|
Telescoping (mechanics)
Telescoping in mechanics describes the movement of one part sliding out from another, lengthening an object (such as a telescope or the lift arm of an aerial work platform) from its rest state. In modern equipment this can be achieved by a hydraulics, but pulleys are generally used for simpler designs such as extendable ladders and amateur radio antennas. See also * Telescoping bolt * Telescopic cylinder * Telescoping (rail cars) In a railway accident, telescoping occurs when the underframe of one vehicle overrides that of another, and smashes through the second vehicle's body. The term is derived from the resulting appearance of the two vehicle bodies: the body of one ... Mechanics Simple machines References {{classicalmechanics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescopic
A telescope is an instrument designed for the observation of remote objects. Telescope(s) also may refer to: Music * The Telescopes, a British psychedelic band ** The Telescopes (album) * ''Telescope'' (album), by Circle, 2007 * ''The Telescope'' (album), by Her Space Holiday, 2006 * ''Telescopes'' (EP), by Waking Ashland, 2006 * "Telescope" (song), by Hayden Panettiere, 2012 * "Telescope", a song by Cheryl Cole from '' A Million Lights'', 2012 * "Telescopes", a song by Reks from ''Grey Hairs'', 2008 Other media * ''Telescope'' (TV series), a 1963–1973 Canadian documentary program * "The Telescope" (''BoJack Horseman''), a 2014 television episode * ''The Telescope'' (magazine), an American monthly for amateur astronomers 1931–1941 * ''The Telescope'' (Magritte), a 1963 painting by René Magritte * Telescope, a type of dolly zoom film/video shot * ''The Telescope'', a 1957 play by R. C. Sherriff Other uses * Telescope (horse) (foaled 2010), an Irish Thoroughbred raceh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
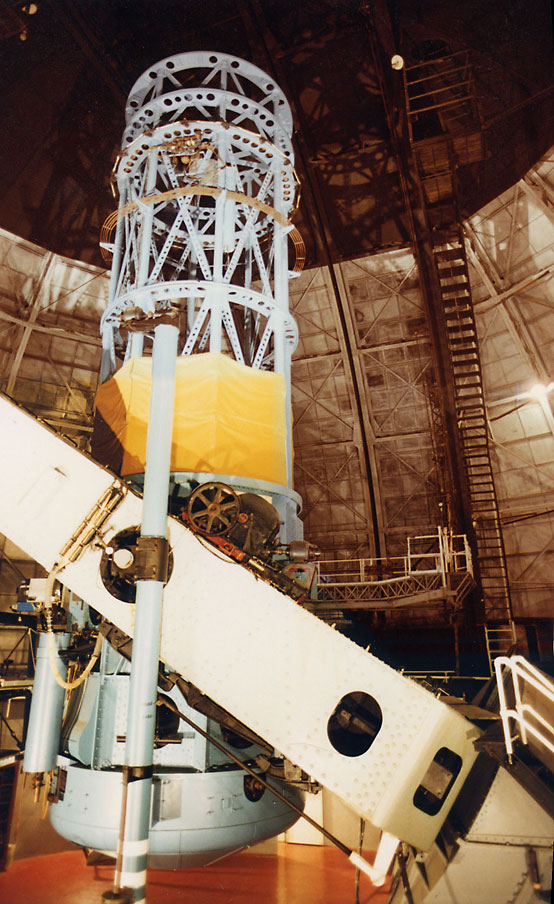
Telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes with glass lenses and were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy. The reflecting telescope, which uses mirrors to collect and focus light, was invented within a few decades of the first refracting telescope. In the 20th century, many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Work Platform
An aerial work platform (AWP), also an aerial device, aerial lift, boom lift, bucket truck, cherry picker, elevating work platform (EWP), mobile elevating work platform (MEWP), or scissor lift, is a mechanical device used to provide temporary access for people or equipment to inaccessible areas, usually at height. There are various distinct types of mechanized access platforms. They are generally used for temporary, flexible access purposes such as maintenance and construction work or by firefighters for emergency access, which distinguishes them from permanent access equipment such as elevators. They are designed to lift limited weights — usually less than a ton, although some have a higher safe working load (SWL) — distinguishing them from most types of cranes. They are usually capable of being set up and operated by a single person. Regardless of the task they are used for, aerial work platforms may provide additional features beyond transport and access, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
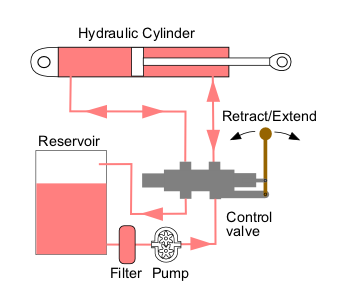
Hydraulic Drive System
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes. Hydraulic systems, like pneumatic systems, are based on Pascal's law which states that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system will transmit that pressure equally everywhere and in all directions. A hydraulic system uses an incompressible liquid as its fluid, rather than a compressible gas. The popularity of hydraulic machinery is due to the large amount of power that can be transferred through small tubes and flexible hoses, the high power density and a wide array of actuators that can make use of this power, and the huge multiplication of forces that c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulleys
Sheave without a rope A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft enabling a taut cable or belt passing over the wheel to move and change direction, or transfer power between itself and a shaft. A pulley may have a groove or grooves between flanges around its circumference to locate the cable or belt. The drive element of a pulley system can be a rope, cable, belt, or chain. History The earliest evidence of pulleys dates back to Ancient Egypt in the Twelfth Dynasty (1991–1802 BC) and Mesopotamia in the early 2nd millennium BC. In Roman Egypt, Hero of Alexandria (c. 10–70 AD) identified the pulley as one of six simple machines used to lift weights. Pulleys are assembled to form a block and tackle in order to provide mechanical advantage to apply large forces. Pulleys are also assembled as part of belt and chain drives in order to transmit power from one rotating shaft to another. Plutarch's ''Parallel Lives'' recounts a scene where Archimedes proved the effectivene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
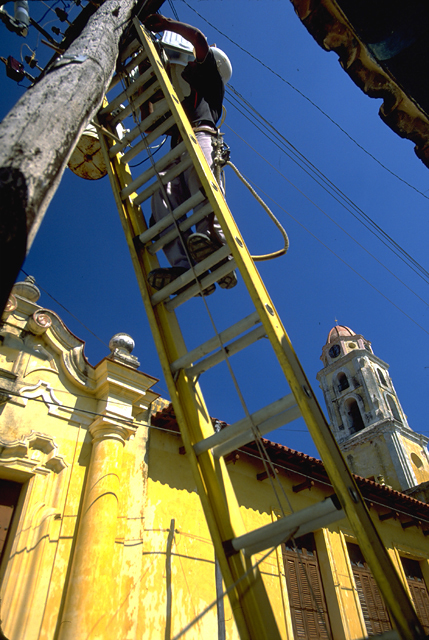
Ladders
A ladder is a Vertical direction, vertical or inclined set of rungs or Step (footing), steps commonly used for climbing or descending. There are two types: rigid ladders that are self-supporting or that may be leaned against a vertical surface such as a wall, and rollable ladders, such as those made of rope or aluminium, that may be hung from the top. The vertical members of a rigid ladder are called stringers or rails (US) or stiles (UK). Rigid ladders are usually portable, but some types are permanently fixed to a structure, building, or equipment. They are commonly made of metal, wood, or fiberglass, but they have been known to be made of tough plastic. Historical usages Ladders are ancient tools and technology. A ladder is featured in a Mesolithic rock painting that is at least 10,000 years old, depicted in the Cuevas de la Araña, Spider Caves in Valencia, Spain. The painting depicts two humans using a ladder to reach a wild honeybee nest to harvest honey. The ladder is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency radio spectrum, spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency, emergency communications. The term ''"radio amateur"'' is used to specify ''"a duly authorized person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without wikt:pecuniary, pecuniary interest"'' (either direct monetary or other similar reward); and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (police and fire), or two-way radio professional services (maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and ''amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through their recommended radio regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescoping Bolt
A telescoping bolt (also known as an overhung bolt) is a firearm bolt which telescopes over, that is, wraps around and past, the breech end of the barrel. This feature reduces the required length of a weapon such as a submachine gun significantly, and it allows compact designs to be balanced around the pistol grip in a way that gives "pointability" more like a pistol's. While it would be simpler and easier to shorten the bolt to fit completely behind the breech, the bolt must have a certain amount of mass in order to operate reliably with a given caliber. The telescoping bolt moves some of that mass forward of the bolt face, resulting in a bolt which may be longer overall, but is shorter behind the bolt face. Though technically a different, distinct concept, nearly all telescoping bolt submachine guns use a magazine A magazine is a periodical literature, periodical publication, print or digital, produced on a regular schedule, that contains any of a variety of subject- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescopic Cylinder
Telescopic cylinders are a special design of a hydraulic cylinder or pneumatic cylinder as well as pulley system which provide an exceptionally long output travel from a very compact retracted length. Typically the collapsed length of a telescopic cylinder is 20 to 40% of the fully extended length depending on the number of stages. Some pneumatic telescoping units are manufactured with retracted lengths of under 15% of overall extended unit length. This feature is very attractive to machine design engineers when a conventional single stage rod style actuator will not fit in an application to produce the required output stroke. Heavy duty telescopic cylinders are usually powered by oil hydraulics, whereas some lighter duty units could also be powered by compressed air. Telescopic cylinders are also referred to as telescoping cylinders and multi-stage telescopic cylinders. An application for telescopic cylinders commonly seen is that of the dump body on a dump truck used in a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescoping (rail Cars)
In a railway accident, telescoping occurs when the underframe of one vehicle overrides that of another, and smashes through the second vehicle's body. The term is derived from the resulting appearance of the two vehicle bodies: the body of one vehicle may appear to be slid inside the other like the tubes of a collapsible telescope – the body sides, roof and underframe of the latter vehicle being forced apart from each other. Telescoping often results in heavy fatalities if the cars telescoped are fully occupied. The car riding on top will often destroy the structure of the car below, crushing those on board (although the physics of the incident may reverse the cars' roles). The chances of telescoping can be reduced by use of anticlimbers and other structural systems which direct crash energy and debris away from the passenger and crew areas. One such energy absorbing system is the Green Buffer, winners of the 2023 Swedish Steel Prize, where a collapsing steel structure in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanics
Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of an object's position relative to its environment. Theoretical expositions of this branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece, for instance, in the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes (see History of classical mechanics and Timeline of classical mechanics). During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, Christiaan Huygens, and Isaac Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. As a branch of classical physics, mechanics deals with bodies that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of light. It can also be defined as the physical science that deals with the motion of and forces on bodies not in the quantum realm. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |