|
Sundaic
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It includes Borneo, Java, and Sumatra in Indonesia, and their surrounding small islands, as well as the Malay Peninsula on the Asian mainland. Extent The area of Sundaland encompasses the Sunda Shelf, a tectonically stable extension of Southeast Asia's continental shelf that was exposed during glacial periods of the last 2 million years. The extent of the Sunda Shelf is approximately equal to the 120-meter isobath. In addition to the Malay Peninsula and the islands of Borneo, Java, and Sumatra, it includes the Java Sea, the Gulf of Thailand, and portions of the South China Sea. In total, the area of Sundaland is approximately 1,800,000 km2. The area of exposed land in Sundaland has fluctuated considerably during the past recent 2 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Sunda And Sahul
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
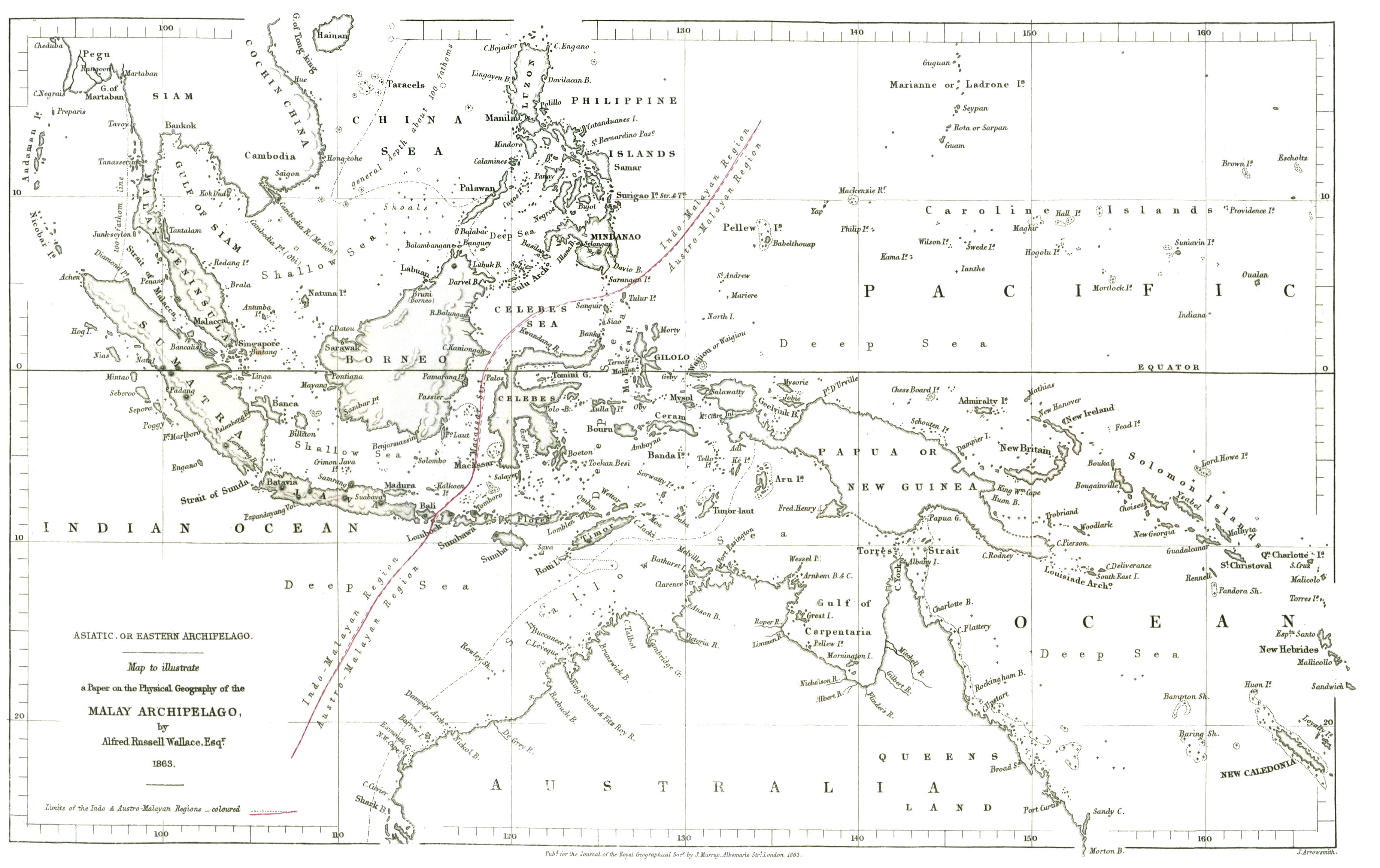
Wallace Line
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and Wallacea, a transitional zone between Asia and Australia. West of the line are found organisms related to Asiatic species; to the east, a mixture of species of Asian and Australian origin is present. Wallace noticed this clear division during his travels through the East Indies in the 19th century. The line runs through Indonesia, between Borneo and Sulawesi (Celebes), and through the Lombok Strait between Bali and Lombok. The distance between Bali and Lombok is small, about . The distributions of many bird species observe the line, since many birds do not cross even the shortest stretches of open ocean water. Some bats have distributions that cross the line, but larger terrestrial mammals are generally limited to one side or the other; exceptions include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transpiration (movement of water from the soil, through roots and bodies of vegetation, on leaves and then into the air). Evapotranspiration is an important part of the local water cycle and climate, as well as measurement of it plays a key role in agricultural irrigation and water resource management. Definition Evapotranspiration is a combination of evaporation and transpiration, measured in order to better understand crop water requirements, irrigation scheduling, and watershed management. The two key components of evapotranspiration are: * Evaporation: the movement of water directly to the air from sources such as the soil and water bodies. It can be affected by factors including heat, humidity, and wind speed. * Transpiration: the move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly overhead (no more than about 23° from the zenith) every day, year-round. Consequently, the equator has a rather stable daytime temperature throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). In terms of climate, the tropics receive sunlight that is more direct than the rest of Earth and are generally hotter and wetter as they aren't affected as much by the solar seasons. The word "tropical" sometimes refers to this sort of climate in the zone rather than to the geographical zone itself. The tropical zone includes deserts and snow-capped mountains, which are not tropical in the climatic sense. The tropics are distinguished from the other climatic and biomatic regions of Earth, which are the middle latitudes and the polar regions on either side of the equatorial zone. The tropics constitute 40% of Earth's surface area and contain 36% of Earth's landmass. , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fluctuations around the Strait of Magellan suggest the peak in glacial surface area was constrained to betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytogeography
Phytogeography (from Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution of plant species and their influence on the earth's surface. Phytogeography is concerned with all aspects of plant distribution, from the controls on the distribution of individual species ranges (at both large and small scales, see species distribution) to the factors that govern the composition of entire communities and floras. Geobotany, by contrast, focuses on the geographic space's influence on plants. Fields Phytogeography is part of a more general science known as biogeography. Phytogeographers are concerned with patterns and process in plant distribution. Most of the major questions and kinds of approaches taken to answer such questions are held in common between phyto- and zoogeographers. Phytogeography in wider sense (or geobot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Timor, Halmahera, Buru, Seram, and many smaller islands. The islands of Wallacea lie between the Sunda Shelf (the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Java, and Bali) to the west, and the Sahul Shelf including Australia and New Guinea to the south and east. The total land area of Wallacea is . Geography Wallacea is defined as the series of islands stretching between the two continental shelves of Sunda and Sahul, but excluding the Philippines. Its eastern border (separating Wallacea from Sahul) is represented by a zoogeographical boundary known as Lydekker's Line, while the Wallace Line (separating Wallacea from Sunda) defines its western border. The Weber Line is the midpoint, at which Asian and Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasian Realm
The Australasian realm is a biogeographic realm that is coincident with, but not (by some definitions) the same as, the geographical region of Australasia. The realm includes Australia, the island of New Guinea (comprising Papua New Guinea and the Indonesian province of Papua), and the eastern part of the Indonesian archipelago, including the island of Sulawesi, the Moluccan islands (the Indonesian provinces of Maluku and North Maluku), and the islands of Lombok, Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, and Timor, often known as the Lesser Sundas. The Australasian realm also includes several Pacific island groups, including the Bismarck Archipelago, Vanuatu, the Solomon Islands, and New Caledonia. New Zealand and its surrounding islands are a distinctive sub-region of the Australasian realm. The rest of Indonesia is part of the Indomalayan realm. In the classification scheme developed by Miklos Udvardy, New Guinea, New Caledonia, Solomon Islands and New Zealand are placed in the Oceania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |