|
TDF Time Signal
ALS162 is a French longwave time signal and standard-frequency radio station and is used for the dissemination of the Metropolitan French national legal time to the public. TéléDiffusion de France broadcast the ALS162 time signal, provided by LNE-SYRTE and LNE-LTFB time laboratories under ANFR (state body for radio frequencies) responsibility, from the Allouis longwave transmitter at 162 kHz, with a power of 800 kW. The current time signal is generated by extremely accurate caesium atomic clocks and phase-modulated on the 162 kHz ( wavelength) carrier signal in a way that is inaudible when listening to the signal using normal Longwave receivers. The ALS162 phase-modulated time signal service requires a more complex receiver than the popular German DCF77 amplitude-modulated time signal service, but the much more powerful transmitter (16 times DCF77's 50 kW) gives it a much greater range of 3,500 km. The signal transmission is almost continuous, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (, , SNCF ) is France's national State-owned enterprise, state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the Rail transport in France, country's national rail traffic along with that of Monaco, including the TGV, on France's high-speed rail network. Its functions include operation of railway services for passengers and freight (through its subsidiaries SNCF Voyageurs and Rail Logistics Europe), as well as maintenance and signalling of rail infrastructure (SNCF#Divisions, SNCF Réseau). The railway network consists of about of route, of which are high-speed lines and electrified. About 14,000 trains are operated daily. In 2010 the SNCF was ranked 22nd in France and 214th globally on the Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500 list. It is the main business of the SNCF Group, which in 2020 had €30 billion of sales in 120 countries. The SNCF Group employs more than 275,000 employees in France and around the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. It is defined such that one radian is the angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an Circular arc, arc that is equal in length to the radius. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit and is currently a dimensionless unit, dimensionless SI derived unit,: "The CGPM decided to interpret the supplementary units in the SI, namely the radian and the steradian, as dimensionless derived units." defined in the SI as 1 rad = 1 and expressed in terms of the SI base unit metre (m) as . Angles without explicitly specified units are generally assumed to be measured in radians, especially in mathematical writing. Definition One radian is defined as the angle at the center of a circle in a plane that wikt:subtend, subtends an arc whose length equals the radius of the circle. More generally, the magnit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
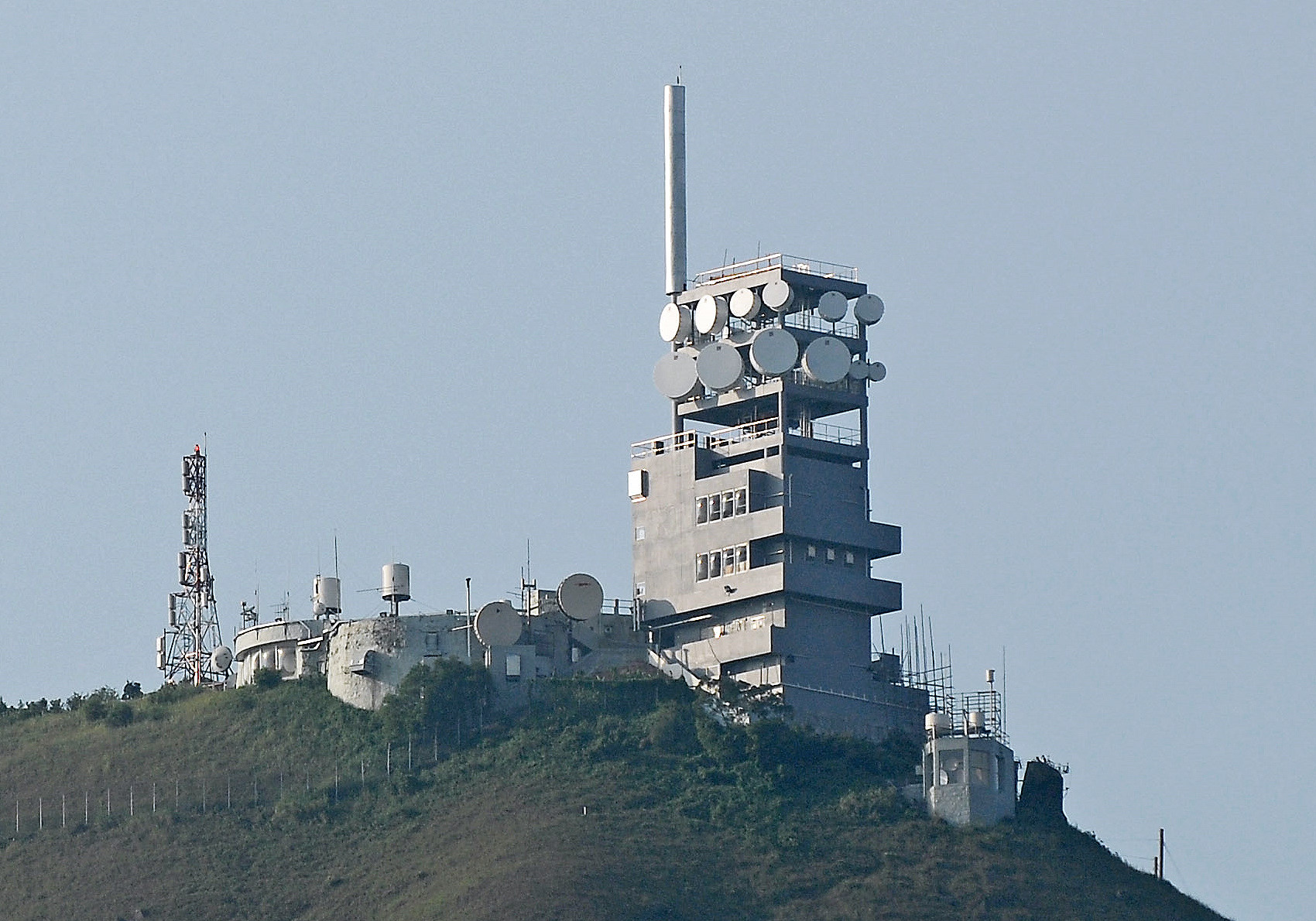
Transmitter Station
A transmitter station or transmission facility is an installation used for transmitting radio frequency signals for wireless communication, broadcasting, microwave link, mobile telephone or other purposes. Choice of location The location may be chosen to fit the coverage area and for VHF-UHF-applications Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight considerations. For lower frequencies a location with good ground conductivity is required. In case of microwave link chains, stations should be in observable ranges of each other. (see Earth bulge) Computer programmes for the terrain profile and abacs are used in addition to on site observations. Avoidance of industrial noise is also taken into consideration. Another parameter may be the government regulations concerning public health requiring a minimum distance to human habitation. The distance depends on the Effective radiated power, power and the frequency of the transmitting signal. Low power stations may be in cities; higher pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its Phase (waves), phase, as in phase modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century beginning with Roberto Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. This original form of AM is sometimes called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM), because the standard method produces sidebands on either side of the carrier frequency. Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to eliminate one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geneva Frequency Plan Of 1975
The Final Acts of the Regional Administrative LF/MF Broadcasting Conference (Regions 1 and 3) Geneva, 1975 is the internationally agreed frequency plan which was drawn up to implement the provisions of the Final Acts of the Regional Administrative LF/MF Broadcasting Conference (Regions 1 and 3) held in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1975. It covers radio broadcasting in the long- and medium-wave bands outside the Americas (a separate agreement being in place for North and South America). The plan was drawn up under the auspices of the World Administrative Radio Conference (WARC) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) with the assistance of the European Broadcasting Union (EBU/UER). The Geneva plan replaced the 1948 Copenhagen plan. It became necessary because of the large number of broadcasting stations in these frequency ranges leading to ever more mutual interference (many countries had refused to ratify the Copenhagen plan and compliance was patchy even among those w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carrier Frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or frequency, are modified by an information bearing signal, called the ''message signal'' or ''modulation signal''. The carrier frequency is usually much higher than the message signal frequency; this is because it is usually impractical to transmit signals with low frequencies over long distances (due to attenuation). The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quartz Clock
Quartz clocks and quartz watches are timepieces that use an electronic oscillator regulated by a quartz crystal to keep time. The crystal oscillator, controlled by the resonant mechanical vibrations of the quartz crystal, creates a signal with very precise frequency, so that quartz clocks and watches are at least an order of magnitude more accurate than mechanical clocks. Generally, some form of digital logic counts the cycles of this signal and provides a numerical time display, usually in units of hours, minutes, and seconds. As the advent of solid-state digital electronics in the 1980s allowed them to be made more compact and inexpensive, quartz timekeepers became the world's most widely used timekeeping technology, used in most clocks and watches as well as computers and other appliances that keep time. Explanation Chemically, quartz is a specific form of a compound called silicon dioxide. Many materials can be formed into plates that will resonate. However, quart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
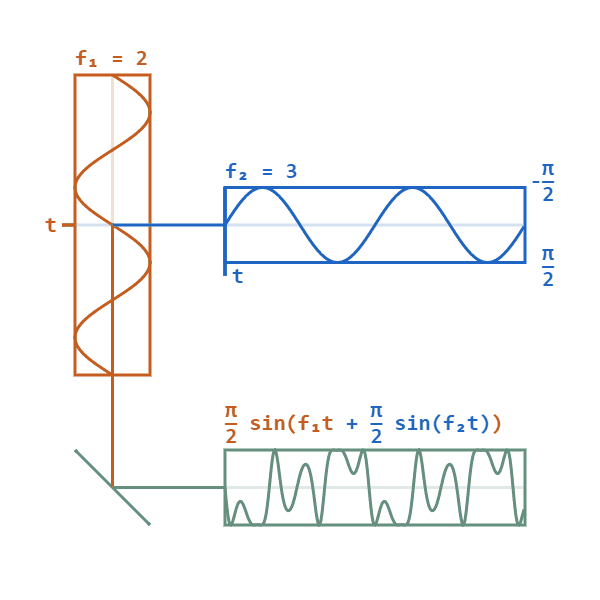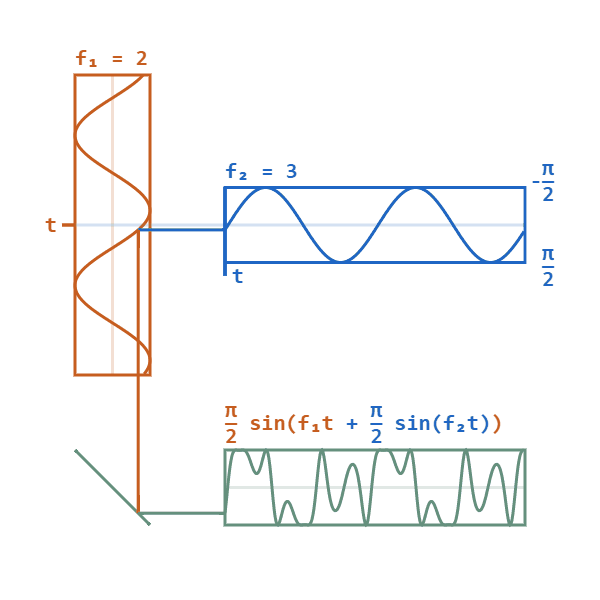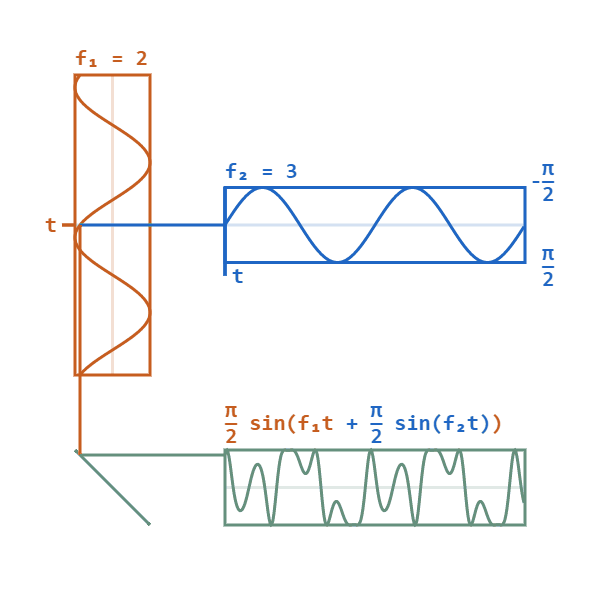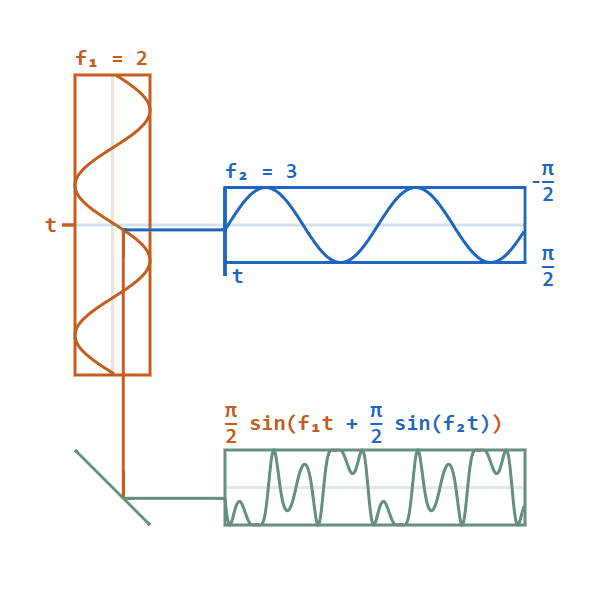
Phase Modulation
Phase modulation (PM) is a signal modulation method for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation, together with frequency modulation. In phase modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the baseband signal modifies the phase of the carrier signal keeping its amplitude and frequency constant. The phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal are maintained constant, but as the amplitude of the message signal changes, the phase of the carrier changes correspondingly. Phase modulation is an integral part of many digital transmission coding schemes that underlie a wide range of technologies like Wi-Fi, GSM and satellite television. However it is not widely used for transmitting analog audio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Call Sign
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be formally assigned by a government agency, informally adopted by individuals or organizations, or even cryptographically encoded to disguise a station's identity. The use of call signs as unique identifiers dates to the landline railroad telegraph system. Because there was only one telegraph line linking all railroad stations, there needed to be a way to address each one when sending a telegram. In order to save time, two-letter identifiers were adopted for this purpose. This pattern continued in radiotelegraph operation; radio companies initially assigned two-letter identifiers to coastal stations and stations on board ships at sea. These were not globally unique, so a one-letter company identifier (for instance, 'M' and two letters as a Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Audio Signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals or a series of binary numbers for Digital signal (signal processing), digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies in the audio frequency range of roughly 20 to 20,000 Hz, which corresponds to the lower and upper Human hearing range, limits of human hearing. Audio signals may be Synthesizer, synthesized directly, or may originate at a transducer such as a microphone, Pickup (music technology), musical instrument pickup, phonograph cartridge, or tape head. Loudspeakers or headphones convert an electrical audio signal back into sound. Digital audio systems represent audio signals in a variety of digital formats.Hodgson, Jay (2010). ''Understanding Records'', p.1. . An audio channel or audio track is an audio signal communications channel in a data storage device, storage device or mixing console. It is used in operations such as multi-track recordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its Phase (waves), phase, as in phase modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century beginning with Roberto Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. This original form of AM is sometimes called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM), because the standard method produces sidebands on either side of the carrier frequency. Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to eliminate one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |