|
Sphingobacteria
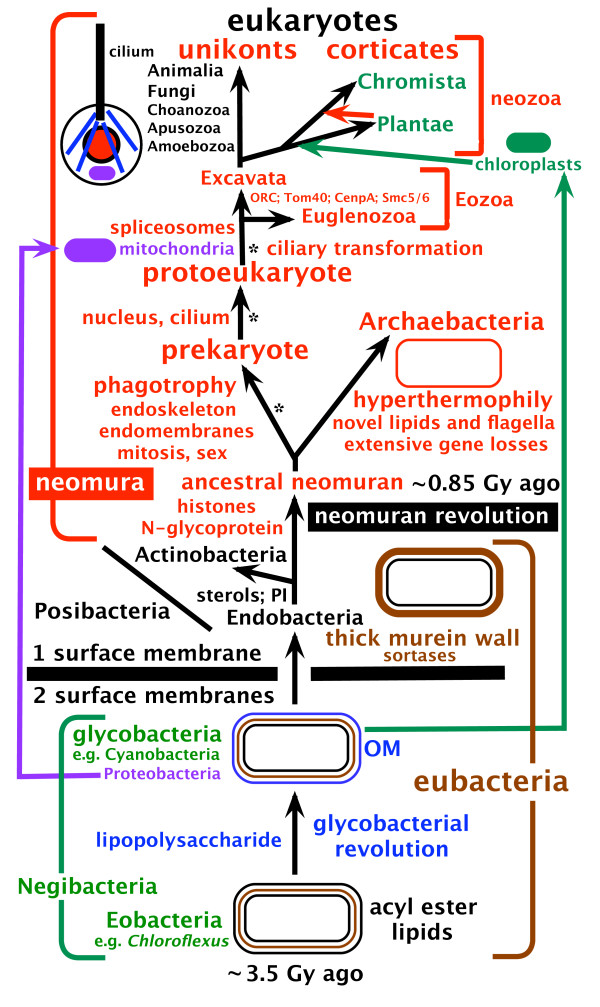
The FCB group is a superphylum of bacteria named after the main member phyla Fibrobacterota, Chlorobiota, and Bacteroidota. The members are considered to form a clade due to a number of conserved signature indels. Cavalier-Smith calls the equivalent grouping a phylum by the name of Sphingobacteria. It contains the classes Chlorobiota, Fibrobacterota, Bacteroidota, and Flavobacteria. However, this megaclassification is not followed by the larger scientific community. An analogous situation is seen with the PVC group/Planctobacteria. Notes See also * List of bacterial orders * List of bacteria genera This article lists the genera of the bacteria. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However many taxonomic names are ... References Superphyla {{Bacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroidota
The phylum Bacteroidota (synonym Bacteroidetes) is composed of three large classes of Gram-negative, nonsporeforming, anaerobic or aerobic, and rod-shaped bacteria that are widely distributed in the environment, including in soil, sediments, and sea water, as well as in the guts and on the skin of animals. Although some ''Bacteroides'' spp. can be opportunistic pathogens, many ''Bacteroidota'' are symbiotic species highly adjusted to the gastrointestinal tract. ''Bacteroides'' are highly abundant in intestines, reaching up to 1011 cells g−1 of intestinal material. They perform metabolic conversions that are essential for the host, such as degradation of proteins or complex sugar polymers. ''Bacteroidota'' colonize the gastrointestinal tract already in infants, as non-digestible oligosaccharides in mother milk support the growth of both ''Bacteroides'' and ''Bifidobacterium'' spp. ''Bacteroides'' spp. are selectively recognized by the immune system of the host through specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroidota–Chlorobiota Group
The FCB group is a superphylum of bacteria named after the main member phyla Fibrobacterota, Chlorobiota, and Bacteroidota. The members are considered to form a clade due to a number of conserved signature indels. Cavalier-Smith calls the equivalent grouping a phylum by the name of Sphingobacteria. It contains the classes Chlorobiota, Fibrobacterota, Bacteroidota, and Flavobacteria. However, this megaclassification is not followed by the larger scientific community. An analogous situation is seen with the PVC group/Planctobacteria. Notes See also * List of bacterial orders * List of bacteria genera This article lists the genera of the bacteria. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However many taxonomic names are ... References Superphyla {{Bacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Taxonomy Database
The Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB) is an online database that maintains information on a proposed nomenclature of prokaryotes, following a phylogenomic approach based on a set of conserved single-copy proteins. In addition to breaking up paraphyletic groups, this method also reassigns taxonomic ranks algorithmically, creating new names in both cases. Information for archaea was added in 2020, along with a species classification based on average nucleotide identity. Each update incorporates new genomes as well as human adjustments to the taxonomy. An open-source tool called GTDB-Tk is available to classify draft genomes into the GTDB hierarchy. The GTDB system, via GTDB-Tk, has been used to catalogue not-yet-named bacteria in the human gut microbiome and other metagenomic sources. The GTDB is incorporated into the ''Bergey's Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria'' in 2019 as its phylogenomic resource. See also * PhyloCode * National Center for Biotechnology Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The All-Species Living Tree Project
The All-Species Living Tree' Project is a collaboration between various academic groups/institutes, such as ARB Project, ARB, SILVA rRNA database project, and List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature, LPSN, with the aim of assembling a database of 16S ribosomal RNA, 16S rRNA sequences of all validly published species of ''Bacteria'' and ''Archaea''. At one stage, 23S ribosomal RNA, 23S sequences were also collected, but this has since stopped. Currently there are over 10,950 species in the aligned dataset and several more are being added either as new species are discovered or species that are not represented in the database are sequenced. Initially the latter group consisted of 7% of species. Similar (and more recent) projects include the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea (GEBA), which focused on whole genome sequencing of bacteria and archaea. Tree The tree was created by maximum likelihood analysis without bootstrap: consequently accuracy is traded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavobacteria (class)
The class Flavobacteriia is composed of a single order of environmental bacteria. According to Bernardet ''et al''., Flavobacteriia are Gram-negative aerobic rods, 2–5 μm long, 0.3–0.5 μm wide, with rounded or tapered ends that are motile by gliding, yellow (cream to orange) colonies on agar, decompose several polysaccharides but not cellulose, G+C contents of 32–37%, and are widely distributed in soil and fresh and seawater habitats. In particular, Flavobacteriia are prominent members of marine biofilms. The type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ... ''Flavobacterium aquatile'' was isolated from a well in Kent, England. Flavobacteriia are a group of commensal bacteria and opportunistic pathogens. '' Flavobacterium psychrophilum'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about 8 phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships between phyla, which are contained in larger clades, like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguished them as a group ("a self-contained unity" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conserved Signature Indels
Conserved signature inserts and deletions (CSIs) in protein sequences provide an important category of molecular markers for understanding phylogenetic relationships. CSIs, brought about by rare genetic changes, provide useful phylogenetic markers that are generally of defined size and they are flanked on both sides by conserved regions to ensure their reliability. While indels can be arbitrary inserts or deletions, CSIs are defined as only those protein indels that are present within conserved regions of the protein. The CSIs that are restricted to a particular clade or group of species, generally provide good phylogenetic markers of common evolutionary descent. Due to the rarity and highly specific nature of such changes, it is less likely that they could arise independently by either convergent or parallel evolution (i.e. homoplasy) and therefore are likely to represent synapomorphy. Other confounding factors such as differences in evolutionary rates at different sites or among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |