|
Spatial ETL
Spatial extract, transform, load (spatial ETL), also known as geospatial transformation and load (GTL), provides the data processing functionality of traditional extract, transform, load (ETL) software, but with a primary focus on the ability to manage spatial data (which may also be called GIS, geographic, or map data). A spatial ETL system may translate data directly from one format to another, or via an intermediate format; the latter being more common when transformation of the data is to be carried out. Transform The transformation phase of a spatial ETL process allows a variety of functions; some of these are similar to standard ETL, but some are unique to spatial data. Spatial data commonly consists of a geographic element and related attribute data; therefore spatial ETL transformations are often described as being either ''geometric transformations'' – transformation of the geographic element – or ''attribute transformations'' – transformations of the related att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
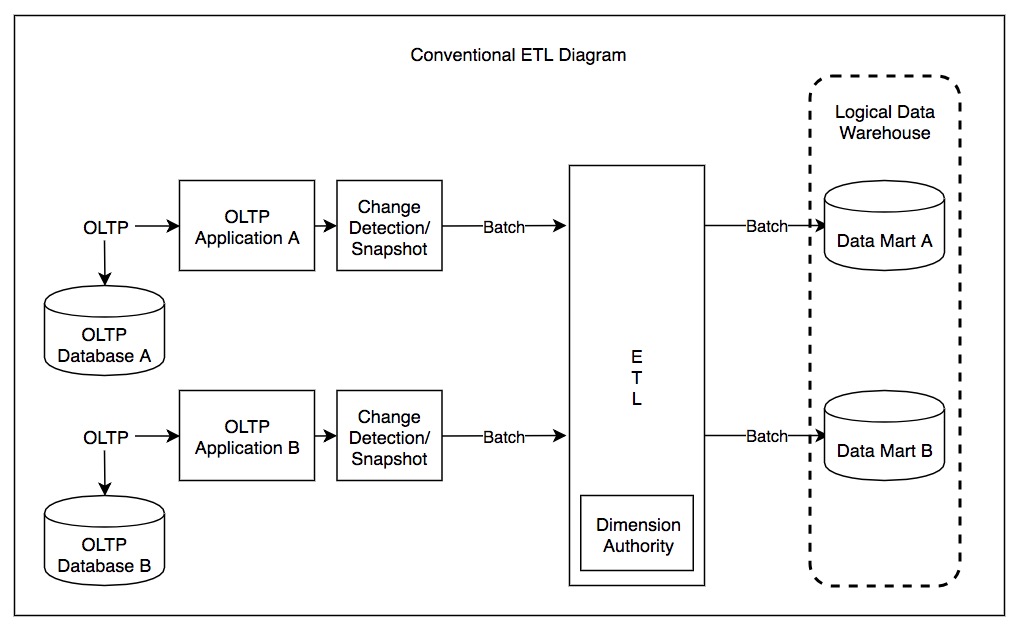
Extract, Transform, Load
In computing, extract, transform, load (ETL) is a three-phase process where data is extracted, transformed (cleaned, sanitized, scrubbed) and loaded into an output data container. The data can be collated from one or more sources and it can also be outputted to one or more destinations. ETL processing is typically executed using software applications but it can also be done manually by system operators. ETL software typically automates the entire process and can be run manually or on reoccurring schedules either as single jobs or aggregated into a batch of jobs. A properly designed ETL system extracts data from source systems and enforces data type and data validity standards and ensures it conforms structurally to the requirements of the output. Some ETL systems can also deliver data in a presentation-ready format so that application developers can build applications and end users can make decisions. The ETL process became a popular concept in the 1970s and is often used in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Conversion
Data conversion is the conversion of computer data from one format to another. Throughout a computer environment, data is encoded in a variety of ways. For example, computer hardware is built on the basis of certain standards, which requires that data contains, for example, parity bit checks. Similarly, the operating system is predicated on certain standards for data and file handling. Furthermore, each computer program handles data in a different manner. Whenever any one of these variables is changed, data must be converted in some way before it can be used by a different computer, operating system or program. Even different versions of these elements usually involve different data structures. For example, the changing of bits from one format to another, usually for the purpose of application interoperability or of the capability of using new features, is merely a data conversion. Data conversions may be as simple as the conversion of a text file from one character encoding syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Database
A spatial database is a general-purpose database (usually a relational database) that has been enhanced to include spatial data that represents objects defined in a geometric space, along with tools for querying and analyzing such data. Most spatial databases allow the representation of simple geometric objects such as points, lines and polygons. Some spatial databases handle more complex structures such as 3D objects, topological coverages, linear networks, and triangulated irregular networks (TINs). While typical databases have developed to manage various numeric and character types of data, such databases require additional functionality to process spatial data types efficiently, and developers have often added ''geometry'' or ''feature'' data types. The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) developed the Simple Features specification (first released in 1997) and sets standards for adding spatial functionality to database systems. The '' SQL/MM Spatial'' ISO/IEC standard is a pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object–relational Database
An object–relational database (ORD), or object–relational database management system (ORDBMS), is a database management system (DBMS) similar to a relational database, but with an object-oriented database model: objects, classes and inheritance are directly supported in database schemas and in the query language. In addition, just as with pure relational systems, it supports extension of the data model with custom data types and methods. An object–relational database can be said to provide a middle ground between relational databases and object-oriented databases. In object–relational databases, the approach is essentially that of relational databases: the data resides in the database and is manipulated collectively with queries in a query language; at the other extreme are OODBMSes in which the database is essentially a persistent object store for software written in an object-oriented programming language, with a programming API for storing and retrieving objects, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) comprises the strategies and technologies used by enterprises for the data analysis and management of business information. Common functions of business intelligence technologies include reporting, online analytical processing, analytics, dashboard development, data mining, process mining, complex event processing, business performance management, benchmarking, text mining, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. BI tools can handle large amounts of structured and sometimes unstructured data to help identify, develop, and otherwise create new strategic business opportunities. They aim to allow for the easy interpretation of these big data. Identifying new opportunities and implementing an effective strategy based on insights can provide businesses with a competitive market advantage and long-term stability, and help them take strategic decisions. Business intelligence can be used by enterprises to support a wide range of business decisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArcGIS
ArcGIS is a family of client, server and online geographic information system (GIS) software developed and maintained by Esri. ArcGIS was first released in 1999 and originally was released as ARC/INFO, a command line based GIS system for manipulating data. ARC/INFO was later merged into ArcGIS Desktop, which was eventually superseded by ArcGIS Pro in 2015. ArcGIS Pro works in 2D and 3D for cartography and visualization, and includes artificial Intelligence (AI). Esri also provides server side ArcGIS software for web maps, known as ArcGIS Server. Product history Prior to the ArcGIS suite, Esri had focused its software development on the command line Arc/INFO workstation program and several Graphical User Interface-based products such as the ArcView GIS 3.x desktop program. Other Esri products included MapObjects, a programming library for developers, and ArcSDE as a relational database management system. The various products had branched out into multiple source trees and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader definition takes into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system-to-system performance. Types of interoperability include syntactic interoperability, where two systems can communicate with each other, and cross-domain interoperability, where multiple organizations work together and exchange information. Types If two or more systems use common data formats and communication protocols and are capable of communicating with each other, they exhibit ''syntactic interoperability''. XML and SQL are examples of common data formats and protocols. Lower-level data formats also contribute to syntactic interoperability, ensuring that alphabetical characters are stored in the same ASCII or a Unicode format in all the commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Management Information System
A management information system (MIS) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization. The study of the management information systems involves people, processes and technology in an organizational context. In a corporate setting, the ultimate goal of using management information system is to increase the value and profits of the business. History While it can be contested that the history of management information system dates as far back as companies using ledgers to keep track of accounting, the modern history of MIS can be divided into five ''eras'' originally identified by Kenneth C. Laudon and Jane Laudon in their seminal textbook ''Management Information Systems.'' * First Era – Mainframe and minicomputer computing * Second Era – Personal computers * Third Era – Client/server networks * Fourth Era – Enterprise computing * Fifth Era – Cloud computing The ''fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing Geographic data and information, geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with Geographic information system software, software tools for managing, Spatial analysis, analyzing, and Cartographic design, visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. It is roughly synonymous with geoinformatics and part of the broader geospatial field, which also includes GPS, remote sensing, etc. Geographic information science, the academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Verification
Data verification is a process in which different types of data are checked for accuracy and inconsistencies after data migration is done. In some domains it is referred to Source Data Verification (SDV), such as in clinical trials. Data verification helps to determine whether data was accurately translated when data is transferred from one source to another, is complete, and supports processes in the new system. During verification, there may be a need for a parallel run of both systems to identify areas of disparity and forestall erroneous data loss. Methods for data verification include double data entry, proofreading and automated verification of data. Proofreading data involves someone checking the data entered against the original document. This is also time consuming and costly. Automated verification of data can be achieved using one way hashes locally or through use of a SaaS based service such as Q by SoLVBL to provide immutable seals to allow verification of the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Data
Geographic data and information is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to Earth (a geographic location or geographic position). It is also called geospatial data and information, georeferenced data and information, as well as geodata and geoinformation. Approximately 90% of government sourced data has a location component. Location information (known by the many names mentioned here) is stored in a geographic information system (GIS). There are also many different types of geodata, including vector files, raster files, geographic databases, web files, and multi-temporal data. Fields of study Geographic data and information are the subject of a number of overlapping fields of study, mainly: * Geocomputation * Geographic information science * Geoinformatics * Geomatics * Geovisualization This is in addition to other more specific branches, such as: * Cartography * Geodesy * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflation
Conflation is the merging of two or more sets of information, texts, ideas, opinions, etc., into one, often in error. Conflation is often misunderstood. It originally meant to fuse or blend, but has since come to mean the same as equate, treating two similar but disparate concepts as the same. Merriam Webster suggest this happened relatively recently, entering their dictionary in 1973. In logic, it is the practice of treating two distinct concepts as if they were one, which produces errors or misunderstandings as a fusion of distinct subjects tends to obscure analysis of relationships which are emphasized by contrasts. However, if the distinctions between the two concepts may appear to be superficial, intentional conflation can be desirable for the sake of conciseness and recall. Communication and reasoning The result of conflating concepts may give rise to fallacies and ambiguity, including the fallacy of four terms in a categorical syllogism. For example, the word "bat" h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
