|
Taphians
In Homeric Greece, the islands of Taphos (Τάφος) lay in the Ionian Sea off the coast of Acarnania in northwestern Greece, home of seagoing and piratical inhabitants, the Taphians (Τάφιοι). Penelope mentions the Taphian sea-robbers when she rebukes the chief of her suitors. Athena is disguised as Mentes, "lord of the Taphian men who love their oars", who accepts the hospitality of Telemachus and speeds him on his journey from Ithaca to Pylos. The Taphians dealt in slaves. By the time of Euripides, the islands were identified with the Echinades: in Euripides' '' Iphigeneia at Aulis'' (405 BCE), the chorus of women from Chalcis have spied the Hellenes' fleet and seen Eurytus who "led the Taphian warriors with the white oar-blades, the subjects of Meges, son of Phyleus, who had left the isles of the Echinades, where sailors cannot land." Modern scholars, such as the editors of the '' Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World'', identify the island of Taphos as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comaetho
In Greek mythology, Comaetho (; Ancient Greek: Κομαιθώ ''Komaithṓ'' means "bright-haired") is a name that may refer to: * Comaetho, a nymph of a spring who incessantly mingles her waters with those of the river god Cydnus, who in one passage of Nonnus' ''Dionysiaca'' is said to be her father, and in another her consort. * Comaetho, a beautiful girl of Patrae who served as priestess in the temple of Artemis Triclaria and was in love with Melanippus. They were not allowed to marry each other, so they met secretly in the temple and had sex together. The outraged goddess sent famine and plague upon the city; to propitiate her, the inhabitants had to sacrifice both Comaetho and Melanippus to her. Since then, a young man and a young girl were sacrificed to the goddess each year until, in accordance with the instructions of the Delphian oracle, a strange king (Eurypylus, son of Euaemon) introduced the worship of a new deity (Dionysus, whose image he brought from Troy) in Patrae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitryon
Amphitryon (; Ancient Greek: Ἀμφιτρύων, ''gen''.: Ἀμφιτρύωνος; usually interpreted as "harassing either side", Latin: Amphitruo), in Greek mythology, was a son of Alcaeus, king of Tiryns in Argolis. His mother was named either Astydameia, the daughter of Pelops and Hippodamia, or Laonome, daughter of Guneus, or else Hipponome, daughter of Menoeceus. Amphitryon was the brother of Anaxo (wife of Electryon), and Perimede, wife of Licymnius. He was a husband of Alcmene, Electryon's daughter, and stepfather of the Greek hero Heracles.Roman, L., & Roman, M. (2010). Mythology Born—according to tradition—in Tiryns, in Argolis in the eastern part of the Peloponnese, Amphitryon became King of Troezen and regent of Mycenae. He was a friend of Panopeus. Having accidentally killed his prospective father-in-law, Electryon, king of Mycenae, Amphitryon was driven out of Mycenae by Electryon's brother, Sthenelus. However, there is an earlier tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
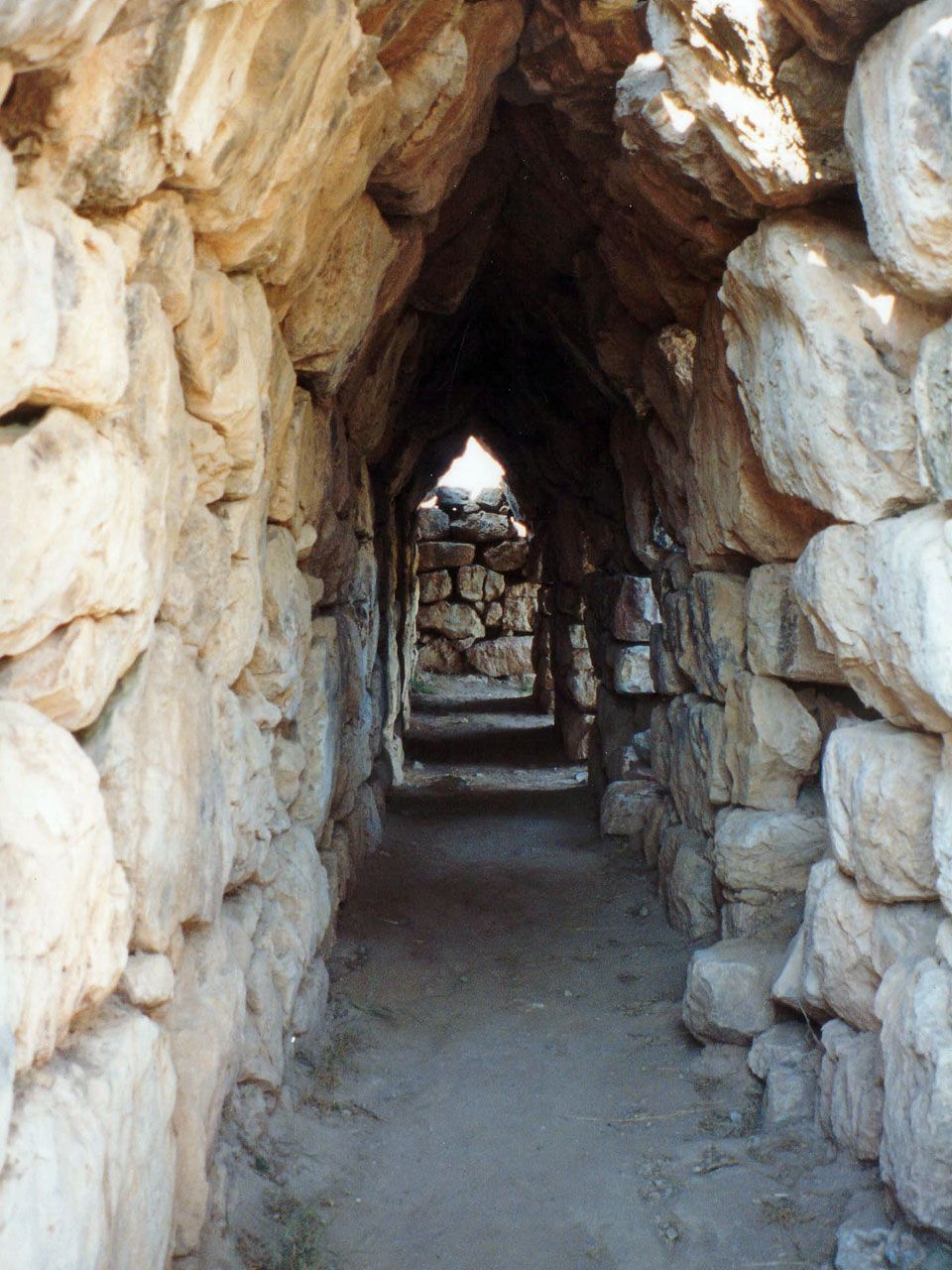
Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; ; or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines, Greece, Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos; and south of Corinth. The site is inland from the Saronic Gulf and built upon a hill rising above sea level. In the second millennium BC, Mycenae was one of the major centres of Greek civilisation, a military stronghold which dominated much of southern Greece, Crete, the Cyclades and parts of southwest Anatolia. The period of History of Greece, Greek history from about 1600 BC to about 1100 BC is called Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean in reference to Mycenae. At its peak in 1350 BC, the citadel and lower town had a population of 30,000 and an area of . The first correct identification of Mycenae in modern literature was in 1700, during a survey conducted by the Venetian engineer Francesco Vandeyk on behalf of Francesco Grimani, the Provveditore Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taphius
In Greek mythology, Taphius (Ancient Greek: Τάφιος) founded the city Taphos on the island of the same name, and was its king. He also gave his name to the Taphians, a people that inhabited Taphos and nearby islands, which formed part of Odysseus's kingdom at the time of the Trojan War. Family According to one genealogy, Taphius was the son of Poseidon and Hippothoë (daughter of Mestor, son of Perseus). However, according to another (more plausible) genealogy, Taphius's father was Pterelaus, the son of Lelex, who ruled in Acarnania. Both versions agree that Taphius had a son, also called Pterelaus ('Pterelaus II') who was immortalized by Poseidon who planted a golden hair in his head. Mythology Hippothoe was carried off by the god who brought her to the Echinadian Islands where he had intercourse with her. There she conceived Taphius who colonized Taphos and called the people Teleboans, because he had gone far from his native land (“telou ebē” τηλοῦ ἔβ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divided into 24 books. It follows the heroic king of Ithaca, Odysseus, also known by the Latin variant Ulysses, and his homecoming journey after the ten-year long Trojan War. His journey from Troy to Ithaca lasts an additional ten years, during which time he encounters many perils and all of his crewmates are killed. In Odysseus's long absence, he is presumed dead, leaving his wife Penelope and son Telemachus to contend with a group of unruly suitors competing for Penelope's hand in marriage. The ''Odyssey'' was first written down in Homeric Greek around the 8th or 7th century BC; by the mid-6th century BC, it had become part of the Greek literary canon. In antiquity, Homer's authorship was taken as true, but contemporary sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leleges
The Leleges (; ) were an aboriginal people of the Aegean Sea, Aegean region, before the Greek people, Greeks arrived. They were distinct from another pre-Hellenic people of the region, the Pelasgians. The exact areas to which they were native are uncertain, since they were apparently pre-literate and the only references to them are in ancient Greek sources. These references are casual and (it is alleged) sometimes fictitious. Likewise, little is known about the language of the ''Leleges''. Many Greek authors link the Leleges to the Carians of south-west Anatolia. Homer names the Leleges among the Trojan Battle Order, Trojan allies alongside the Carians, Pelasgians, Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonians and Paphlagonia, Gaucones. Etymology It is thought that the name ''Leleges'' is an exonym, in a long-extinct language, rather than an endonym (or autonym). That is, during the Bronze Age the word ''lulahi'' apparently meaning "strangers" was used in the Luwian language and in other Anatolian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mentes (King Of The Taphians)
In Greek mythology, Mentes (Ancient Greek: Μέντης ''Méntēs'') is the name of the King of the Taphians and the son of Anchialus. He is mentioned in the ''Odyssey''. Mythology In Book I, the Goddess Athena disguises herself as Mentes, an old family friend of Odysseus, when she goes to visit his son, Telemachus. Athena, disguised as him, tells Telemachus that he is sailing to the city of Temese with his own crew, claiming that he is in search of bronze. Mentes (truly Athena) recommends that Telemachus should call a counsel to try to remove the suitors of Penelope. Then he should see King Nestor at Pylos and King Menelaus of Sparta, to make inquiries as to the whereabouts of his father. Upon his return, but he should kill the suitors, either by stealth or publicly.Homer, ''Odysea'', 1,96-325. Although Mentes had hardly any appearances in Greek myths of earlier antiquity, he became a symbol of a guardian and a mentor. Later, his name got a derogatory flavor and became a sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrington Atlas Of The Greek And Roman World
The ''Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World'' is a large-format English language atlas of ancient Europe, Asia, and North Africa, edited by Richard Talbert, Richard J. A. Talbert. The time period depicted is roughly from Archaic Greece, archaic Greek civilization (pre-550 BC) through Late Antiquity (640 AD). The atlas was published by Princeton University Press in 2000. The book was the winner of the 2000 Association of American Publishers PROSE Awards, Award for Best Professional/Scholarly Multivolume Reference Work in the Humanities. Overview The main (atlas) volume contains 102 color topographic maps, covering territory from the British Isles and the Azores and eastward to Afghanistan and western China. The size of the volume is 33 x 48 cm. A 45-page gazetteer is also included in the atlas volume. The atlas is accompanied by a map-by-map directory on CD-ROM, in Portable Document Format, PDF format, including a search index. The map-by-map directory is also availab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiryns
Tiryns ( or ; Ancient Greek: Τίρυνς; Modern Greek: Τίρυνθα) is a Mycenaean archaeological site in Argolis in the Peloponnese, and the location from which the mythical hero Heracles was said to have performed his Twelve Labours. It lies south of Mycenae. Tiryns was a hill fort with occupation ranging back seven thousand years, from before the beginning of the Bronze Age. It reached its height of importance between 1400 and 1200 BC, when it became one of the most important centers of the Mycenaean world, and in particular in Argolis. Its most notable features were its palace, its Cyclopean tunnels and especially its walls, which gave the city its Homeric epithet of "mighty walled Tiryns". Tiryns became associated with the myths surrounding Heracles, as the city was the residence of the hero during his labors, and some sources cite it as his birthplace. The famous megaron of the palace of Tiryns has a large reception hall, the main room of which had a throne place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterelaos
The name Pterelaus (; Ancient Greek: Πτερέλαος) is attributed to two related individuals in Greek mythology: * Pterelaus, son of King Lelex of Megara * Pterelaus, son of Taphius.Apollodorus2.4.5/ref> Notes References *Apollodorus Apollodorus ( Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: :''Note: A ..., ''The Library'' with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes, Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921. ISBN 0-674-99135-4Online version at the Perseus Digital Library. * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lelex
In Greek mythology, Lelex (; Ancient Greek: Λέλεξ, ''gen.'' Λέλεγος) may refer to the following personages: *Lelex (king of Sparta), the first king of Sparta. * Lelex (king of Megara), king of Megara. * Lelex, one of the Calydonian hunters, who was described as "the gray-haired hero Lelex". Coming from Narycus in Opuntian Locris, he was already a mature man during that hunt.Ovid, ''Metamorphoses'' 8.299 ff. Notes References * Pausanias, ''Description of Greece'' with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D., and H.A. Ormerod, M.A., in 4 Volumes. Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1918Online version at the Perseus Digital Library* Pausanias, ''Graeciae Descriptio.'' ''3 vols''. Leipzig, Teubner. 1903.Greek text available at the Perseus Digital Library * Pseudo-Apollodorus The ''Bibliotheca'' (Ancient Greek: ), is a compendium of Greek myths and heroic legends, genealogical tables and histories arranged in three bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cities and colonies. In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, Poseidon was venerated as a chief deity at Pylos and Thebes, with the cult title "earth shaker"; in the myths of isolated Arcadia, he is related to Demeter and Persephone and was venerated as a horse, and as a god of the waters.Seneca quaest. Nat. VI 6 :Nilsson Vol I p.450 Poseidon maintained both associations among most Greeks: he was regarded as the tamer or father of horses, who, with a strike of his trident, created springs (the terms for horses and springs are related in the Greek language).Nilsson Vol I p.450 His Roman equivalent is Neptune. Homer and Hesiod suggest that Poseidon became lord of the sea when, following the overthrow of his father Cronus, the world was divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |