|
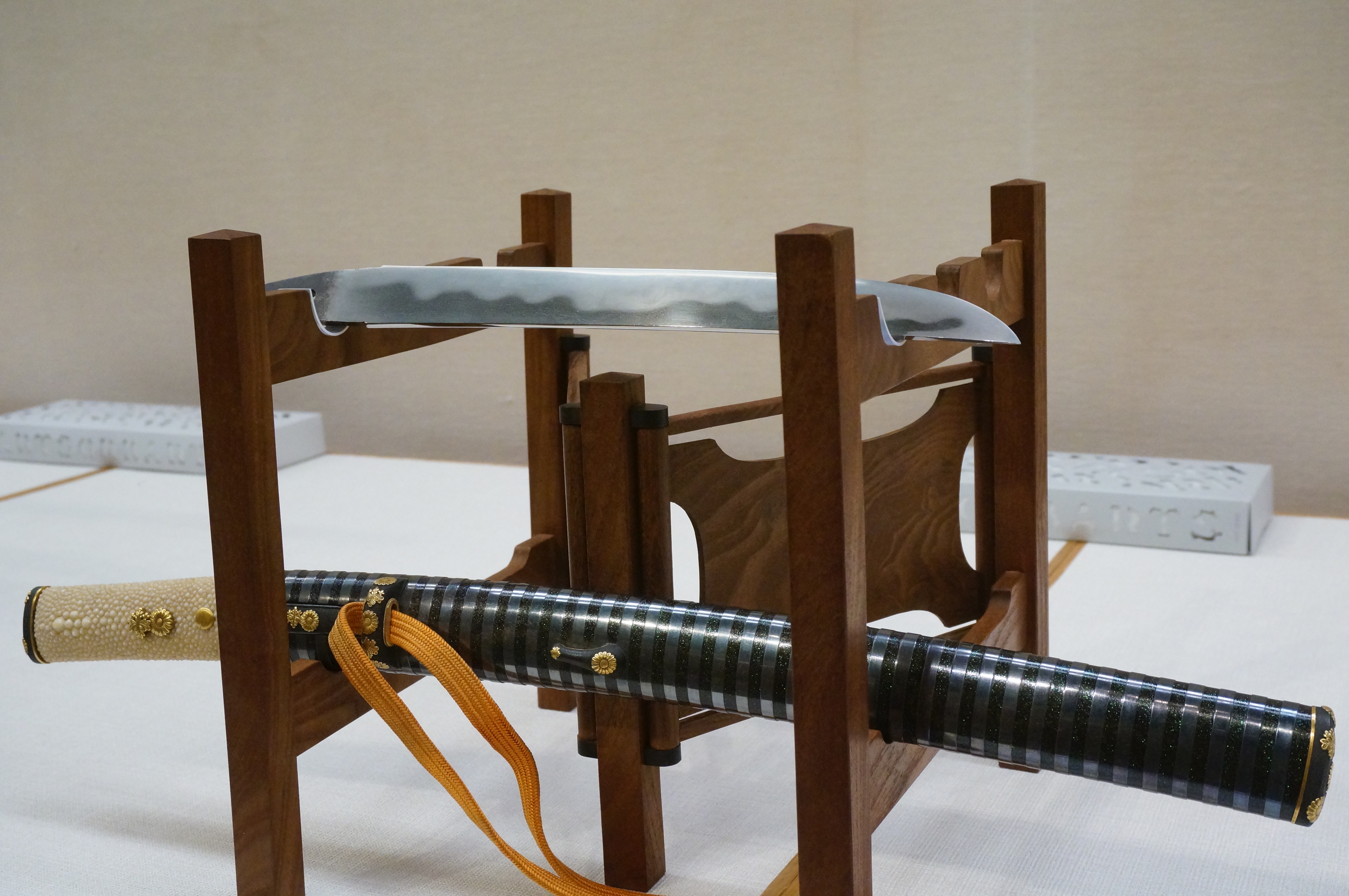
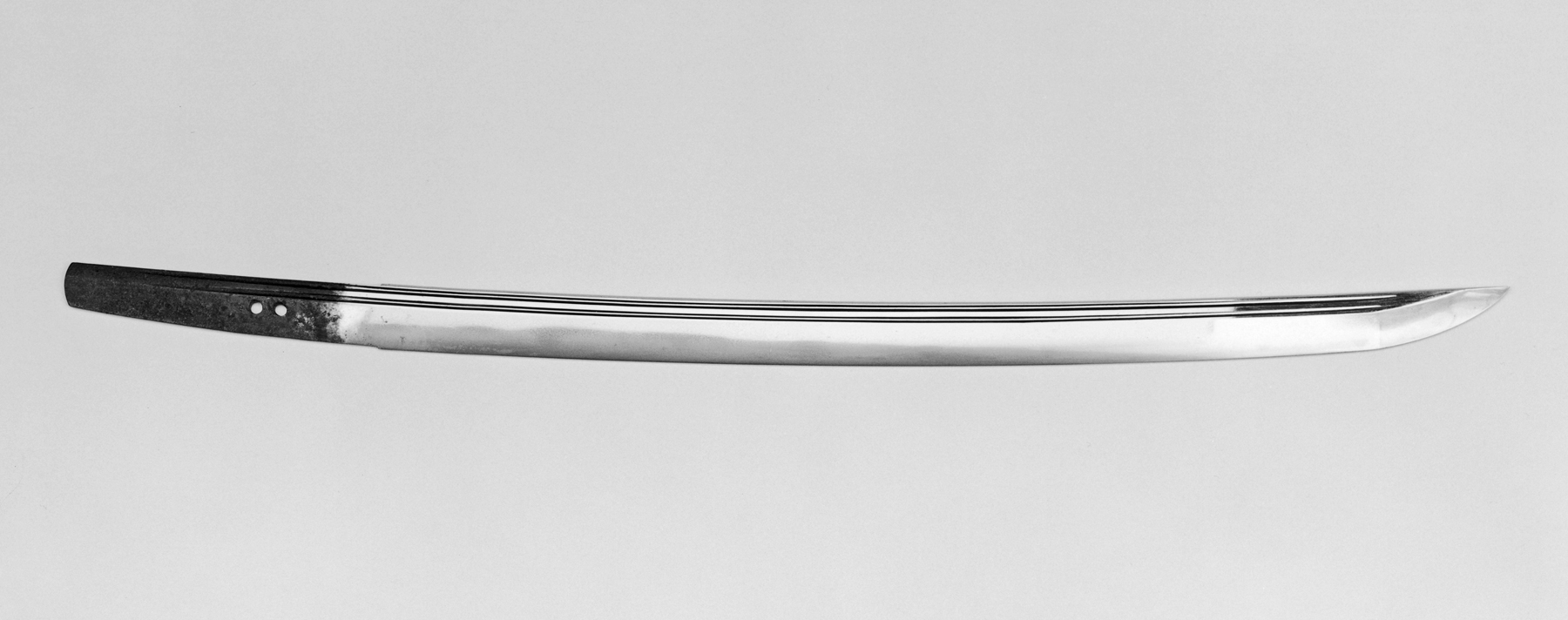
Tantō
A is a traditionally made Japanese knife () that was worn by the samurai class of feudal Japan. The dates to the Heian period, when it was mainly used as a weapon but evolved in design over the years to become more ornate. were used in traditional martial arts () and in the ''seppuku'' suicide ritual. The term has seen a resurgence in the West since the 1980s as referring to a point style of modern tactical knives, designed for piercing or stabbing, though the style is not present on any traditional tantō. A Tanto knife may refer to an American style of blade based of the Japanese , usually with a squared rather than curved tip. Description The is a single or double edged dagger with a length between (1 Japanese ). The was designed primarily as a stabbing weapon, but the edge can be used for cutting, slashing as well. are generally Forging, forged in the style (without a ridgeline), meaning that their sides have no ridge line and are nearly flat, unlike the structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Sword
A is one of several types of traditionally made swords from Japan. Bronze swords were made as early as the Yayoi period (1,000 BC – 300 AD), though most people generally refer to the curved blades made from the Heian period (794–1185) to the present day when speaking of "Japanese swords". There are many types of Japanese swords that differ by size, shape, field of application, and method of manufacture. Some of the more commonly known types of Japanese swords are the ''uchigatana'', ''tachi'', ''ōdachi'', ''wakizashi'', and ''tantō''. Etymology The word ''katana'' was used in ancient Japan and is still used today, whereas the old usage of the word ''nihontō'' is found in the poem the Song of ''Nihontō'', by the Song dynasty poet Ouyang Xiu. The word ''nihontō'' became more common in Japan in the late Tokugawa shogunate. Due to importation of Western swords, the word ''nihontō'' was adopted to distinguish it from the . ''Meibutsu'' (noted swords) is a special designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seppuku
, also known as , is a form of Japanese ritualistic suicide by disembowelment. It was originally reserved for samurai in their code of honor, but was also practiced by other Japanese people during the Shōwa era (particularly officers near the end of World War II) to restore honor for themselves or for their families. As a samurai practice, ''seppuku'' was used voluntarily by samurai to die with honor rather than fall into the hands of their enemies (and likely be tortured), as a form of capital punishment for samurai who had committed serious offenses, or performed because they had brought shame to themselves. The ceremonial disembowelment, which is usually part of a more elaborate ritual and performed in front of spectators, consists of plunging a short blade, traditionally a '' tantō'', into the belly and drawing the blade from left to right, slicing the belly open. If the cut is deep enough, it can sever the abdominal aorta, causing death by rapid exsanguination. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daishō
The —"large and small"—is a Japanese term for a matched pair of traditionally made Japanese swords (''nihonto'') worn by the samurai class in feudal Japan. The etymology of the word ''daishō'' becomes apparent when the terms ''daitō'', meaning long sword, and ''shōtō'', meaning short sword, are used; ''daitō'' + ''shōtō'' = ''daishō''. A ''daishō'' is typically depicted as a ''katana'' and ''wakizashi'' (or a '' tantō'') mounted in matching '' koshirae'', but originally the ''daishō'' was the wearing of any long and short ''katana'' together. The ''katana/wakizashi'' pairing is not the only ''daishō'' combination as generally any longer sword paired with a ''tantō'' is considered to be a ''daishō''. ''Daishō'' eventually came to mean two swords having a matched set of fittings. A ''daishō'' could also have matching blades made by the same swordsmith, but this was in fact uncommon and not necessary for two swords to be considered to be a ''daishō'', as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katana
A is a Japanese sword characterized by a curved, single-edged blade with a circular or squared guard and long grip to accommodate two hands. Developed later than the ''tachi'', it was used by samurai in feudal Japan and worn with the edge facing upward. Since the Muromachi period, many old ''tachi'' were cut from the root and shortened, and the blade at the root was crushed and converted into a ''katana''. The specific term for ''katana'' in Japan is and the term ''katana'' (刀) often refers to single-edged swords from around the world. Etymology and loanwords The word ''katana'' first appears in Japanese in the ''Nihon Shoki'' of 720. The term is a compound of ''kata'' ("one side, one-sided") + ''na'' ("blade"),1995, (''w:Daijisen, Daijisen'') (in Japanese), w:Tōkyō, Tōkyō: w:Shogakukan, Shogakukan, , entry available onlinhere/span> in contrast to the double-sided ''Tsurugi (sword), tsurugi''. The ''katana'' belongs to the ''nihontō'' family of swords, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantojutsu
Tantōjutsu (短刀術) is a Japanese term for a variety of traditional Japanese knife fighting systems that used the tantō (短刀), as a knife or dagger. Historically, many women used a version of the tantō, called the kaiken, for self-defense, but onna-musha, warrior women in pre-modern Japan learned one of the tantōjutsu arts to fight in battle. Martial arts that practise tantōjutsu Tantō with blunt wooden or plastic blades are used to practice martial arts. Metal blades can be used in more advanced training and in demonstrations. Styles that use tantō: Budō (Gendai): * Aikido * Shorinji Kempo Bugei: * Yanagi-ryū Aiki Bugei (Yoshida-ha Shidare Yanagi-ryū) * Ogawa-ryu Bugei Bujutsu (Koryū): * Kashima Shin-ryū (this ''ryū (school), ryūha'' uses term Kaikenjutsu) * Takamura-ha Shindo Yoshin-ryu * Tendō-ryū See also * Kaiken (dagger) * Wakizashi References Japanese martial arts Japanese martial arts terminology Edged and bladed weapons {{Martialart-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aikuchi
Japanese sword mountings are the various housings and associated fittings ('' tosogu'') that hold the blade of a Japanese sword when it is being worn or stored. refers to the ornate mountings of a Japanese sword (e.g. ''katana'') used when the sword blade is being worn by its owner, whereas the '' shirasaya'' is a plain undecorated wooden mounting composed of a '' saya'' and '' tsuka'' that the sword blade is stored in when not being used. Components *: The '' fuchi'' is a hilt collar between the '' tsuka'' and the ''tsuba''. *: The '' habaki'' is a wedge-shaped metal collar used to keep the sword from falling out of the '' saya'' and to support the fittings below; fitted at the ''ha-machi'' and ''mune-machi'' which precede the '' nakago''. *: A hook-shaped fitting used to lock the ''saya'' to the '' obi'' while drawing. *: The ''kashira'' is a butt cap (or pommel) on the end of the ''tsuka''. *: The '' kōgai'' is a spike for hair arranging carried sometimes as part of katan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade And Mounting For A Tantō Soshu Yukimitsu
A blade is the sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are intended to cut. This includes early examples made from flaked stones like flint or obsidian, evolving through the ages into metal forms like copper, bronze, and iron, and culminating in modern versions made from steel or ceramics. Serving as one of humanity's oldest tools, blades continue to have wide-ranging applications, including in combat, cooking, and various other everyday and specialized tasks. Blades function by concentrating force at the cutting edge. Design variations, such as serrated edges found on bread knives and saws, serve to enhance this force concentration, adapting blades for specific functions and materials. Blades thus hold a significant place both historically and in contemporary society, reflecting an evolution in material technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachi
A is a type of sabre-like traditionally made Japanese sword (''nihonto'') worn by the samurai class of feudal Japan. ''Tachi'' and '' uchigatana'' ("''katana''") generally differ in length, degree of curvature, and how they were worn when sheathed, the latter depending on the location of the , or signature, on the tang. The ''tachi'' style of swords preceded the development of the ''katana'', which was not mentioned by name until near the end of the twelfth century. ''Tachi'' were the mainstream Japanese swords of the Kotō period between 900 and 1596. Even after the Muromachi period (1336–1573), when ''katana'' became the mainstream, ''tachi'' were often worn by high-ranking samurai. History The production of swords in Japan is divided into specific time periods: * (ancient swords, until around 900) * (old swords, around 900–1596) * (new swords, 1596–1780) * (new new swords, 1781–1876) * (modern or contemporary swords, 1876–present) The predecessor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakizashi
The is one of the traditionally made Japanese swords ('' nihontō'') worn by the samurai in feudal Japan. Its name refers to the practice of wearing it inserted through one's ''obi'' or sash at one's side, whereas the larger '' tachi'' sword was worn slung from a cord. History and use The production of swords in Japan is divided into specific time periods:Transition of kotō, shintō, shinshintō, and gendaitō. Nagoya Japanese Sword Museum Touken World * ''Jokotō'' (ancient swords, until around AD 900) * ''Kotō'' (old swords from around 900–1596) * ''Shintō'' (new swords 1596–1780) * ''Shinshintō'' (newer swords 1781–1876) * ''Gendaitō'' (modern or contemporary swords 1876–present) The ''wakizashi'' has a blade between in length. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanboku-chō Period
The , also known as the Northern and Southern Courts period, was a period in Japanese history between 1336-1392 CE, during the formative years of the Ashikaga shogunate, Muromachi (Ashikaga) shogunate. Ideologically, the two courts fought for 50 years, with the South giving up to the North in 1392. In reality the Northern court was under the power of the Ashikaga shogunate and had little real independence. The destruction of the Kamakura shogunate of 1333 and the failure of the Kenmu Restoration in 1336 opened up a legitimacy crisis for the new shogunate. Institutional changes in the estate system (''shōen'') that formed the bedrock of the income of nobles and warriors altered the status of the various social groups. The establishment of the Ashikaga shogunate broadened the economic base of the warriors, while undercutting the noble proprietors. However, this trend had started already with the Kamakura Shogun#Shogunate, ''bakufu''. Background During the early period, there ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
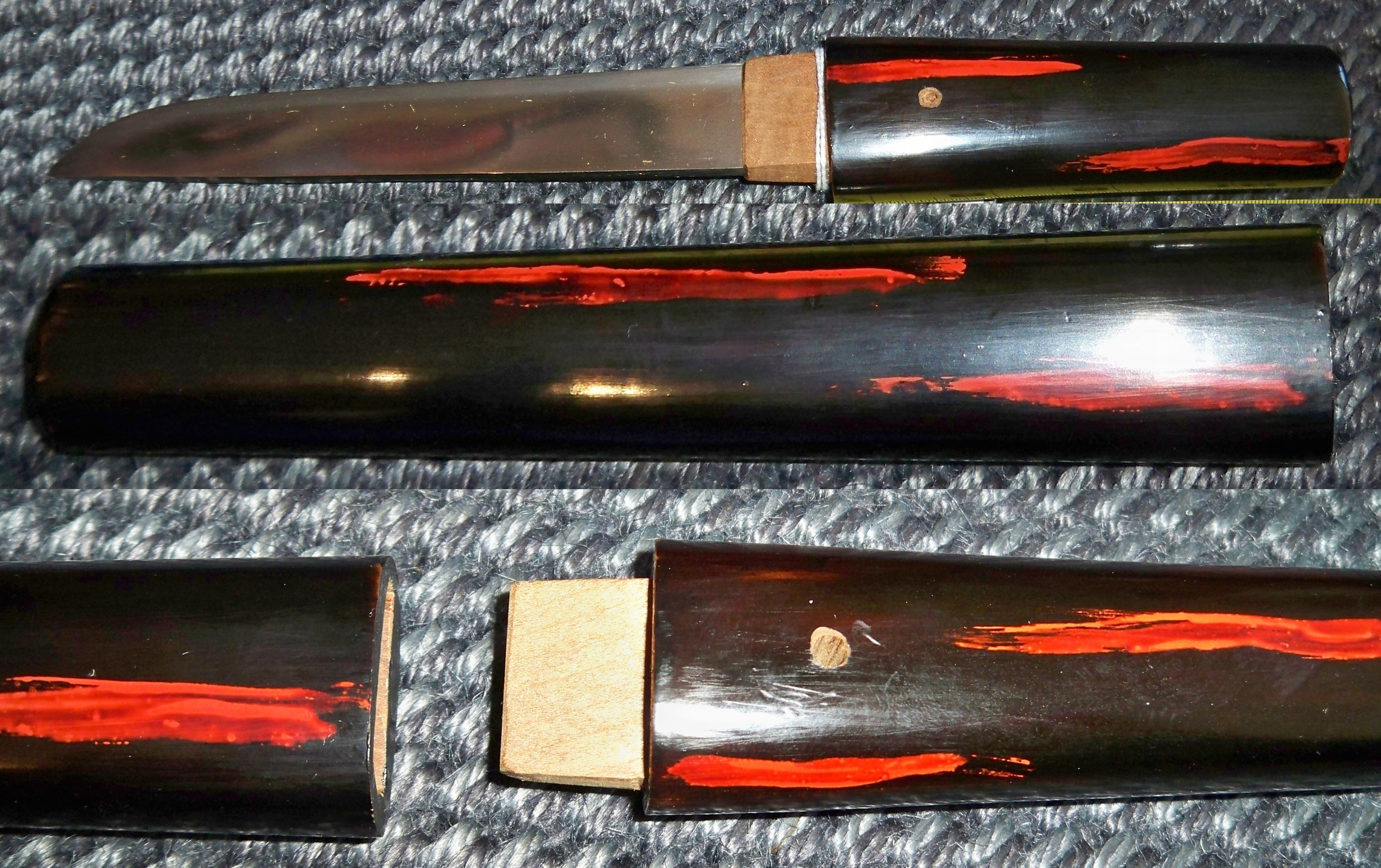
Kaiken (dagger)
A is a long, single or (very rarely) double-edged Japanese knife usually without ornamental fittings housed in a plain but lacquered mount. Uses The was once carried by men and women of the samurai class in Japan. It was useful for self-defense in indoor spaces where the long-bladed katana and intermediate-length were inconvenient. Women carried them in their kimono either in a pocket-like space () or in the sleeve pouch () for self-defense and for ritual suicide by slashing the veins in the left side of the neck. When a samurai woman married, she was expected to carry a with her when she moved in with her husband. The was also carried concealed in its by the lower classes who were not permitted to wear swords, in particular by criminals in the Edo period. In modern Japan, a is worn as a traditional accessory for the (referee) in sumo matches for the highest ranks. However, a real blade is not used. No one legally wears or carries a today in Japan, as this is a vio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |