|
Taxoid
Taxoids are a class of derivatives from taxol, that is, paclitaxel. They were developed for their anticancer chemotherapeutic properties. Taxoids are usually treated as synonymous with taxanes; for example, a major medical dictionary defines the two terms with the same definition phrasing, and in another the phrasing varies slightly but conveys nearly identical meaning. Taxoids are chemically taxane-derived diterpenoids, which do occur in nature, in the genera ''Taxus'' and '' Austrotaxus'' of yew trees. The taxoids class and the taxanes class both include paclitaxel (trade names Taxol, Abraxane, Onxol, Nov-Onxol) and docetaxel Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cel ... (trade names Taxotere, Docecad). References Mitotic inhibitors {{antineoplastic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cell lung cancer. It may be used by itself or along with other chemotherapy medication. It is given by intravenous infusion, slow injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, cytopenia (low blood cell counts), numbness, shortness of breath, Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, nausea, vomiting, and muscle pains. Other severe side effects include allergic reactions and future cancers. Docetaxel induced pneumotoxicity is also a well recognized adverse effect which has to be identified timely and treated after withholding the drug. Side effects are more common in people with liver problems. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Docetaxel is in the taxane family of medications. It works by disrupting the normal function o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxane
Taxanes are a class of diterpenes. They were originally identified from plants of the genus ''Taxus'' (yews), and feature a taxadiene core. Paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere) are widely used as chemotherapy agents. Cabazitaxel was FDA approved to treat hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Taxanes present difficulties in Pharmaceutical formulation, formulation as medicines because they are poorly soluble in water. Production As their name suggests, taxanes were first derived from natural sources, but some have been semisynthesis, semisynthesized. Paclitaxel was originally derived from the Pacific yew tree. Taxanes are difficult to synthesize because of their numerous chiral centres—taxol has 11 of these. Recently, the presence of taxanes in the shells and leaves of ''Corylus avellana'' (the common hazel plant) has been reported. Mechanism of action The principal mechanism of action of the taxane class of drugs is the disruption of microtubule function. Microtubule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel, sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer. It is administered by intravenous injection. There is also an albumin-bound formulation. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, numbness, allergic reactions, muscle pains, and diarrhea. Other side effects include heart problems, increased risk of infection, and lung inflammation. There are concerns that use during pregnancy may cause birth defects. Paclitaxel is in the taxane family of medications. It works by interference with the normal function of microtubules during cell division. Paclitaxel was isolated in 1971 from the Pacific yew and approved for medical use in 1993. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It has been made from precursors, and through cell culture. Medical use Paclitaxel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy regimen, regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a cure, curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim only to prolong life or to Palliative care, reduce symptoms (Palliative care, palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''oncology#Specialties, medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' now means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to induce DNA damage (naturally occurring), DNA damage (so that DNA repair can augment chemotherapy). This meaning excludes the more-selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all synonyms of one another: they are ''synonymous''. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words may often be synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, ''long'' and ''extended'' in the context ''long time'' or ''extended time'' are synonymous, but ''long'' cannot be used in the phrase ''extended family''. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms. Lexic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diterpenoid
Diterpenes are a class of terpenes composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol. Some diterpenes are known to be antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory. Structures As with most terpenes a huge number of potential structures exists, which may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. Biosynthesis Diterpenes are derived from the addition of one IPP unit to FPP to form geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). From GGPP, structural diversity is achieved mainly by two classes of enzymes; the diterpene synthases and cytochromes P450. Several diterpenes are produced by plants and cyanobacteria. GGPP is also the precursor for the synthesis of the phytane by the action of the enzyme geranyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
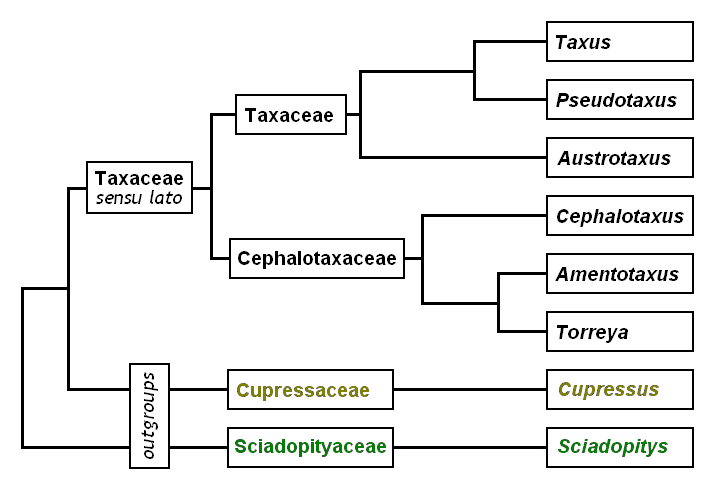
Taxus
''Taxus'' is a genus of coniferous trees or shrubs known as yews in the family Taxaceae. Yews occur around the globe in temperate zones of the northern hemisphere, northernmost in Norway and southernmost in the South Celebes. Some populations exist in tropical highlands. The oldest known fossil species are from the Early Cretaceous. Morphology They are relatively slow-growing and can be very long-lived, and reach heights of , with trunk girth averaging . They have reddish bark, lanceolate, flat, dark-green leaves long and broad, arranged spirally on the stem, but with the leaf bases twisted to align the leaves in two flat rows either side of the stem. The male cones are globose, across, and shed their pollen in early spring. Yews are mostly dioecious, but occasional individuals can be variably monoecious, or change sex with time. The seed cones are highly modified, each cone containing a single seed long partly surrounded by a modified scale which develops into a soft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrotaxus
''Austrotaxus spicata'', the New Caledonia yew or southern yew, is a species of yew, the sole species in the genus ''Austrotaxus''. It is related to the other yews in the genera ''Taxus'' and '' Pseudotaxus''. It is endemic to New Caledonia, occurring in the central and northern parts of the island at 300-1,350 m altitude. It is a dioecious coniferous shrub or small tree, reaching 5–20 m (rarely 25 m) tall with reddish bark. The leaves are lanceolate, flat, 8–12 cm long (up to 17 cm on young plants) and 4 mm broad, dark green above, with two paler green stomatal bands below; they are arranged spirally on the stem. The seed cones are drupe-like, 20–25 mm long, with a fleshy aril almost completely surrounding the single seed In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yew Tree
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees. It is most prominently given to any of various coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Taxus'': * European yew or common yew (''Taxus baccata'') * Pacific yew or western yew ('' Taxus brevifolia'') * Canadian yew ('' Taxus canadensis'') * Chinese yew (''Taxus chinensis'') * Japanese yew (''Taxus cuspidata'') * Florida yew ('' Taxus floridana'') * Mexican yew ('' Taxus globosa'') * Sumatran yew (''Taxus sumatrana'') * Himalayan yew ('' Taxus wallichiana'') * '' Taxus masonii'' (Eocene fossil yew) It is also used for any of various coniferous plants in the families Taxaceae and Cephalotaxaceae: * White-berry yew ('' Pseudotaxus chienii'') * New Caledonian yew or southern yew (''Austrotaxus spicata'') * Catkin-yew (''Amentotaxus sp.'') * Plum-yew (''Cephalotaxus sp.'') Various coniferous plants in the family Podocarpaceae, superficially similar to other yews, are also known by this name: * Prince Albert's yew (''Saxegotha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |