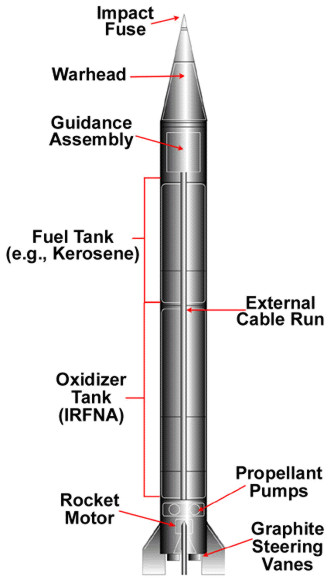
|
Tactical Ballistic Missile
A tactical ballistic missile (TBM), or battlefield range ballistic missile (BRBM), is a ballistic missile designed for short-range battlefield use. Typically, range (aeronautics), range is less than . Tactical ballistic missiles are usually mobile to ensure survivability and quick deployment, as well as carrying a variety of warheads to target enemy facilities, assembly areas, artillery, and other targets behind the front lines. Warheads can include conventional high explosive, Chemical warfare, chemical, Biological warfare, biological, or nuclear warheads. Typically tactical nuclear weapons are limited in their total yield compared to strategic nuclear weapons. Design Tactical ballistic missiles fill the gap between conventional rocket artillery and longer-range short-range ballistic missiles. Tactical missiles can carry heavy payloads deep behind enemy lines in comparison to rockets or gun artillery, while having better mobility and less expense than the more strategic thea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Oxygen
Liquid oxygen, sometimes abbreviated as LOX or LOXygen, is a clear cyan liquid form of dioxygen . It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which is ongoing. Physical properties Liquid oxygen has a clear cyan color and is strongly paramagnetic: it can be suspended between the poles of a powerful horseshoe magnet. Liquid oxygen has a density of , slightly denser than liquid water, and is cryogenic with a freezing point of and a boiling point of at . Liquid oxygen has an expansion ratio of 1:861 and because of this, it is used in some commercial and military aircraft as a transportable source of breathing oxygen. Because of its cryogenic nature, liquid oxygen can cause the materials it touches to become extremely brittle. Liquid oxygen is also a very powerful oxidizing agent: organic materials will burn rapidly and energetically in liquid oxygen. Further, if soaked in liquid oxygen, some materials su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Propellant Rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants (fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder. The inception of gunpowder rockets in warfare can be credited to the ancient Chinese, and in the 13th century, the Mongols played a pivotal role in facilitating their westward adoption. All rockets used some form of solid or powdered propellant until the 20th century, when liquid-propellant rockets offered more efficient and controllable alternatives. Because of their simplicity and reliability, solid rockets are still used today in military armaments worldwide, model rockets, solid rocket boosters and on larger applications. Since solid-fuel rockets can remain in storage for an extended period without much propellant degradation, and since they almost always launch reliably, they have been frequently used in military applications such as missiles. The lower performance of solid propellants (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Water (missile)
Blue Water was a British battlefield nuclear missile of the early 1960s, intended to replace the MGM-5 Corporal, which was becoming obsolete. With roughly the same role and range as Corporal, the solid-fuel Blue Water was far simpler to use and would be significantly easier to support in the field. It was seen as a replacement for Corporal both in the UK as well as other NATO operators, notably Germany and possibly Turkey. The design traces its history to the shorter-ranged but otherwise similar Red Rose design of 1954. In 1958, significantly changed requirements led to it being renamed despite the missile itself remaining almost unchanged. The Blue Water missile entered testing in 1962 was generally successful, and praised in the industry. However, when Germany purchased the MGM-29 Sergeant instead of Blue Water, and it appeared Turkey would do the same, the UK government decided to cancel its development instead of continuing to develop a missile that would be used only by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Hussein (missile)
al-Husayn () was a short-range ballistic missile developed in Ba'athist Iraq. An upgraded version of Scud missile, the al-Husayn was widely used by the Iraqi Army during the Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988) and the Persian Gulf War (1990–1991). Development The origins of the al-Husayn could be traced back to the first stages of the war with Iran. Iraq was the first belligerent to use long range artillery rockets during the Iran–Iraq War, firing limited numbers of FROG-7s at the towns of Dezful and Ahvaz. Iran responded with Scud-Bs obtained from Libya. These missiles can hit a target 185 miles away, therefore key Iraqi cities like Sulaymaniya, Kirkuk, and Baghdad itself came within the range of this weapon. Iraq, which also deployed the Scud-B, was conversely unable to strike the main Iranian industrial centers, including the capital, Tehran, because these are located more than 300 miles from the border. To surmount the Iranian advantage, Iraqi engineers designed a program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid-propellant Rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket uses a rocket engine burning liquid rocket propellant, liquid propellants. (Alternate approaches use gaseous or Solid-propellant rocket , solid propellants.) Liquids are desirable propellants because they have reasonably high density and their combustion products have high Specific impulse, specific impulse (''I''sp). This allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low. Types Liquid rockets can be monopropellant rockets using a single type of propellant, or bipropellant rockets using two types of propellant. Tripropellant rockets using three types of propellant are rare. Liquid oxidizer propellants are also used in hybrid rockets, with some of the advantages of a solid rocket. Bipropellant liquid rockets use a liquid fuel such as liquid hydrogen or RP-1, and a liquid oxidizer such as liquid oxygen. The engine may be a cryogenic rocket engine, where the fuel and oxidizer, such as hydrogen and oxygen, are gases which hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Samoud 2
Al-Samoud (الصمود, alternately ''Al-Samed'', which means steadfastness in Arabic)Miller, David: ''Conflict Iraq: Weapons and tactics of US and Iraqi Forces.'' Zenith imprint, 2003, page 22. was a liquid-propellant rocket tactical ballistic missile developed by Iraq in the years between the Gulf War and the 2003 Invasion of Iraq. The Iraqi army also developed a solid-fuel rocket version known as Ababil-100. Development The missile was essentially a scaled-down Scud, though parts were mostly derived from the Soviet S-75 Dvina surface-to-air missile. The first test-firing was carried out as early as 1997 and was supervised by UNSCOM. The production started in 2001, and the goal was the assembly of ten missiles each month. The Al Samoud 2 was not fully operational by 2003, but some of them had been already delivered to the Iraqi army. Engine The rocket engine evolved from the S-75 Dvina design and the thrust vector controls from the Scud. The system also included an Ira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scud Missile
A Scud missile is one of a series of tactical ballistic missiles developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It was exported widely to both Second and Third World countries. The term comes from the NATO reporting name attached to the missile by Western intelligence agencies. The Russian names for the missile are the R-11 (the first version), and the R-17 (later R-300) Elbrus (later developments). The name Scud has been widely used to refer to these missiles and the wide variety of derivative variants developed in other countries based on the Soviet design. Scud missiles have been used in combat since the 1970s, mostly in wars in the Middle East. They became familiar to the Western public during the 1991 Persian Gulf War, when Iraq fired dozens at Saudi Arabia and Israel. In Russian service, it has been replaced by the 9K720 Iskander. Development The first use of the term ''Scud'' was in the NATO name SS-1b Scud-A, applied to the R-11 Zemlya ballistic missile. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc List of non-communist socialist states, socialist republics in Central and Eastern Europe in May 1955, during the Cold War. The term "Warsaw Pact" commonly refers to both the treaty itself and its resultant military alliance, the Warsaw Pact OrganisationPage 22, �NATO and OSCE, Partners or Rivals?��, Edward Killham (WPO) (also known as ‘Warsaw Treaty Organization’ (‘WTO’)). The Warsaw Pact was the military complement to the Comecon, Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon), the economic organization for the Eastern Bloc states. Dominated by the Soviet Union, the Warsaw Pact was established as a balance of power or counterweight to the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. The term ''Cold war (term), cold war'' is used because there was no direct fighting between the two superpowers, though each supported opposing sides in regional conflicts known as proxy wars. In addition to the struggle for ideological and economic influence and an arms race in both conventional and Nuclear arms race, nuclear weapons, the Cold War was expressed through technological rivalries such as the Space Race, espionage, propaganda campaigns, Economic sanctions, embargoes, and sports diplomacy. After the end of World War II in 1945, during which the US and USSR had been allies, the USSR installed satellite state, satellite governments in its occupied territories in Eastern Europe and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MGM-52 Lance
The MGM-52 Lance was a mobile field artillery tactical surface-to-surface missile (tactical ballistic missile) system used to provide both W70, nuclear and conventional fire support to the United States Army. The missile's warhead was developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. It was replaced by MGM-140 ATACMS, which was initially intended to likewise have a nuclear capability during the Cold War. Deployment The first Lance missiles were deployed in 1972, replacing (together with the US-Navy's nuclear-tipped RIM-2D and RIM-8E/B/D) the earlier MGR-1 Honest John, Honest John rocket and MGM-29 Sergeant, Sergeant SRBM ballistic missile, greatly reducing the weight and bulk of the system, while improving both accuracy and mobility. A Lance battery (two fire units) consisted of two M113 armored personnel carrier variants, M752 launchers (one missile each) and two M688 auxiliary vehicles (two missiles each), for a total six missiles; the firing rate per unit was approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transporter Erector Launcher
A transporter erector launcher (TEL) is a missile vehicle with an integrated tractor unit that can transport, elevate to a firing position and launch one or more rockets or missiles. History Such vehicles exist for both surface-to-air missiles and surface-to-surface missiles. Early on, such missiles were launched from fixed sites and had to be loaded onto trucks for transport, making them more vulnerable to attack, since once they were spotted by the enemy they could not easily be relocated, and if they were it often took hours or even days to prepare them for launch once they reached their new site. Usually a number of TELs and TELARs are linked to one command post vehicle (CP or CPV). They may use target information from target acquisition, designation and guidance radar (TADAGR or TAR). Transporter erector launcher and radar (TELAR) A transporter erector launcher and radar (TELAR) is a type of TEL that also incorporates part or all of the radar system necessary for firi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |