|
Stalinist Repressions In Mongolia
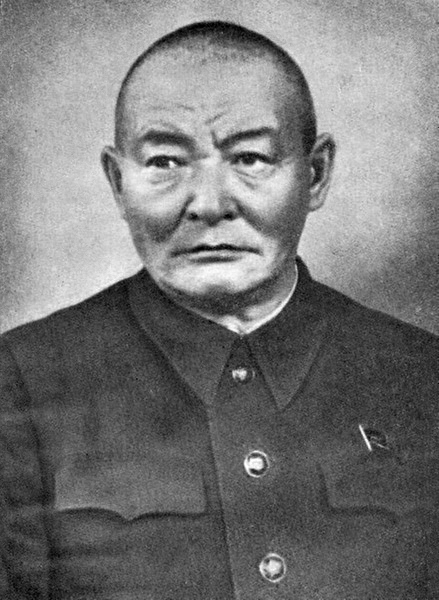
The Stalinist repressions in Mongolia ( mn, Их Хэлмэгдүүлэлт, Ikh Khelmegdüülelt, ''"Great Repression"'') refers to an 18 month period of heightened political violence and persecution in the Mongolian People's Republic between 1937 and 1939. The repressions were an extension of the Stalinist purges (also known as the Great Purge) unfolding across the Soviet Union around the same time. Soviet NKVD advisors, under the nominal direction of Mongolia's ''de facto'' leader Khorloogiin Choibalsan, persecuted thousands of individuals and organizations perceived as threats to the Mongolian revolution and the growing Soviet influence in the country. As in the Soviet Union, methods of repression included torture, show trials, executions, and imprisonment in remote forced labor camps, often in Soviet gulags. Estimates differ, but anywhere between 20,000 and 35,000 "enemies of the revolution" were executed, a figure representing three to five percent of Mongolia's total po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Mongolia
Various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu (3rd century BC–1st century AD), the Xianbei state ( AD 93–234), the Rouran Khaganate (330–555), the First (552–603) and Second Turkic Khaganates (682–744) and others, ruled the area of present-day Mongolia. The Khitan people, who used a para-Mongolic language, founded an empire known as the Liao dynasty (916–1125), and ruled Mongolia and portions of North China, northern Korea, and the present-day Russian Far East. In 1206, Genghis Khan was able to unite the Mongol tribes, forging them into a fighting force which went on to establish the largest contiguous empire in world history, the Mongol Empire (1206–1368). After the fragmentation of the Mongol Empire, Mongolia came to be ruled by the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) based in Khanbaliq (modern Beijing) and administered as part of the Lingbei Province. Buddhism in Mongolia began with the Yuan emperors' conversion to and dissemination of Tibetan Buddhism. After colla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent ( Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navaandorjiin Jadambaa
Navaandorjiin Jadambaa ( Mongolian: Наваандоржийн Жадамбаа; 1900–1939) was the first republican Head of State of Mongolia. He became Acting Chairman of the State Great Hural in November 1924 following the death of the Bogd Khan, as he was replaced by Peljidiin Genden Peljidiin Genden ( mn, Пэлжидийн Гэндэн; 1892 or 1895 – November 26, 1937) was a prominent political leader of the Mongolian People's Republic who served as the country's first President (1924 to 1927; Navaandorjiin Jadambaa wa ... only a day later. Usually a regency would follow the death of the Bogd Khan until his reincarnation had reached his majority; however, in this case the search for the reincarnation of the Bogd Khan was banned and the country has maintained a republican constitution ever since. {{DEFAULTSORT:Jadambaa, Navaandorjiin 1900 births 1939 deaths Speakers of the State Great Khural Heads of state of Mongolia Communist rulers Communism in Mongolia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tseren-Ochiryn Dambadorj
Tseren-Ochiryn Dambadorj ( mn, Цэрэн-Очирын Дамбадорж; 1898 – June 25, 1934) was a Mongolian politician who served as Chairman of the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party from 1921 to 1928. He was expelled from the party in 1928 for his rightist policies and died in Moscow, USSR in 1934. Born in Niislel Khüree in 1898, Dambadorj attended Manchu and Russian Interpreter's School in the capital before moving onto the Russian gynamsium and then secondary school in Troitskosavsk. He joined the Mongolian People's Party (MPP) in 1921, was acting chairman of the MPP Central Committee in March 1921. After the Outer Mongolian Revolution of 1921 he was elected vice chairman (January to March 1922) and then chairman of the MPP Central Committee from March 15, 1922, to January 12, 1923, and again from August 31, 1924, to October 27, 1928. At the Third Party Congress in 1924, Dambadorj along with leftist leader Rinchingiin Elbegdorj, led calls for the arrest and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamsrangiin Tseveen
Jamsrangiin Tseveen ( mn, Жамсрангийн Цэвээн; russian: Цыбен Жамцаранович Жамцарано; often romanized to Jamtsarano), (1880 – May 14, 1942) was a Buryats, Buryat scholar and one of the leading figures in Mongolian politics and especially academia in the 1920s. Early life Tseveen was born in the Aginsk district of Transbaikalia in 1880. He went to school in Chita, Zabaykalsky Krai, Chita and later to Badmaev's Buryat private school in St. Petersburg. From 1898 to 1902, he attended the Teacher's seminary in Irkutsk, where he began to visit neighbouring Buryat clans and to collect epics and materials related to shamanism, and Mongol law. Scientific career In 1902 he and his friend Baradin returned to St. Petersburg and became auditors at the St. Petersburg University. A professor arranged for them to travel to Buryatia in 1903 to collect more material. Tseveen went to the northwest Baikal area and Olkhon island, and his work proved succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajvaagiin Danzan
Ajvaagiin Danzan ( mn, Ажваагийн Данзан; 1895–1932),Sanders, Alan J. K. (1996). ''Historical Dictionary of Mongolia''. Scarecrow Press, also known as Japan Danzan or Little Danzan, was chairman of Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party (MPRP) from January 2, 1923, to August 31, 1924. Born to peasant parents in Tüsheet Khan Province (present day east central Mongolia) in 1895, Danzan traveled to Japan in 1916, thus earning the moniker he carried later in life to distinguish him from his contemporary namesake, party leader Soliin Danzan. He joined the Mongolian People's Party in 1921, was elected vice-chairman of the party central committee from 1922 to 1923, and then chairman from 1923 to 1924. Danzan was party chairman during the Third Party Congress in 1924 that saw the purge and execution of former party chairman Soliin Danzan. After serving again as party deputy chairman from 1924 to 1925, he became a diplomatic envoy with postings in Soviet Russia (1925 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soliin Danzan
Soliin Danzan ( mn, Солийн Данзан; 1885–1924)Batbayar, Ts. (1996). ''Modern Mongolia: A Concise History.'' Offset Printing, Mongolian Center for Scientific and Technological Information was a central figure in Mongolia's early revolutionary movement. He was a founding member of the Mongolian People's Party (later renamed the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party or MPRP) in 1919 and later served as chairman of the Party Central Committee in 1921. Danzan orchestrated the purge and execution of Mongolia's first prime minister, Dogsomyn Bodoo in 1922, but then was himself purged and executed in 1924. Early life and revolution Danzan was born in Tüsheet Khan Province in 1885. As a young man he made his living as a horse thief. Later he went on to work in Niislel Khüree (present day Ulaanbaatar) as a customs official in the Ministry of Finance. In 1919 Danzan, Dansrabilegiin Dogsom, and Damdin Sükhbaatar together established the clandestine nationalist group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogsomyn Bodoo
Dogsomyn Bodoo, (1885–1922) was a prominent early 20th century Mongolian politician who was one of the founding members of the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party. He was elected leader of the provisional revolutionary government and following the Outer Mongolian Revolution of 1921 became the country's first Prime Minister from July 1921 to January 1922. A power struggle led to his resignation on January 7, 1922. He was subsequently charged with treason for conspiring to overthrow the government, and was executed on August 31, 1922. Early life Bodoo was born in 1885 in Mandshir Hutagt in present-day Töv Province. He obtained his elementary education at the Manjusri Monastery and then studied at the Mongolian Language and Literature School in Khüree (present-day Ulan Bator). He later became a scribe at the ''Shaviyn Yaam'' (religious affairs office) and then a Mongolian Language teacher at the Russian-Mongolian School for Translators. He was literate in Mongolian, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist International
The Communist International (Comintern), also known as the Third International, was a Soviet-controlled international organization founded in 1919 that advocated world communism. The Comintern resolved at its Second Congress to "struggle by all available means, including armed force, for the overthrow of the international bourgeoisie and the creation of an international Soviet republic as a transition stage to the complete abolition of the state". The Comintern was preceded by the 1916 dissolution of the Second International. The Comintern held seven World Congresses in Moscow between 1919 and 1935. During that period, it also conducted thirteen Enlarged Plenums of its governing Executive Committee, which had much the same function as the somewhat larger and more grandiose Congresses. Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union, dissolved the Comintern in 1943 to avoid antagonizing his allies in the later years of World War II, the United States and the United Kingdom. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian People's Party
The Mongolian People's Party (MPP) is a social democratic political party in Mongolia. It was founded as a communist party in 1920 by Mongolian revolutionaries and is the oldest political party in Mongolia. The party played an important role in the Mongolian Revolution of 1921, which was inspired by the Bolsheviks' October Revolution. Following independence, it governed Mongolia as a one-party socialist state. The party changed its name to the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party (MPRP) and joined the Communist International in 1924. As the MPRP, the party was organized on the basis of democratic centralism, a principle conceived by Vladimir Lenin which entails democratic and open discussion on policy on the condition of unity in upholding the agreed upon policies. The highest body of the party was the Party Congress, convened every fifth year. When the Party Congress was not in session, the Central Committee was the highest body, but since they met normally only once a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'. At the time of the word's origins in ancient Greece, the Greeks conceived it as rule by the best-qualified citizens—and often contrasted it favorably with monarchy, rule by an individual. The term was first used by such ancient Greeks as Aristotle and Plato, who used it to describe a system where only the best of the citizens, chosen through a careful process of selection, would become rulers, and hereditary rule would actually have been forbidden, unless the rulers' children performed best and were better endowed with the attributes that make a person fit to rule compared with every other citizen in the polity. Hereditary rule in this understanding is more related to oligarchy, a corrupted form of aristocracy where there is rule by a few, but not by the best. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-Mongolism
Pan-Mongolism is an irredentist idea that advocates cultural and political solidarity of Mongols. The proposed territory, called "Greater Mongolia" ( mn, Даяар Монгол, ''Dayaar Mongol''), also known as (Хамаг Монгол) which means "Whole Mongolia" usually includes the independent state of Mongolia, the Chinese regions of Inner Mongolia and Dzungaria (in Xinjiang), and the Russian republic of Buryatia. Sometimes the autonomous republic Tuva, the Altai Republic and parts of Zabaykalsky Krai and Irkutsk Oblast are included as well. , all areas in Greater Mongolia except Mongolia have non-Mongol majorities. The nationalist movement emerged in the 20th century in response to the collapse of the Qing dynasty and the possibility of an independent Mongolian state. After the Red Army helped to establish the Mongolian People's Republic, Mongolian foreign policy prioritised seeking recognition of independence over territorial expansion. After the 1990 Mongolian Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |