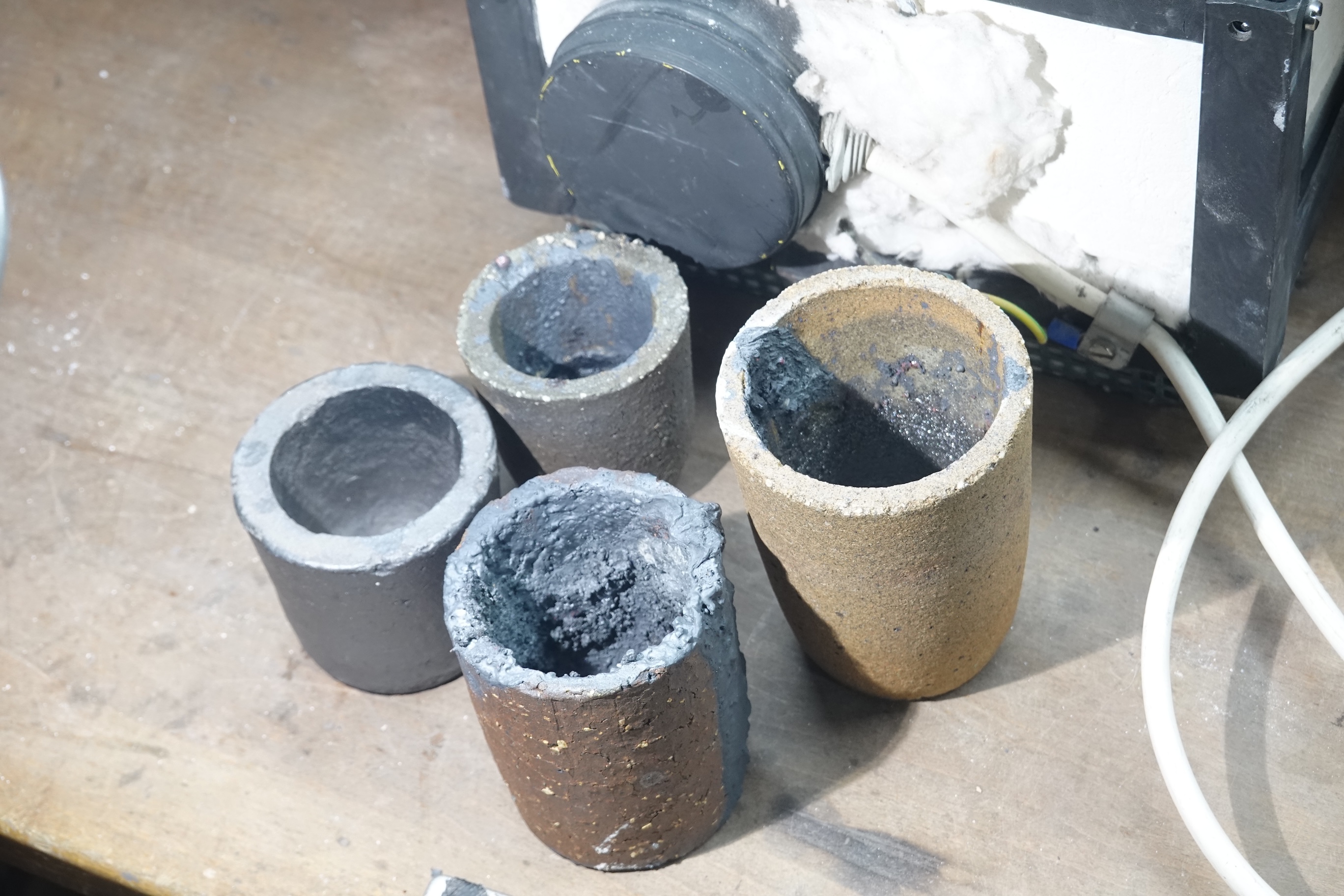
Crucible
A crucible is a container in which metals or other substances may be melted or subjected to very high temperatures. Although crucibles have historically tended to be made out of clay, they can be made from any material that withstands temperatures high enough to melt or otherwise alter its contents. History Typology and chronology The form of the crucible has varied through time, with designs reflecting the process for which they are used, as well as regional variation. The earliest crucible forms derive from the sixth/fifth millennium B.C. in Eastern Europe and Iran. Chalcolithic Crucibles used for copper smelting were generally wide shallow vessels made from clay that lacks refractory properties which is similar to the types of clay used in other ceramics of the time. During the Chalcolithic period, crucibles were heated from the top by using blowpipes.Hauptmann A., 2003, ''Developments in copper Metallurgy During the Fourth and Third Millennia B.C. at Feinan'', Jordan, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auride
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
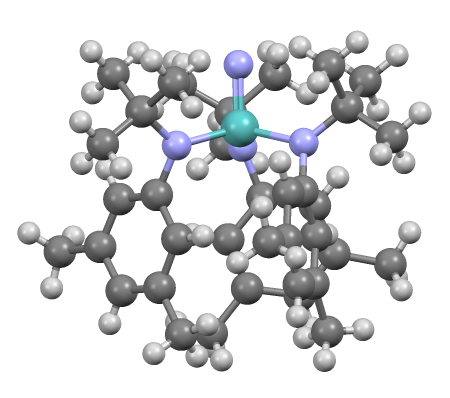
Pentagonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, a pentagonal bipyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the centre with seven ligands at the corners of a pentagonal bipyramid. A perfect pentagonal bipyramid belongs to the molecular point group ''D5h''. The pentagonal bipyramid is a case where bond angles surrounding an atom are not identical (see also trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry). This is one of the three common shapes for heptacoordinate transition metal complexes, along with the capped octahedron and the capped trigonal prism. Pentagonal bipyramids are claimed to be promising coordination geometries for lanthanide-based single-molecule magnets, since they present no extradiagonal crystal field terms, therefore minimising spin mixing, and all of their diagonal terms are in first approximation protected from low-energy vibrations, minimising vibronic coupling. Examples * Iodine heptafluoride (IF7) with 7 bonding groups * Rhenium heptafluoride (ReF7) * Peroxo chromium Chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix '' octa''. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo(CO)6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, , which is not octahedral in the mathematical sense due to the orientation of the bonds, is referred to as octahedral. The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Amides
Metal amides (systematic name metal azanides) are a class of coordination compounds composed of a metal center with amide ligands of the form NR2−. Amido complexes of the parent amido ligand NH2− are rare compared to complexes with diorganylamido ligand, such as dimethylamido. Amide ligands have two electron pairs available for bonding. File:Tris(dimethylamino)aluminium dimer.png, Tris(dimethylamino)aluminium dimer File:Ti(NMe2)4.png, Tetrakis(dimethylamino)titanium File:Ta(NMe2)5.png, Pentakis(dimethylamido)tantalum Geometry and structure In principle, the M-NX2 group could be pyramidal or planar. The pyramidal geometry is not observed. In many complexes, the amido is a bridging ligand. Some examples have both bridging and terminal amido ligands. Bulky amide ligands have a lesser tendency to bridge. Amide ligands may participate in metal-ligand π-bonding giving a complex with the metal center being co-planar with the nitrogen and substituents. Metal bis(trimethylsilyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wade-Mingos Rules
In chemistry the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory (PSEPT) provides electron counting rules useful for predicting the structures of clusters such as borane and carborane clusters. The electron counting rules were originally formulated by Kenneth Wade, and were further developed by others including Michael Mingos; they are sometimes known as Wade's rules or the Wade–Mingos rules. The rules are based on a molecular orbital treatment of the bonding. These notes contained original material that served as the basis of the sections on the 4''n'', 5''n'', and 6''n'' rules. These rules have been extended and unified in the form of the Jemmis ''mno'' rules. Predicting structures of cluster compounds Different rules (4''n'', 5''n'', or 6''n'') are invoked depending on the number of electrons per vertex. The 4''n'' rules are reasonably accurate in predicting the structures of clusters having about 4 electrons per vertex, as is the case for many boranes and carboranes. For such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium Iodide
Thallium iodide can refer to: * Thallium(I) iodide (thallium monoiodide), TlI * Thallium triiodide Thallium triiodide, more precisely thallium(I) triiodide is a chemical compound of thallium and iodine with empirical formula . Unlike the other thallium trihalides, which contain thallium(III), is actually a thallium(I) salt containing thallium( ..., TlI3 {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, causing damage to cells and tissues. For this reason it is excreted by most animals in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is notoriously toxic. It occurs naturally in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. It has various Allotropes of arsenic, allotropes, but only the grey form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is also a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices, and a component of the III–V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the persistent tox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |