|
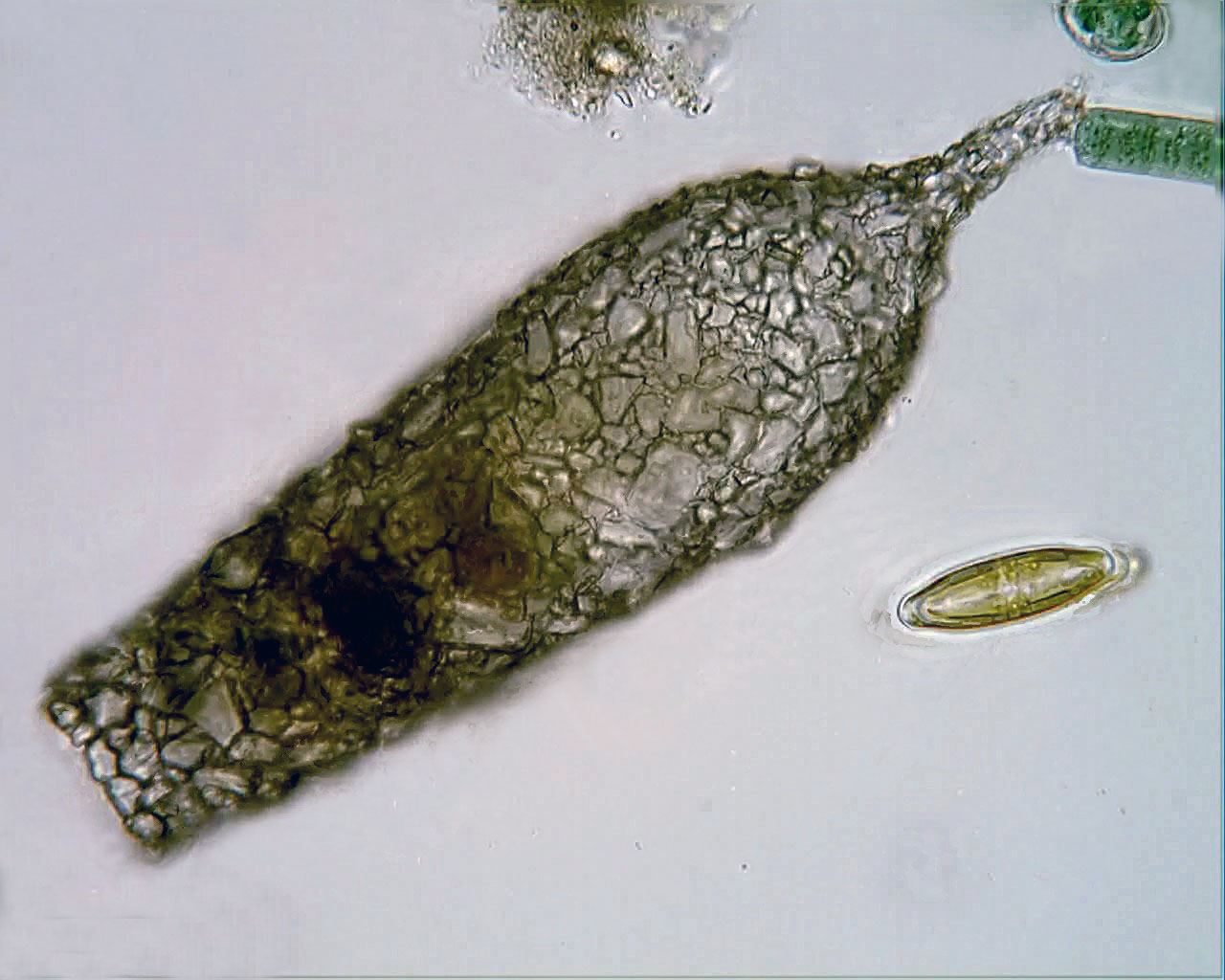
Stercomata
Stercomata (or stercomes) are extracellular pellets of waste material produced by some groups of foraminiferans, including xenophyophoreans and komokiaceans, ''Gromia'', and testate amoebae. The pellets are ovoid (egg-shaped), brownish in color, and on average measure from 10-20 µm in length. Stercomata are composed of small mineral grains and undigested waste products held together by strands of glycosaminoglycans. The term “sterkome” was first used Schaudinn in 1899 to describe the balls of undigested food remains produced by the testate amoeba ''Trichosphaerium sieboldi'', the foraminiferan ''Saccammina sphaerica'', and the gromiid ''Gromia dujardinii''. Schaudinn conducted feeding experiments on live individuals of ''Trichosphaerium sieboldi'' kept in culture dishes to confirm that stercomata were accumulations of waste material produced as a byproduct of feeding. Taxonomic distribution Foraminifera Stercomata are produced by members of several different subclades of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell biology), ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a "Test (biology), test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and Textularia in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthos, benthic), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typically produce a test (biology), test, or shell, which can have eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophyophorea
Xenophyophorea is a clade of foraminiferans. Members of this class are multinucleate unicellular organisms found on the ocean floor throughout the world's oceans, at depths of . They are a kind of foraminiferan that extract minerals from their surroundings and use them to form an exoskeleton known as a test. They were first described by Henry Bowman Brady in 1883. They are abundant on abyssal plains, and in some regions are the dominant species. Fifteen genera and 75 species have been described, varying widely in size. The largest, ''Syringammina fragilissima'', is among the largest known coenocytes, reaching up to in diameter. Naming and classification The name Xenophyophora means "bearer of foreign bodies", from the Greek. This refers to the sediments, called xenophyae, which are cemented together to construct their tests. In 1883, Henry Bowman Brady classified them as primitive Foraminifera. Later they were placed within the sponges. In the beginning of the 20th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komokiacea
The Komokiacea are a small group of amoeboid protozoa, considered to be foraminifera, though there have been suggestions that they are a separate group, closely related to foraminifera. Komokiacea are rather large organisms, often exceeding 300 micrometers in maximum dimensions. Along with Xenophyophores they dominate the macro- and megabenthic fauna in the deep sea and are commonly referred to as "giants protists". The komokiacean body consists of a central tube with several branching tubules that contain diffuse protoplasm and numerous waste pellets (stercomata). They often incorporate fine grain material between the tubules. However, in other forms such as that of the genus Lana the body is a loose mass of branching tubules with no centre of organization. Komokiacea serve often as a substrate for benthic meiofaunal organisms such as foraminifera, fungi and other deep-sea taxa. They are fragile and often get fragmented during analysis in the laboratory, which leads to a large n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
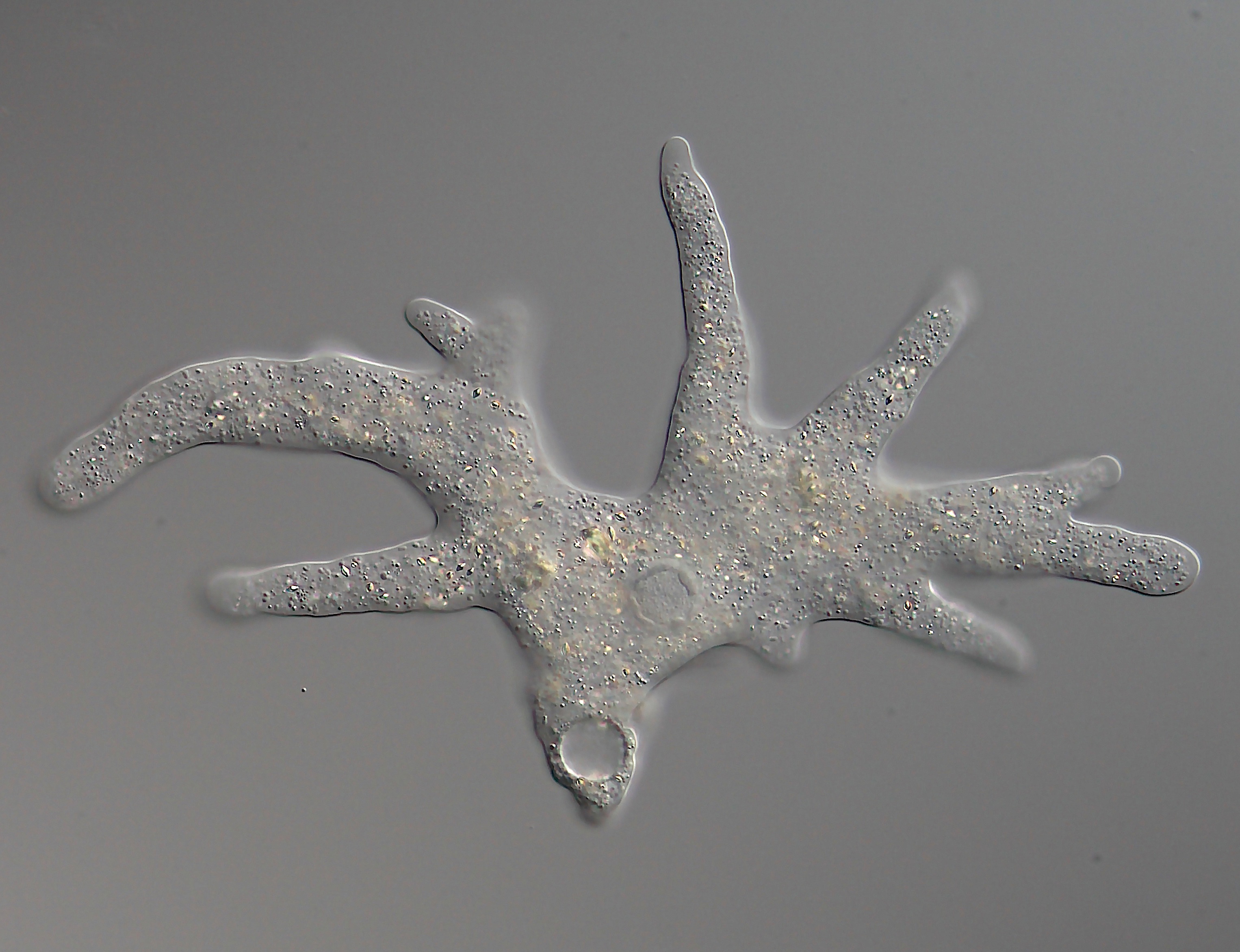
Gromia
''Gromia'' is a genus of protists, closely related to foraminifera, which inhabit marine and freshwater environments. It is the only genus of the family Gromiidae. ''Gromia'' are ameboid, producing filose pseudopodia that extend out from the cell's proteinaceous test through a gap enclosed by the cell's oral capsule. The test, a shell made up of protein that encloses the cytoplasm, is made up of several layers of membrane, which resemble honeycombs in shape — a defining character of this genus. ''Gromia'' were first discovered in shallow waters, with members of the best-characterized species ''Gromia oviformus'' often found inhabiting rock surfaces, sediments, or seaweed holdfasts. However, research from the 1990s and early 2000s identified gromiids inhabiting depths up to 4,392 m, leading to several new deep-sea ''Gromia'' species being described and recognized. A recent study of the deep sea species ''Gromia sphaerica'' revealed that it produces traces on the seafloor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testate Amoebae
Testate amoebae (formerly thecamoebians, Testacea or Thecamoeba) are a polyphyletic group of unicellular amoeboid protists, which differ from naked amoebae in the presence of a test that partially encloses the cell, with an aperture from which the pseudopodia emerge, that provides the amoeba with shelter from predators and environmental conditions. The test of some species is produced entirely by the amoeba and may be organic, siliceous or calcareous depending on the species (autogenic tests), whereas in other cases the test is made up of particles of sediment collected by the amoeba which are then agglutinated together by secretions from within the cell (xenogenic tests). A few taxa (Hyalosphenidae) can build either type, depending on the circumstances and availability of foreign material. The assemblage referred to as "testate amoebae" is actually composed of several, unrelated groups of organisms. However, some features they all share that have been used to group them together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures. Hepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endomyxa
Endomyxa is a subphylum of Rhizaria The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many foramini .... References External links Bikont subphyla {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many foraminifera and radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, ''Guttulinopsis vulgaris'', a cellular slime mold, has also been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters (synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeleton (thecae or loricas), which is in differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopodia
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Some pseudopodial cells are able to use multiple types of pseudopodia depending on the situation: Most of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially altered bilirubin, and dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. Feces are discharged through the anus or cloaca during defecation. Feces can be used as fertilizer or soil conditioner in agriculture. They can also be burned as fuel or dried and used for construction. Some medicinal uses have been found. In the case of human feces, fecal transplants or fecal bacteriotherapy are in use. Urine and feces together are called excreta. Skatole is the principal compound responsible for the unpleasant smell of feces. Characteristics The distinctive odor of feces is due to skatole, and thiols (sulfur-containing compounds), as well as amines and carboxylic acids. Skatole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecalith
A fecalith is a stone made of feces. It is a hardening of feces into lumps of varying size and may occur anywhere in the intestinal tract but is typically found in the colon. It is also called appendicolith when it occurs in the appendix and is sometimes concomitant with appendicitis. They can also obstruct diverticula. It can possibly form secondary to fecal impaction. A '' fecaloma'' is a more severe form of fecal impaction, and a hardened fecaloma may be considered to be a giant fecalith. The term is from Greek líthos=stone. Diagnosis * CT Scan * Projectional radiography * Ultrasound Complications A small fecalith is one cause of both appendicitis and acute diverticulitis. File:AppendicolithPlainCT.png, Appendicolith as seen on CT File:AppendicolithPlainXray.png, Appendicolith as seen on plain X ray See also * Bezoar * Fecal impaction A fecal impaction is a solid, immobile bulk of feces that can develop in the rectum as a result of chronic constipation. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |