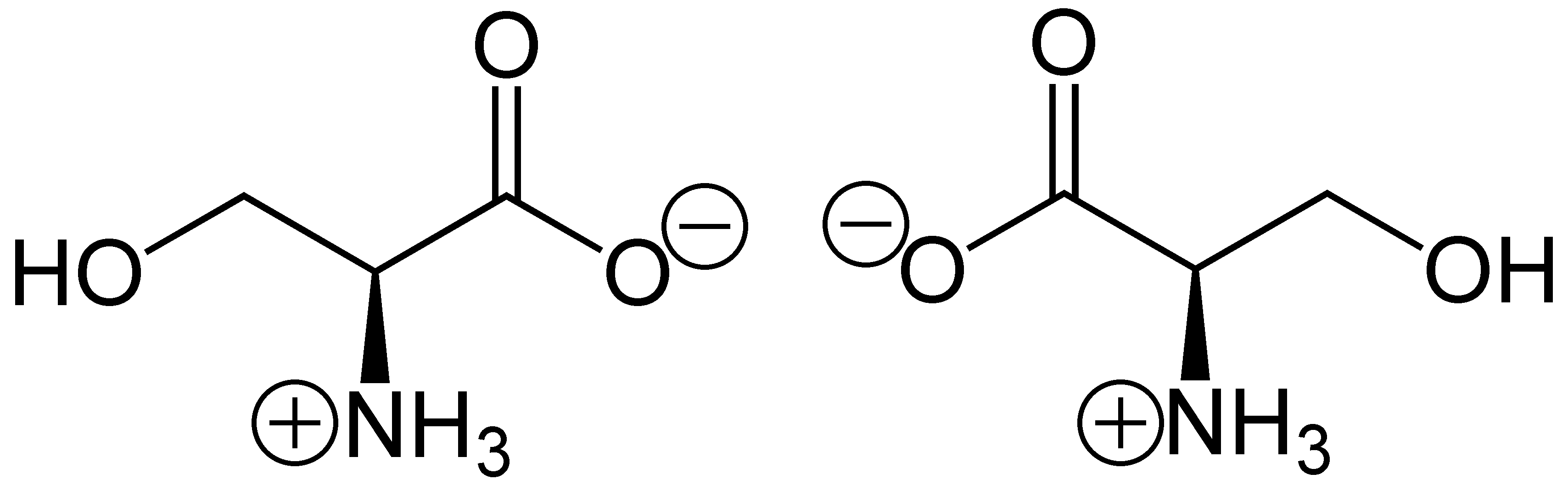|
Sphingoid Base
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. These compounds play important roles in signal transduction and cell recognition. Sphingolipidoses, or disorders of sphingolipid metabolism, have particular impact on neural tissue. A sphingolipid with an R group consisting of a hydrogen atom only is a ceramide. Other common R groups include phosphocholine, yielding a sphingomyelin, and various sugar monomers or dimers, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively. Cerebrosides and globosides are collectively known as glycosphingolipids. Structure The long-chain bases, sometimes simply known as sphingoid bases, are the first non-transient products of '' de novo'' sphingolipid synthesis in both yeast and mammals. These compounds, specifically known as phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphingolipids General Structures
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. These compounds play important roles in signal transduction and cell recognition. Sphingolipidoses, or disorders of sphingolipid metabolism, have particular impact on neural tissue. A sphingolipid with an R group consisting of a hydrogen atom only is a ceramide. Other common R groups include phosphocholine, yielding a sphingomyelin, and various sugar monomers or dimers, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively. Cerebrosides and globosides are collectively known as glycosphingolipids. Structure The long-chain bases, sometimes simply known as sphingoid bases, are the first non-transient products of '' de novo'' sphingolipid synthesis in both yeast and mammals. These compounds, specifically known as phytos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Novo Synthesis
In chemistry, ''de novo'' synthesis () refers to the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules such as sugars or amino acids, as opposed to recycling after partial degradation. For example, nucleotides are not needed in the diet as they can be constructed from small precursor molecules such as formate and aspartate. Methionine, on the other hand, is needed in the diet because while it can be degraded to and then regenerated from homocysteine, it cannot be synthesized ''de novo''. Nucleotide ''De novo'' pathways of nucleotides do not use free bases: adenine (abbreviated as A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), thymine (T), or uracil (U). The purine ring is built up one atom or a few atoms at a time and attached to ribose throughout the process. Pyrimidine ring is synthesized as orotate and attached to ribose phosphate and later converted to common pyrimidine nucleotides. Cholesterol Cholesterol is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. Cholestero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoethanolamine
Phosphorylethanolamine or phosphoethanolamine is an ethanolamine derivative that is used to construct two different categories of phospholipids. One category termed a glycerophospholipid and the other a sphingomyelin, or more specifically within the sphingomyelin class, a sphingophospholipid. Phosphorylethanolamine is a polyprotic acid with two pKa values at 5.61 and 10.39. Phosphorylethanolamine has been falsely promoted as a cancer treatment. Effectiveness As a potential drug, phosphorylethanolamine has undergone human clinical trials. These were halted when no evidence of benefit was found. Edzard Ernst has called Phosphorylethanolamine "the most peculiar case of Brazilian quackery". Legality There has been ongoing controversy and litigation in Brazil with regard to its use as a cancer treatment without approval by the National Health Surveillance Agency. For years, Gilberto Chierice, a Chemistry Professor at the São Carlos campus of the University of São Paulo, used reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphingomyelin
Sphingomyelin (SPH, ˌsfɪŋɡoˈmaɪəlɪn) is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphocholine and ceramide, or a ethanolamine, phosphoethanolamine head group; therefore, sphingomyelins can also be classified as sphingophospholipids. In humans, SPH represents ~85% of all sphingolipids, and typically make up 10–20 mol % of plasma membrane lipids. Sphingomyelin was first isolated by Germans, German chemist Johann Ludwig Wilhelm Thudichum, Johann L.W. Thudicum in the 1880s. The structure of sphingomyelin was first reported in 1927 as N-acyl-sphingosine-1-phosphorylcholine. Sphingomyelin content in mammals ranges from 2 to 15% in most tissues, with higher concentrations found in nerve tissues, red blood cells, and the ocular lenses. Sphingomyelin has significant structural and functional roles in the cell. It is a plasma membrane component and parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells. The word ''ceramide'' comes from the Latin ''cera'' (wax) and ''amide''. Ceramide is a component of vernix caseosa, the waxy or cheese-like white substance found coating the skin of newborn human infants. Pathways for ceramide synthesis There are three major pathways of ceramide generation. First, the sphingomyelinase pathway uses an enzyme to break down sphingomyelin in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells. The word ''ceramide'' comes from the Latin ''cera'' (wax) and ''amide''. Ceramide is a component of vernix caseosa, the waxy or cheese-like white substance found coating the skin of newborn human infants. Pathways for ceramide synthesis There are three major pathways of ceramide generation. First, the sphingomyelinase pathway uses an enzyme to break down sphingomyelin in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramides
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells. The word ''ceramide'' comes from the Latin ''cera'' (wax) and ''amide''. Ceramide is a component of vernix caseosa, the waxy or cheese-like white substance found coating the skin of newborn human infants. Pathways for ceramide synthesis There are three major pathways of ceramide generation. First, the sphingomyelinase pathway uses an enzyme to break down sphingomyelin in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyl Group
In chemistry, an acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group (). In organic chemistry, the acyl group (IUPAC name: alkanoyl) is usually derived from a carboxylic acid, in which case it has the formula , where R represents an alkyl group that is linked to the carbon atom of the group by a single bond. Although the term is almost always applied to organic compounds, acyl groups can in principle be derived from other types of acids such as sulfonic acids and phosphonic acids. In the most common arrangement, acyl groups are attached to a larger molecular fragment, in which case the carbon and oxygen atoms are linked by a double bond. Compounds Well-known acyl compounds are the acyl chlorides, such as acetyl chloride (CH3COCl) and benzoyl chloride (C6H5COCl). These compounds, which are treated as sources of acylium cations, are good reagents for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts (X− in the depicted formula is an undefined counteranion). Humans are capable of some ''de novo synthesis'' of choline but require additional choline in the diet to maintain health. Dietary requirements can be met by choline per se or in the form of choline phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine. Choline is not formally classified as a vitamin despite being an essential nutrient with an amino acid–like structure and metabolism. In most animals, choline phospholipids are necessary components in cell membranes, in the membranes of cell organelles, and in very low-density lipoproteins. Choline is required to produce acetylcholine – a neurotransmitter – and ''S''-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a universal methyl donor. Upon methylation SAM is transformed into homocysteine. Symptomatic choline deficiency causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and muscle dama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |