|
Taste Bud
Taste buds are clusters of taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, the cheek, and epiglottis. These structures are involved in detecting the five elements of taste perception: saltiness, sourness, bitterness, sweetness and savoriness (umami). A popular assumption assigns these different tastes to different regions of the tongue; in actuality, these tastes can be detected by any area of the tongue. Via small openings in the tongue epithelium, called taste pores, parts of the food dissolved in saliva come into contact with the taste receptors. These are located on top of the taste receptor cells that constitute the taste buds. The taste receptor cells send information detected by clusters of various receptors and ion channels to the gustatory areas of the brain via the seventh, ninth and tenth cra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
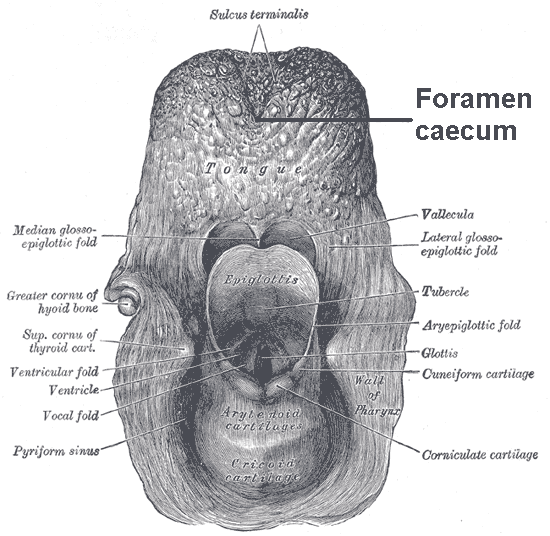
Terminal Sulcus (tongue)
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to bone. The four paired extri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Papillae
Lingual papillae (: papilla, ) are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circumvallate (or vallate), fungiform, filiform, and foliate. All except the filiform papillae are associated with taste buds. Structure In living subjects, lingual papillae are more readily seen when the tongue is dry. There are four types of papillae present on the tongue in humans: Filiform papillae Filiform papillae () are the most numerous of the lingual papillae. They are fine, small, cone-shaped papillae found on the anterior surface of the tongue. They are responsible for giving the tongue its texture and are responsible for the sensation of touch. Unlike the other kinds of papillae, filiform papillae do not contain taste buds. They cover most of the front two-thirds of the tongue's surface. They appear as very small, conical or cyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifurcation
Bifurcation or bifurcated may refer to: Science and technology * Bifurcation theory, the study of sudden changes in dynamical systems ** Bifurcation, of an incompressible flow, modeled by squeeze mapping the fluid flow * River bifurcation, the forking of a river into its distributaries * Bifurcation lake, a lake that flows into two different drainage basins * Bifurcated bonding, a single hydrogen atom participates in two hydrogen bonds * Bifurcated stick grip, a type of aircraft control column Other uses * Bifurcation (law), the division of issues in a trial See also * Aortic bifurcation, the point at which the abdominal aorta bifurcates into the left and right common iliac arteries * Tracheal bifurcation, or the carina of trachea (Latin: ''bifurcatio tracheae'') * Bifurcation diagram * Bifurcate merging, a kinship system * False dilemma A false dilemma, also referred to as false dichotomy or false binary, is an informal fallacy based on a premise that erroneously limits wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemoreceptor
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance ( endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemoreceptor is a neuron, or in the form of a neurotransmitter that can activate a nerve fiber if the chemoreceptor is a specialized cell, such as taste receptors, or an internal peripheral chemoreceptor, such as the carotid bodies. In physiology, a chemoreceptor detects changes in the normal environment, such as an increase in blood levels of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia) or a decrease in blood levels of oxygen (hypoxia), and transmits that information to the central nervous system which engages body responses to restore homeostasis. In bacteria, chemoreceptors are essential in the mediation of chemotaxis. Cellular chemoreceptors In prokaryotes Bacteria utilize complex long helical proteins as chemoreceptors, permitting signals to travel lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustentacular Cell
A sustentacular cell is a type of cell primarily associated with structural support, they can be found in various tissues. * Sustentacular cells of the olfactory epithelium (also called supporting cells or Sertoli cells) have been shown to be involved in the phagocytosis of dead neurons, odorant transformation and xenobiotic metabolism. * One type of sustentacular cell is the Sertoli cell, in the testicle. It is located in the walls of the seminiferous tubules and supplies nutrients to sperm. They are responsible for the differentiation of spermatids, the maintenance of the blood-testis barrier, and the secretion of inhibin, androgen-binding protein and Müllerian-inhibiting factor. * The organ of Corti in the inner ear and taste bud Taste buds are clusters of taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esopha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratinisation
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin in vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types: the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and the harder, derived forms found only among sauropsids (reptiles and birds). Spider silk is classified as keratin, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Papillae
Lingual papillae (: papilla, ) are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circumvallate (or vallate), fungiform, filiform, and foliate. All except the filiform papillae are associated with taste buds. Structure In living subjects, lingual papillae are more readily seen when the tongue is dry. There are four types of papillae present on the tongue in humans: Filiform papillae Filiform papillae () are the most numerous of the lingual papillae. They are fine, small, cone-shaped papillae found on the anterior surface of the tongue. They are responsible for giving the tongue its texture and are responsible for the sensation of touch. Unlike the other kinds of papillae, filiform papillae do not contain taste buds. They cover most of the front two-thirds of the tongue's surface. They appear as very small, conical or cyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Ebner's Glands
Von Ebner's glands, also called Ebner's glands or gustatory glands, are exocrine glands found in the mouth. More specifically, they are serous salivary glands which reside adjacent to the moats surrounding the circumvallate and foliate papillae just anterior to the posterior third of the tongue in its submucosa, anterior to the terminal sulcus. These glands are named after Victor von Ebner, an Austrian histologist. Von Ebner's glands secrete lingual lipase, beginning the process of lipid hydrolysis in the mouth. These glands empty their serous secretion into the base of the moats around the foliate and circumvallate papillae. This secretion presumably flushes material from the mouth to enable the taste buds to respond rapidly to changing stimuli. Von Ebner's glands are innervated by cranial nerve IX, the glossopharyngeal nerve. See also *List of distinct cell types in the adult human body The list of human cell types provides an enumeration and description of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumvallate Papillae
Lingual papillae (: papilla, ) are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circumvallate (or vallate), fungiform, filiform, and foliate. All except the filiform papillae are associated with taste buds. Structure In living subjects, lingual papillae are more readily seen when the tongue is dry. There are four types of papillae present on the tongue in humans: Filiform papillae Filiform papillae () are the most numerous of the lingual papillae. They are fine, small, cone-shaped papillae found on the anterior surface of the tongue. They are responsible for giving the tongue its texture and are responsible for the sensation of touch. Unlike the other kinds of papillae, filiform papillae do not contain taste buds. They cover most of the front two-thirds of the tongue's surface. They appear as very small, conical or cyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper Medulla oblongata, medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the Basal plate (neural tube), basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest. Structure From the anterior portion of the medulla oblongata, the glossopharyngeal nerve passes laterally across or below the Flocculus (cerebellar), flocculus, and leaves the skull through the central part of the jugular foramen. From the superior and inferior ganglia in jugular foramen, it has its own sheath of dura mater. The inferior ganglion on the inferior surface of petrous part of temporal is related with a tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |