|
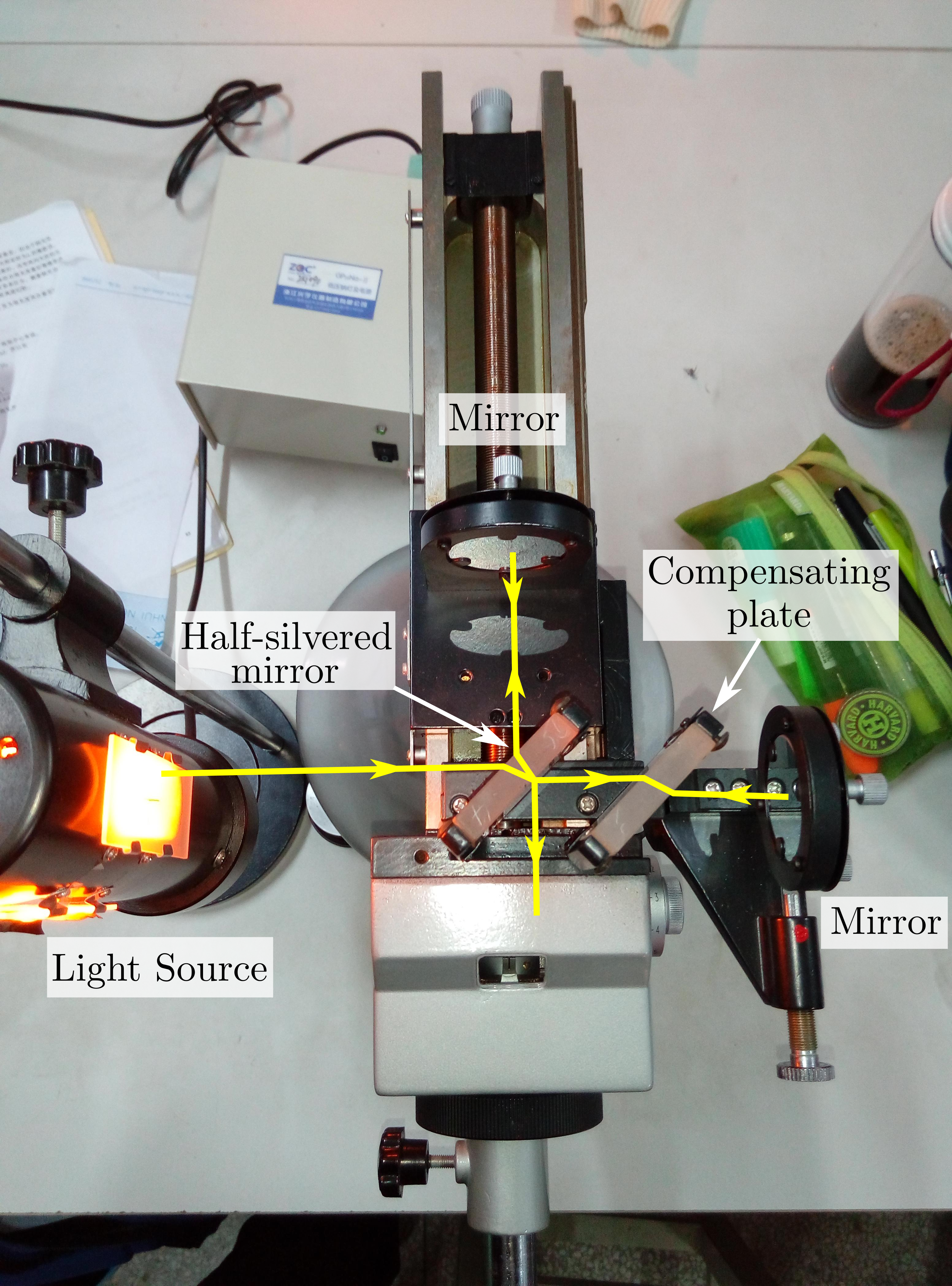
TAMA 300
TAMA 300 is a gravitational wave detector located at the Mitaka campus of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. It is a project of the gravitational wave studies group at the Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR) of the University of Tokyo. The ICRR was established in 1976 for cosmic ray studies, and is currently developing the Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA). TAMA 300 was preceded in Mitaka by a 20m prototype TAMA 20 in years 1991-1994. Later the prototype was moved underground to Kamioka mine and renamed LISM. It operated 2000-2002 and established seismic quietness of the underground location. Construction of the TAMA project started in 1995. Data were collected from 1999 to 2004. It adopted a Fabry–Pérot Michelson interferometer (FPMI) with power recycling. It is officially known as the 300m Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Antenna due to having 300 meter long (optical) arms. The goal of the project was to develop advanced techniques nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gravitational Wave Detector
A gravitational-wave detector (used in a gravitational-wave observatory) is any device designed to measure tiny distortions of spacetime called gravitational waves. Since the 1960s, various kinds of gravitational-wave detectors have been built and constantly improved. The present-day generation of laser interferometers has reached the necessary sensitivity to detect gravitational waves from astronomical sources, thus forming the primary tool of gravitational-wave astronomy. The first direct observation of gravitational waves was made in September 2015 by the Advanced LIGO observatories, detecting gravitational waves with wavelengths of a few thousand kilometers from a merging binary of stellar black holes. In June 2023, four pulsar timing array collaborations presented the first strong evidence for a gravitational wave background of wavelengths spanning light years, most likely from many binaries of supermassive black holes. Challenge The direct detection of gravitational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Astronomical Observatory Of Japan
The (NAOJ) is an astronomy, astronomical research organisation comprising several facilities in Japan, as well as an observatory in Hawaii and Chile. It was established in 1988 as an amalgamation of three existing research organizations - the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory of the University of Tokyo, International Latitude Observatory of Mizusawa, and a part of Research Institute of Atmospherics of Nagoya University. In the 2004 reform of national research organizations, NAOJ became a division of the National Institutes of Natural Sciences, Japan, National Institutes of Natural Sciences. Facilities ;Mitaka Campus (Mitaka, Tokyo. ) :The Headquarters, Astronomy Data Center, Advanced Technology Center, Public Relations Center :Solar Flare Telescope, Sunspot Telescope, TAMA 300 gravitational wave detector :Tokyo Photoelectric Meridian Circle :Historical instruments: Solar Tower Telescope, 65cm refractor dome, 20cm refractor dome ;Nobeyama Radio Observatory (Minamimaki, Nagano. ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gravitational Wave
Gravitational waves are oscillations of the gravitational field that Wave propagation, travel through space at the speed of light; they are generated by the relative motion of gravity, gravitating masses. They were proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as the gravitational equivalent of Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves. In 1916, Albert Einstein demonstrated that gravitational waves result from his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, instead asserting that gravity has instantaneous effect everywhere. Gravitational waves therefore stand as an important relativistic phenomenon that is absent from Newtonian physics. Gravitational-wave astronomy has the advantage that, unlike elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Institute For Cosmic Ray Research
The Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR) of the University of Tokyo (東京大学宇宙線研究所 ''Tōkyōdaigaku Uchūsen Kenkyūsho'') was established in 1976 for the study of cosmic rays. The gravitational wave studies group is currently constructing the detector KAGRA located at the Kamioka Observatory. Facilities * Kashiwa Campus of the University of Tokyo * Akeno Observatory * Kamioka Observatory * Norikura Observatory Current projects *Super-Kamiokande - Detection of neutrinos and search for proton decays in a large water tank *Tibet - Search for point sources of VHE cosmic gamma rays at Tibet heights *Telescope Array Project - Aiming at highest energy cosmic ray physics by detecting weak light from atmosphere"New Ground-Based Arrays to Probe Cosmic Powerhouses" By Dennis Normile Science 30 April 1999: 734-735 *Gravitational Wave Group - Constructing the gravitational wave detector KAGRA The Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA) is a large interferometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo (, abbreviated as in Japanese and UTokyo in English) is a public research university in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Founded in 1877 as the nation's first modern university by the merger of several pre-westernisation era institutions, its direct precursors include the '' Tenmongata'', founded in 1684, and the Shōheizaka Institute. Although established under its current name, the university was renamed in 1886 and was further retitled to distinguish it from other Imperial Universities established later. It served under this name until the official dissolution of the Empire of Japan in 1947, when it reverted to its original name. Today, the university consists of 10 faculties, 15 graduate schools, and 11 affiliated research institutes. As of 2023, it has a total of 13,974 undergraduate students and 14,258 graduate students. The majority of the university's educational and research facilities are concentrated within its three main Tokyo campuses: Hongō, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
KAGRA
The Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA) is a large interferometer designed to detect gravitational waves predicted by the general theory of relativity. KAGRA is a Michelson interferometer that is isolated from external disturbances: its mirrors and instrumentation are suspended and its laser beam operates in a vacuum. The instrument's two arms are three kilometres long and located underground at the Kamioka Observatory which is near the Kamioka section of the city of Hida in Gifu Prefecture, Japan. KAGRA is a project of the gravitational wave studies group at the Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR) of the University of Tokyo. It became operational on 25 February 2020, when it began data collection. It is Asia's first gravitational wave observatory, the first in the world built underground, and the first whose detector uses cryogenic mirrors. The cryogenic mirrors reduce the thermal noise and the underground location acts to significantly reduce the noise from seism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fabry–Pérot Interferometer
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces (i.e.: thin mirrors). Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is named after Charles Fabry and Alfred Perot, who developed the instrument in 1899. ''Etalon'' is from the French ''étalon'', meaning "measuring gauge" or "standard". Etalons are widely used in telecommunications, lasers and spectroscopy to control and measure the wavelengths of light. Recent advances in fabrication technique allow the creation of very precise tunable Fabry–Pérot interferometers. The device is technically an interferometer when the distance between the two surfaces (and with it the resonance length) can be changed, and an etalon when the distance is fixed (however, the two terms are often used interchangeably). Basic description The heart of the Fabry–Pérot interferometer is a pair of partially reflective glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Michelson Interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson in 1887. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test. The Michelson interferometer is employed in many scientific experiments and became well known for its use by Michelson and Edward Morley in the famous Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) in a configuration which would have detected the Earth's motion through the supposed luminiferous aether that most physicists a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way, where Earth is located. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a " dumbbell" shape; the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda and the Milky Way galaxies, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CLIO
In Greek mythology, Clio ( , ; ), also spelled Kleio, Сleio, or Cleo, is the muse of history, or in a few mythological accounts, the muse of lyre-playing. Etymology Clio's name is derived from the Greek root κλέω/κλείω (meaning "to recount", "to make famous" or "to celebrate"). The name's traditional Latinisation is Clio, Lewis and Short, ''A Latin Dictionary: Founded on Andrews' Edition of Freund's Latin Dictionary: Revised, Enlarged, and in Great Part Rewritten by Charlton T. Lewis, Ph.D. and Charles Short, LL.D''. The Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1879, ''s.v.'' but some modern systems such as the American Library Association-Library of Congress system use ''K'' to represent the original Greek '' kappa'', and ''ei'' to represent the diphthong ''ει'' ( epsilon iota), thus ''Kleio''. Depiction Clio, sometimes referred to as "the Proclaimer", is often represented with an open parchment scroll, a book, or a set of tablets. She is also shown with the heroic trum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kamioka Mine
The is a neutrino and gravitational waves laboratory located underground in the Mozumi mine of the Kamioka Mining and Smelting Co. near the Kamioka section of the city of Hida in Gifu Prefecture, Japan. A set of groundbreaking neutrino experiments have taken place at the observatory over the past two decades. All of the experiments have been very large and have contributed substantially to the advancement of particle physics, in particular to the study of neutrino astronomy and neutrino oscillation. The mine The Mozumi mine is one of two adjacent mines owned by the Kamioka Mining and Smelting Co. (a subsidiary of the Mitsui Mining and Smelting Co. Mitsui Kinzoku''). The mine is famous as the site of one of the greatest mass-poisonings in Japanese history. From 1910 to 1945, the mine operators released cadmium from the processing plant into the local water. This cadmium caused what the locals called itai-itai disease. The disease caused weakening of the bones and extreme pain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, Optical fiber, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, Nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, interactome, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |