|
Story Of Wenamun
The Story of Wenamun (alternately known as the Report of Wenamun, The Misadventures of Wenamun, Voyage of Unamūn, or nformallyas just Wenamun) is a literary text written in hieratic in the Late Egyptian language. It is only known from one incomplete copy discovered in 1890 at al-Hibah, Egypt, and subsequently purchased in 1891 in Cairo by the Russian Egyptologist Vladimir Goleniščev. It was found in a jar together with the Onomasticon of Amenope and the Tale of Woe. The papyrus is now in the collection of the Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts, Moscow, and officially designated as ''Papyrus Pushkin 120''. The hieratic text was published by Korostovcev 1960, and the hieroglyphic text was published by Gardiner 1932 (as well as on-line). Discovery The two-page papyrus is unprovenanced. It was reported to have been discovered in an illicit excavation at al-Hibah, Egypt, and was bought by Vladimir Golenishchev in 1891-92. Golenishchev published the manuscript in 1897-99. The text The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushkin Museum
The Pushkin State Museum of Fine Arts (russian: Музей изобразительных искусств имени А. С. Пушкина, abbreviated as ) is the largest museum of European art in Moscow, located in Volkhonka street, just opposite the Cathedral of Christ the Saviour (Moscow), Cathedral of Christ the Saviour. The International musical festival ''Sviatoslav Richter's December nights'' has been held in the Pushkin Museum since 1981. Etymology Despite its name, the museum has no direct association with the Russian poet Alexander Pushkin, other than as a posthumous commemoration. The facility was founded by professor Ivan Tsvetaev (father of the poet Marina Tsvetaeva). Tsvetaev persuaded the millionaire and philanthropist Yury Nechaev-Maltsov, Yuriy Nechaev-Maltsov and the architect Roman Klein of the urgent need to give Moscow a fine arts museum. After going through a number of name changes, particularly in the transition to the Soviet era and the return of the Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Golenishchev
Vladimir Semyonovich Golenishchev (russian: Владимир Семёнович Голенищев; 29 January 1856 – 5 August 1947), formerly also known as Wladimir or Woldemar Golenischeff, was one of the first and most accomplished Russian Egyptologists. Life Golenishchev, the son of a well-to-do merchant, was educated at the Saint Petersburg University. In 1884–85 he organized and financed excavations in Wadi Hammamat, followed by the research at Tell el-Maskhuta in 1888–89. In the course of the following two decades he travelled to Egypt more than sixty times and brought back an enormous collection of more than 6,000 ancient Egyptian antiquities, including such priceless relics as the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus, the Story of Wenamun, the Alexandrian World Chronicle, and various Fayum portraits. He also published the so-called Hermitage papyri, including the Prophecy of Neferti, now stored in the Hermitage Museum. Having sold his collection to the Moscow Museum of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinedjem I
Pinedjem I was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes in Ancient Egypt from 1070 to 1032 BC and the ''de facto'' ruler of the south of the country from 1054 BC. He was the son of the High Priest Piankh. However, many Egyptologists today believe that the succession in the Amun priesthood actually ran from Piankh to Herihor to Pinedjem I. Reign According to the new hypothesis regarding the succession of the Amun priesthood, Pinedjem I was too young to succeed to the High Priesthood of Amun after the death of Piankh. Herihor instead intervened to assume this office. After Herihor's death, Pinedjem I finally claimed this office which had once been held by his father Piankh. This interpretation is supported by the decorations from the Temple of Khonsu at Karnak where Herihor's wall reliefs here are immediately followed by those of Pinedjem I with no intervening phase for Piankh and also by the long career of Pinedjem I who served as High Priest of Amun and later as king at Thebes. He inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-first Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXI, alternatively 21st Dynasty or Dynasty 21) is usually classified as the first Dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian Third Intermediate Period, lasting from 1077 BC to 943 BC. History After the reign of Ramesses III, a long, slow decline of royal power in Egypt followed. The pharaohs of the Twenty-first Dynasty ruled from Tanis, but were mostly active only in Lower Egypt, which they controlled. This dynasty is described as 'Tanite' because its political capital was based at Tanis. Meanwhile, the High Priests of Amun at Thebes effectively ruled Middle and Upper Egypt in all but name. The later Egyptian Priest Manetho of Sebennytos states in his Epitome on Egyptian royal history that "the 21st Dynasty of Egypt lasted for 130 years".Kenneth A. Kitchen, The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt (1100–650 BC), 3rd edition, 1986, Warminster: Aris & Phillips Ltd, p.531 Pharaohs of the 21st Dynasty Timeline of the 21st Dynasty ImageS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
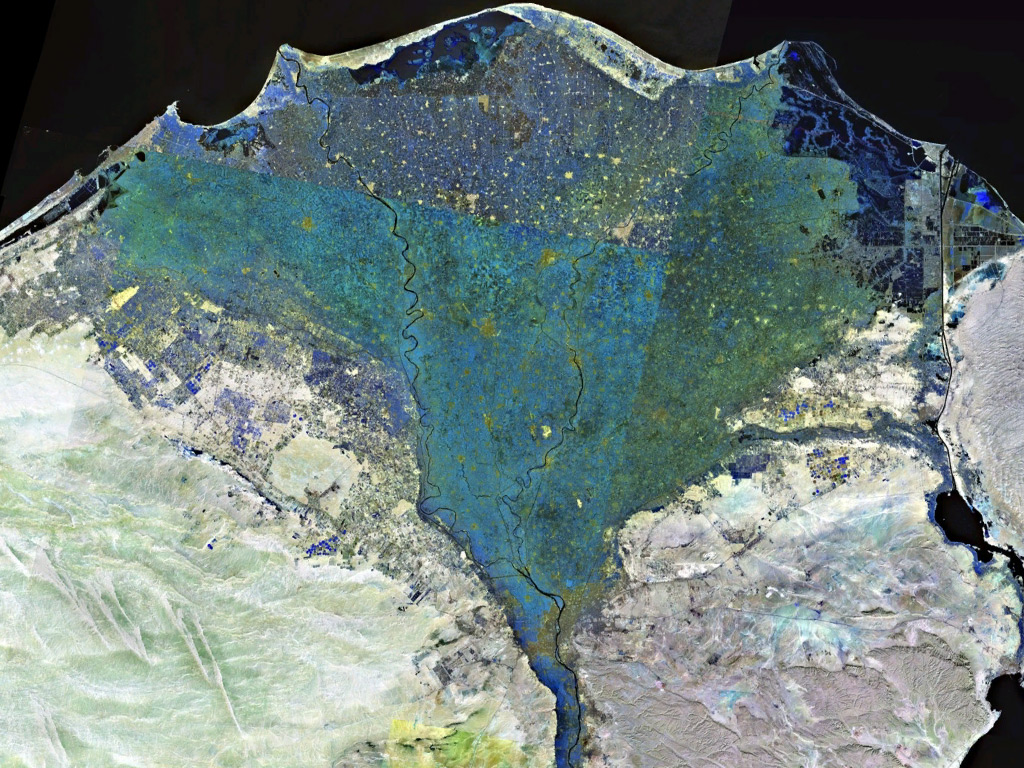
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smendes I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Smendes was the founder of the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt and succeeded to the throne after burying Ramesses XI in Lower Egypt – territory which he controlled. His Egyptian nomen or birth name was actually Nesbanebdjed meaning "He of the Ram, Lord of Mendes", but it was translated into Greek as Smendes by later classical writers such as Josephus and Sextus Africanus. According to the Story of Wenamun from , Smendes was a governor of Lower Egypt during the Era of the Renaissance under the reign of Ramesses XI, however, Egyptologists have questioned the historical accuracy of that story. Family Smendes may have been a son of a lady named Hrere. Hrere was a Chief of the Harem of Amun-Re and likely the wife of a high priest of Amun. If Hrere was Smendes' mother, then he was a brother of Nodjmet and through her brother-in-law of the High Priests Herihor and Piankh. Smendes was married to Tentamun B, likely a daughter of Ramesses IX. They may have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piankh
Piankh was a High Priest of Amun during the 21st Dynasty. Chronological and genealogical position While the High Priest of Amun Piankh (or Payankh) has been assumed to be a son-in-law of Herihor and his heir to the Theban office of the High Priest of Amun, recent studies by Karl Jansen-Winkeln of the surviving temple inscriptions and monumental works by Herihor and Piankh in Upper Egypt imply that Piankh was actually Herihor's predecessor. Piankh held a number of official positions including High Priest of Amun, King's scribe, King's son of Kush, Overseer of the foreign countries to the South, overseer of the granaries and commander of the archers of the whole of pperEgypt. He was succeeded in office by either Herihor or his son Pinedjem. Family The identity of Piankh's wife has not been established beyond doubt. In the Temple of Luxor there is a graffito of which only rudimentary traces of the beginning of her name have survived. These have been interpreted as either an "h" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herihor
Herihor was an Egyptian army officer and High Priest of Amun at Thebes (1080 BC to 1074 BC) during the reign of Pharaoh Ramesses XI. Chronological and genealogical position Traditionally his career was placed before that of the High Priest of Amun, Piankh, since it was believed that the latter was his son. However, this filiation was based on an incorrect reconstruction by Karl Richard Lepsius of a scene in the Temple of Khonsu. It is now believed that the partly preserved name of the son of Herihor depicted there was not , but rather . Since then, Karl Jansen-Winkeln has argued that Piankh preceded rather than succeeded Herihor as High Priest at Thebes and that Herihor outlived Ramesses XI before being succeeded in this office by Pinedjem I, Piankh's son. If Jansen-Winkeln is correct, Herihor would have served in office as High Priest, after succeeding Piankh, for longer than just 6 years, as is traditionally believed. The following paragraphs contain several statements based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Priest Of Amun
The High Priest of Amun or First Prophet of Amun ('' ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn'') was the highest-ranking priest in the priesthood of the ancient Egyptian god Amun. The first high priests of Amun appear in the New Kingdom of Egypt, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty. History The priesthood of Amun rose in power during the early Eighteenth dynasty through significant tributes to the god Amun by ruler such as Hatshepsut and more importantly Thutmose III. The Amun priesthood in Thebes had four high-ranking priests: * The Chief Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr tpj n jmn''), also referred to as the Chief Priest of Amun. * The Second Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr snnw n jmn''), also referred to as the Second Priest of Amun. * The Third Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr ḫmtnw n jmn khemet-nu''), also referred to as the Third Priest of Amun. * The Fourth Prophet of Amun at Karnak (''ḥm nṯr jfdw n jmn''), also referred to as the Fourth Priest of Amun. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This dynasty is generally considered to be the start of the decline of Ancient Egypt. History Background Upon the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt descended into a period of civil war, as attested by the Elephantine stela built by Setnakhte. The circumstances of Twosret's demise are uncertain, as she may have died peacefully during her reign or been overthrown by Setnakhte, who was likely already middle aged at the time. 20th Dynasty A consistent theme of this dynasty was the loss of pharaonic power to the High Priests of Amun. Horemheb, a pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty, had restored the traditional Ancient Egyptian religion and the priesthood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses XI
Menmaatre Ramesses XI (also written Ramses and Rameses) reigned from 1107 BC to 1078 BC or 1077 BC and was the tenth and final pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt and as such, was the last king of the New Kingdom period. He ruled Egypt for at least 29 years although some Egyptologists think he could have ruled for as long as 30. The latter figure would be up to 2 years beyond this king's highest known date of Year 10 of the ''Whm Mswt'' era or Year 28 of his reign. One scholar, Ad Thijs, has suggested that Ramesses XI could even have reigned as long as 33 years. It is believed that Ramesses ruled into his Year 29 since a graffito records that the general and High Priest of Amun Piankh returned to Thebes from Nubia on III Shemu day 23—or just 3 days into what would have been the start of Ramesses XI's 29th regnal year. Piankh is known to have campaigned in Nubia during Year 28 of Ramesses XI's reign (or Year 10 of the Whm Mswt) and would have returned home to Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |