|
Taenia Solium
''Taenia solium'', the pork tapeworm, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm that uses humans (''Homo sapiens'') as its definitive host and pigs and boars (family Suidae) as the Host (biology)#Types of hosts, intermediate or secondary hosts. It is transmitted to pigs through human feces that contain the parasite eggs and contaminate their fodder. Pigs ingest the morula, eggs, which develop into larvae, then into oncospheres, and ultimately into infective tapeworm cysts, called cysticerci. Humans acquire the cysts through consumption of uncooked or under-cooked pork and the cysts grow into adult worms in the small intestine. There are two forms of human infection. One is "primary hosting", called taeniasis, and is due to eating under-cooked pork that contains the cysts, resulting in adult worms in the intestines. This form generally is asymptomatic, without symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test). Pre-symptomatic is the adjective categorising the time periods during which the medical conditions are asymptomatic. Subclinical and paucisymptomatic are other adjectives categorising either the asymptomatic infections (i.e., subclinical infections), or the psychosomatic illnesses and mental disorders expressing a subset of symptoms but not the entire set an explicit medical diagnosis requires. Examples An example of an asymptomatic disease is cytomegalovirus (CMV) which is a member of the herpes virus family. "It is estimated that 1% of all newborns are infected with CMV, but the majority of infections are asymptomatic." (Knox, 1983; Kumar et al. 1984) In some diseases, the proportion of asymptomatic cases can be important. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly an amino acid) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the ligand to be measured. ELISA has been used as a medical diagnosis, diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme, and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's Enzyme substrate, substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crysta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
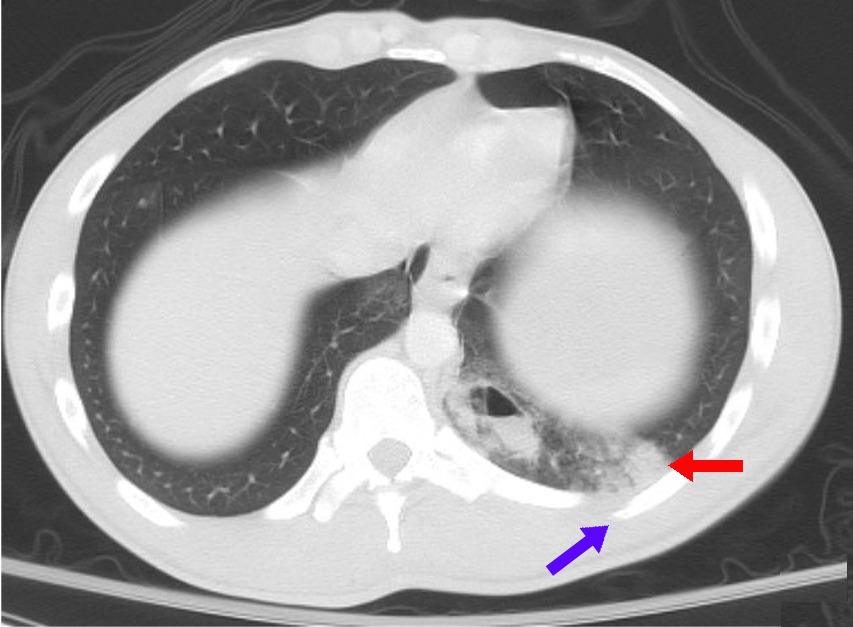
Computed Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic. The individuals of many taxonomic groups of animals, primarily invertebrates, are hermaphrodites, capable of producing viable gametes of both sexes. In the great majority of tunicates, mollusks, and earthworms, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which either partner can act as the female or male. Hermaphroditism is also found in some fish species, but is rare in other vertebrate groups. Most hermaphroditic species exhibit some degree of self-fertilization. The distribution of self-fertilization rates among animals is similar to that of plants, suggesting that similar pressures are operating to direct the evolution of selfing in animals and plants. A rough estimate of the number of hermaphroditic animal species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive System
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.Reproductive System 2001 Body Guide powered by Adam Animals In mammals, the major organs of the reproductive system include the external gen ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proglottids
Cestoda is a Class (biology), class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, commonly known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish-infecting parasites. All cestodes are parasitism, parasitic; many have complex Life history theory, life histories, including a stage in a Host (biology)#Definitive and secondary hosts, definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larvae develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strobilation
Strobilation or transverse fission is a form of asexual reproduction consisting of the spontaneous transverse segmentation of the body. It is observed in certain cnidarians and helminths. This mode of reproduction is characterized by high offspring output, which, in the case of the parasitic tapeworms, is of great significance. Strobilation in cnidarians *The process starts with preliminary morphological changes. In particular, the cnidarian's tentacles tend to be reabsorbed. *Neck-formation: transverse constrictions appear near the upper extremity of the animal. A strobilating polyp is called a strobila while the non-strobilating polyp is called a scyphistoma or scyphopolyp. * Segmentation: the number of constriction sites increases and migrates down the body length, transforming the body into a sequence of disks. The fissures intensify until the initial body is divided into equally spaced, separate segments. The oral end of the polyp becomes the oral end of the ephyra. *Meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about long connecting the stomach to the jejunum, the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb, and ends at the duodenojejunal flexure marked by the suspensory muscle of duodenum. The duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (transverse) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Overview The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms ''anterior intestine'' or ''proximal intestine'' may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostellum (helminth)
Rostellum (meaning "small beak", from the Latin ' for "beak"; pl. rostella) in helminthology in a protruding part of the anterior end of tapeworms. It is a retractable, cone-like muscular structure that is located on the apical end of the scolex, and in most species is armed with hooks, the organs of attachment to the host's intestinal wall. It is a parasitic adaptation in some cestodes for firm attachment in the gastrointestinal tract and is structurally different from one species to another (or even absent is some species), thereby becoming an important diagnostic feature. Structure A rostellum is a knob-like protrusion at the extreme anterior end of a tapeworm, as an extension of the tegument. It is globular, spiny structure when it protrudes, and a circular hollow pit when retracted. It is structurally composed of a number of concentric rows of hooks. The number and arrangement of the hooks are species specific. The two basic types of hooks are those of the upper row, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucker (zoology)
A sucker in zoology is a specialised attachment organ of an animal. It acts as an adhesion device in parasitic worms, several flatworms, cephalopods, certain fishes, amphibians, and bats. It is a muscular structure for suction on a host or substrate. In parasitic annelids, flatworms and roundworms, suckers are the organs of attachment to the host tissues. In tapeworms and flukes, they are a parasitic adaptation for attachment on the internal tissues of the host, such as intestines and blood vessels. In roundworms and flatworms they serve as attachment between individuals particularly during mating. In annelids, a sucker can be both a functional mouth and a locomotory organ. The structure and number of suckers are often used as basic taxonomic diagnosis between different species, since they are unique in each species. In tapeworms there are two distinct classes of suckers, namely "bothridia" for true suckers, and " bothria" for false suckers. In digeneal flukes there are usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |