|
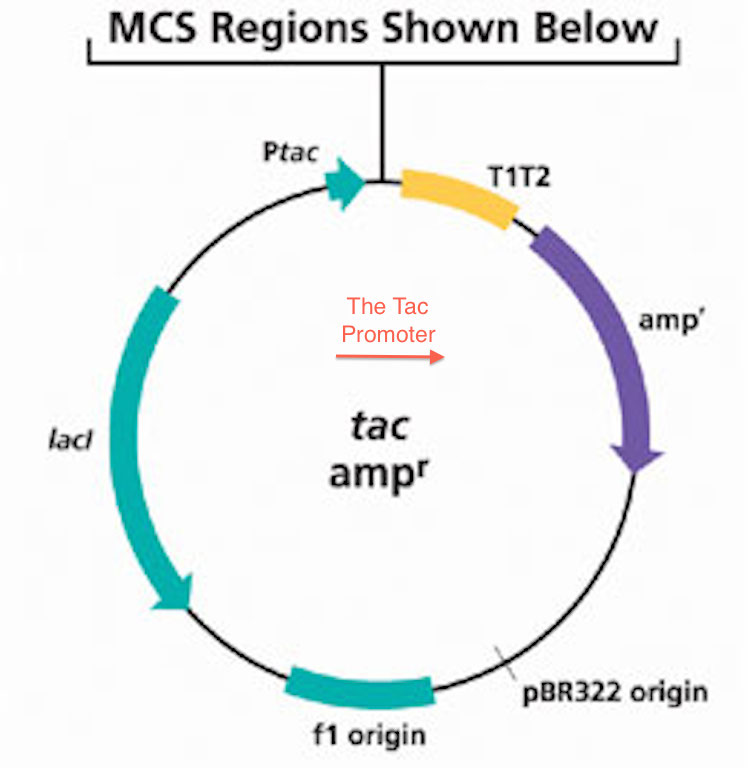
Tac-Promoter
The Tac-Promoter (abbreviated as Ptac), or tac vector is a synthetically produced DNA promoter, produced from the combination of promoters from the trp and lac operons. It is commonly used for protein production in ''Escherichia coli''. Two hybrid promoters functional in ''Escherichia coli'' were constructed. These hybrid promoters, tacI and tacII, were derived from sequences of the trp and the lac UV5 promoters. In the first hybrid promoter (tacI), the DNA upstream of position –20 with respect to the transcriptional start site was derived from the trp promoter. The DNA downstream of position –20 was derived from the lac UV5 promoter. In the second hybrid promoter (tacII), the DNA upstream of position –11 at the Hpa I site within the Pribnow box was derived from the trp promoter. The DNA downstream of position –11 is a 46-base-pair synthetic DNA fragment that specifies part of the hybrid Pribnow box and the entire lac operator. It also specifies a Shine–Dalgarno sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism. Overview For transcription to take place, the enzyme that synthesizes RNA, known as RNA polymerase, must attach to the DNA near a gene. Promoters contain specific DNA sequences such as response elements that provide a secure initial binding site for RNA polymerase and for proteins called transcription factors that recruit RNA polymerase. These transcription factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tac Promoter
TAC, or tac, may refer to: People * Pablo Tac, US scholar * Pham Cong Tac, a leader of the Cao Dai religion Places * Tác, a village in Fejér County, Hungary Organisations * TAC (building automation), a Swedish building automation company * Tactical Air Command, a former command of the US Air Force * Technical Advisory Council, a committee advising the US FCC * Technical Assistance Center, a company's internal support group for external customers * The Aleut Corporation, Alaska, United States, a Native Regional Corporation * The Analysis Corporation, a private intelligence firm * The Ant Commandos, a company which produces video game console peripherals * The Asatru Community, an inclusive Norse Pagan/Heathen sect; see Kindred (Heathenism) * The Athletics Congress, US sports governing body, became USATF in 1992 * The Architects Collaborative, Cambridge, Massachusetts, US * Thomas Aquinas College, a college with multiple campuses in the US * Transport Accident Commission, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast Artificial Chromosome
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast, ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae' which is then ligated into a bacterial plasmid. By inserting large fragments of DNA, from 100–1000 kb, the inserted sequences can be cloned and physically mapped using a process called chromosome walking. This is the process that was initially used for the Human Genome Project, however due to stability issues, YACs were abandoned for the use of bacterial artificial chromosomebr> The bakers' yeast ''S. cerevisiae'' is one of the most important experimental organisms for studying eukaryotic molecular genetics. Beginning with the initial research of the Rankin et al., Strul et al., and Hsaio et al., the inherently fragile chromosome was stabilized by discovering the necessary autonomously replicating sequence (ARS); a refined YAC utilizing this data was described in 1983 by Murray et al. The primary components of a YAC are the ARS, centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Artificial Chromosome
A human artificial chromosome (HAC) is a microchromosome that can act as a new chromosome in a population of human cells. That is, instead of 46 chromosomes, the cell could have 47 with the 47th being very small, roughly 6–10 megabases (Mb) in size instead of 50–250Mb for natural chromosomes, and able to carry new genes introduced by human researchers. Ideally, researchers could integrate different genes that perform a variety of functions, includindisease defense Alternative methods of creating transgenes, such as utilizing yeast artificial chromosomes and bacterial artificial chromosomes, lead to unpredictable problems. The genetic material introduced by these vectors not only leads to different expression levels, but the inserts also disrupt the original genome. HACs differ in this regard, as they are entirely separate chromosomes. This separation from existing genetic material assumes that no insertional mutants would arise. This stability and accuracy makes HACs preferabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside
Isopropyl β--1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) is a molecular biology reagent. This compound is a molecular mimic of allolactose, a lactose metabolite that triggers transcription of the ''lac'' operon, and it is therefore used to induce protein expression where the gene is under the control of the lac operator. Mechanism of action Like allolactose, IPTG binds to the lac repressor and releases the tetrameric repressor from the lac operator in an allosteric manner, thereby allowing the transcription of genes in the lac operon, such as the gene coding for beta-galactosidase, a hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of β-galactosides into monosaccharides. But unlike allolactose, the sulfur ( S) atom creates a chemical bond which is non-hydrolyzable by the cell, preventing the cell from metabolizing or degrading the inducer. Therefore, its concentration remains constant during an experiment. IPTG uptake by ''E. coli'' can be independent of the action of lactose perme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Gene Expression
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are widely observed in biology, for example to trigger developmental pathways, respond to environmental stimuli, or adapt to new food sources. Virtually any step of gene expression can be modulated, from Transcriptional regulation, transcriptional initiation, to RNA processing, and to the post-translational modification of a protein. Often, one gene regulator controls another, and so on, in a gene regulatory network. Gene regulation is essential for viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes as it increases the versatility and adaptability of an organism by allowing the cell to express protein when needed. Although as early as 1951, Barbara McClintock showed interaction between two genetic loci, Activator (''Ac'') and Dissociator (''Ds''), in the color f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many RNA viruses is composed of negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Background A DNA transcription unit encoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Factor
A sigma factor (σ factor or specificity factor) is a protein needed for initiation of Transcription (biology), transcription in bacteria. It is a bacterial transcription initiation factor that enables specific binding of RNA polymerase (RNAP) to gene promoter (biology), promoters. It is homologous to archaeal transcription factor B and to Eukaryote, eukaryotic factor TFIIB. The specific sigma factor used to initiate transcription of a given gene will vary, depending on the gene and on the environmental signals needed to initiate transcription of that gene. Selection of promoters by RNA polymerase is dependent on the sigma factor that associates with it. They are also found in plant chloroplasts as a part of the bacteria-like plastid-encoded polymerase (PEP). The sigma factor, together with RNA polymerase, is known as the RNA polymerase Enzyme#Cofactors, holoenzyme. Every molecule of RNA polymerase holoenzyme contains exactly one sigma factor subunit, which in the model bacterium '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant Proteins
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining two or more fragments from different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, differing only in the nucleotide sequence. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA because they can be made of material from two different species like the mythical chimera. rDNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA can be joined to bacterial DNA, or human DNA can be joined with fungal D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as Transfer RNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) and Small nuclear RNA, small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional List of RNAs, non-coding RNA. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and viruses—to generate the macromolecule, macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, ''i.e.'' observable trait. The genetic information stored in DNA represents the genotype, whereas the phenotype results from the "interpretation" of that informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |