|
Tairyūji (Anan)
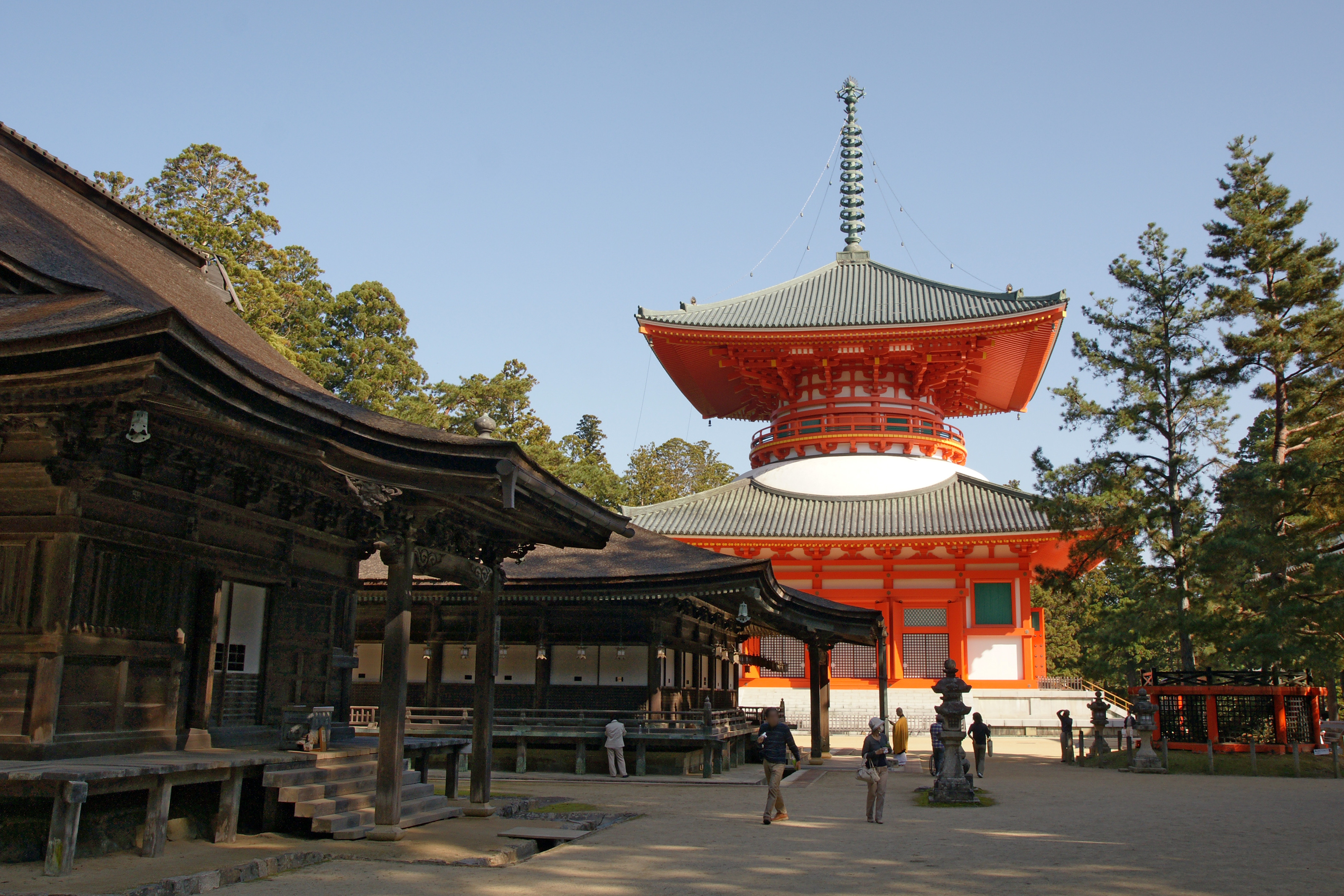
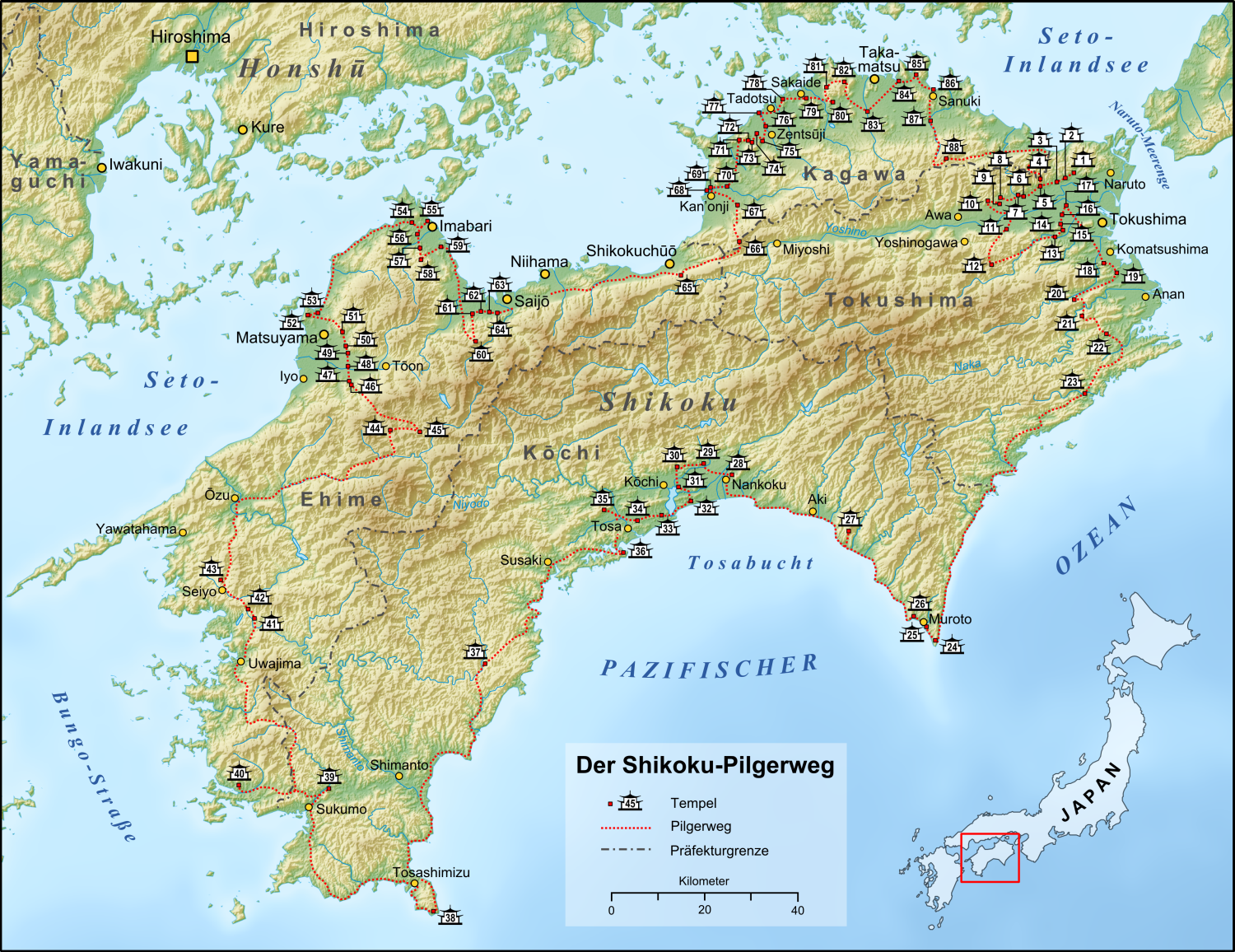
Tairyūji or Tairyū-ji (Tairyū Temple, Great Dragon Temple) (Japanese: ) is a Koyasan Shingon temple in Anan city, Tokushima Prefecture, Japan. Temple # 21 on the Shikoku 88 temple pilgrimage. The main image is of Ākāśagarbha Bodhisattva. History :*The temple was constructed during Emperor Kanmu's era. :*In the Tenshō (天正, 1573-1592) era, the temple was destroyed by Chōsokabe Motochika (長宗我部 元親) force. :*In the Edo era, the temple was rebuilt with the support of Hachisuka clan (蜂須賀氏). :* Typhoon No. 6 in July 2011 caused a 400-year-old cedar tree to break and broke through the main hall roof. Cultural properties Following structures in the temple were designated as Tangible Cultural Properties of Japan on June 21, 2013: *Main Hall: built in 1852 *Kōbō-Daishi Hall: built in 1877 *Hexagon Sutra Hall: built in 1856 *Treasure Stupa: built in 1861 *Entrance Gate: built 1806 *Bell Tower Gate: built in 1903 See also * Shikoku 88 temple pilgrimage Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Era
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by prolonged peace and stability, urbanization and economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu prevailed at the Battle of Sekigahara and established hegemony over most of Japan, and in 1603 was given the title ''shogun'' by Emperor Go-Yōzei. Ieyasu resigned two years later in favor of his son Hidetada, but maintained power, and defeated the primary rival to his authority, Toyotomi Hideyori, at the Siege of Osaka in 1615 before his death the next year. Peace generally prevailed from this point on, making samurai largely redundant. Tokugawa shoguns continued Ieyasu's policies of conformity, including a for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Tokushima Prefecture
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of development which leads to awakening and full liberation from '' dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes such as asceticism or sensual indulgence. Teaching that ''dukkha'' arises alongside attachment or clinging, the Buddha advised meditation practices and eth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingon Buddhism
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asian Buddhism. It is a form of Japanese Esoteric Buddhism and is sometimes called "Tōmitsu" (東密 lit. "Esoteric uddhismof Tō-ji"). The word ''shingon'' is the Japanese reading of the Chinese word ('), which is the translation of the Sanskrit word mantra. The Zhēnyán lineage was founded in China (c. 7th–8th centuries) by Indian vajrācāryas (esoteric masters) like Śubhakarasiṃha, Vajrabodhi and Amoghavajra. These esoteric teachings would later flourish in Japan under the auspices of a Buddhist monk named Kūkai (, 774–835), who traveled to Tang China and received these esoteric transmissions from a Chinese master named Huiguo (746–805). Kūkai established his tradition at Mount Kōya (in Wakayama Prefecture), which remains the central pilgrimage center of Shingon Buddhism. The practice of the Shingon school stresses that one is able to atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tairyūji Ropeway
The is a Japanese aerial lift line in Tokushima Prefecture, operated by Shikoku Cable. Opened in 1992, the line climbs to Tairyū-ji, the 21st temple of the Shikoku Pilgrimage. Basic data *System: Aerial tramway, 2 track cables and 2 haulage ropes *Distance: *Vertical interval **Between two ends: **Maximum: *Maximum gradient: 30° *Operational speed: 5.0 Metre per second, m/s *Passenger capacity per a cabin: 101 *Stations: 2 *Time required for single ride: 10 minutes See also *List of aerial lifts in Japan External links Shikoku Cable official website Aerial tramways in Japan 1992 establishments in Japan Anan, Tokushima {{Japan-cable-line-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikoku Pilgrimage
The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (''Kōbō Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history, large numbers of pilgrims, known as , still undertake the journey for a variety of ascetic, pious, and tourism-related purposes. The pilgrimage is traditionally completed on foot, but modern pilgrims use cars, taxis, buses, bicycles, or motorcycles, and often augment their travels with public transportation. The standard walking course is approximately long and can take anywhere from 30 to 60 days to complete. In addition to the 88 "official" temples of the pilgrimage, there are 20 ''bekkaku'' (別格) temples, which are officially associated with the Shikoku Pilgrimage (and hundreds more ''bangai'' (番外) temples, simply meaning "outside the numbers," which are not considered part of the official 88). To complete the pilgrimage, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Properties Of Japan
A is administered by the Government of Japan, Japanese government's Agency for Cultural Affairs (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology), and includes Tangible Cultural Properties of Japan, tangible properties (structures and works of art or craft); Intangible Cultural Properties of Japan, intangible properties (performing arts and craft techniques); Mingei, folk properties both tangible and intangible; Monuments of Japan, monuments historic, scenic and natural; Cultural Landscapes of Japan, cultural landscapes; and Groups of Traditional Buildings, groups of traditional buildings. Cultural Properties of Japan#Buried Cultural Properties, Buried properties and Conservation Techniques for Cultural Properties, conservation techniques are also protected. Together these cultural properties are to be preserved and utilized as the heritage of the Japanese people. Not all Cultural Properties of Japan were created in Japan; some are from China, Korea or other countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hachisuka Clan
The are descendants of Emperor Seiwa (850-880) of Japan and are a branch of the Ashikaga clan through the Shiba clan (Seiwa Genji) of the Minamoto clan. History Ashikaga Ieuji (13th century), son of Ashikaga Yasuuji, was the first to adopt the name Shiba. The Shiba were ''Shugo'' (Governors) of Echizen, Owari, and other provinces, and during the Ashikaga shogunate were one of three families (Shiba, Hosokawa and Hatakeyama) from which the '' Kyoto-kanryo'' (Prime Minister of the Shōgun) could be chosen. Shiba Masaaki, the descendant of Shiba Takatsune (1305–1367), established himself in Hachisuka, near the Kiso River at the border of Owari and Mino provinces, whence he took the name Hachisuka. In the 16th century, the Hachisuka clan came to prominence thanks to its head, Hachisuka Koroku. His uncle held Hachisuka Castle and he lived first in Miyaushiro Castle, which was his mother's family home. Koroku served the Oda clan, being instrumental in several of the early victori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chōsokabe Motochika
was a prominent ''daimyō'' in Japanese Sengoku period, Sengoku-period. He was the 21st chief of the Chōsokabe clan of Tosa Province (present-day Kōchi Prefecture), the ruler of Shikoku, Shikoku region. Early life and rise He was the son and heir of Chōsokabe Kunichika and his mother was a daughter of the Saitō clan of Mino Province. His childhood name was Yasaburō (弥三郎). He is said to have been born in Okō Castle in the Nagaoka district of Tosa. Motochika was a quiet youth and his father was said to have fretted about the boy's gentle nature (he seems to have been nicknamed Himewako, or 'Little Princess'); Kunichika's worries evaporated when Motochika later proved himself a skilled and brave warrior. When Motochika came of age, his father had already begun to draw away from the Ichijō family, and Motochika would carry on his work. In 1560, at the Battle of Tonomoto, Chōsokabe Kunichika captured Nagahama castle from the Motoyama clan. In response to this, Motoyama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenshō (Momoyama Period)
was a after ''Genki (era), Genki'' and before ''Bunroku''. This period spanned the years from July 1573 through December 1592 during the Sengoku era.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Tenshō''" i ''Japan encyclopedia'', p. 961 n.b., Louis-Frédéric is pseudonym of Louis-Frédéric Nussbaum, ''see'Deutsche Nationalbibliothek Authority File. The reigning emperors were and . Change of era * 1573 : The new era name was created to mark a number of regional wars. The era name was inspired by a passage from the Chinese classic ''Tao Te Ching by'' Laozi: :"Those who are at peace with nature bring all under Heaven into its correct pattern" (清静者為天下正). The era name ''Tenshō'' was suggested by Oda Nobunaga. The previous era ended, and a new one commenced in ''Genki'' 4, the 28th day of the 7th month. Events of the ''Tenshō'' era European dates up to October 4, 1582 are given in the Julian calendar. Dates since October 15, 1582 are given in the Gregorian calendar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Kanmu
, or Kammu, was the 50th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 桓武天皇 (50) retrieved 2013-8-22. according to the traditional order of succession. Kammu reigned from 781 to 806, and it was during his reign that the scope of the emperor's powers reached its peak. His reign saw the transition from the Nara period to the Heian period. Traditional narrative Kammu's personal name ('' imina'') was .Brown, p. 277 He was the eldest son of Prince Shirakabe (later known as Emperor Kōnin), and was born prior to Shirakabe's ascension to the throne. According to the , Yamabe's mother, Yamato no Niigasa (later called Taka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |