|
Solar Minimum
Solar minimum is the regular period of least solar activity in the Sun's 11-year solar cycle. During solar minimum, sunspot and solar flare activity diminishes, and often does not occur for days at a time. On average, the solar cycle takes about 11 years to go from one solar minimum to the next, with duration observed varying from 9 to 14 years. The date of the minimum is described by a smoothed average over 12 months of sunspot activity, so identifying the date of the solar minimum usually can only happen 6 months after the minimum takes place. Solar minimum is contrasted with the solar maximum, when hundreds of sunspots may occur. Solar minimum and solar maximum Solar minima and maxima are the two extremes of the Sun's 11-year and 400-year activity cycle. At a maximum, the Sun is peppered with sunspots, solar flares erupt, and the Sun hurls billion-ton clouds of electrified gas into space. Sky watchers may see more auroras, and space agencies must monitor radiation storms for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period (MWP), also known as the Medieval Climate Optimum or the Medieval Climatic Anomaly, was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region that lasted from to . Climate proxy records show peak warmth occurred at different times for different regions, which indicate that the MWP was not a globally uniform event. Some refer to the MWP as the ''Medieval Climatic Anomaly'' to emphasize that climatic effects other than temperature were also important. The MWP was followed by a regionally cooler period in the North Atlantic and elsewhere, which is sometimes called the Little Ice Age (LIA). Possible causes of the MWP include increased solar activity, decreased volcanic activity, and changes in ocean circulation. Research The Medieval Warm Period (MWP) is generally thought to have occurred from –, during the European Middle Ages. In 1965, Hubert Lamb, one of the first paleoclimatologists, published research based on data from botany, historical document res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
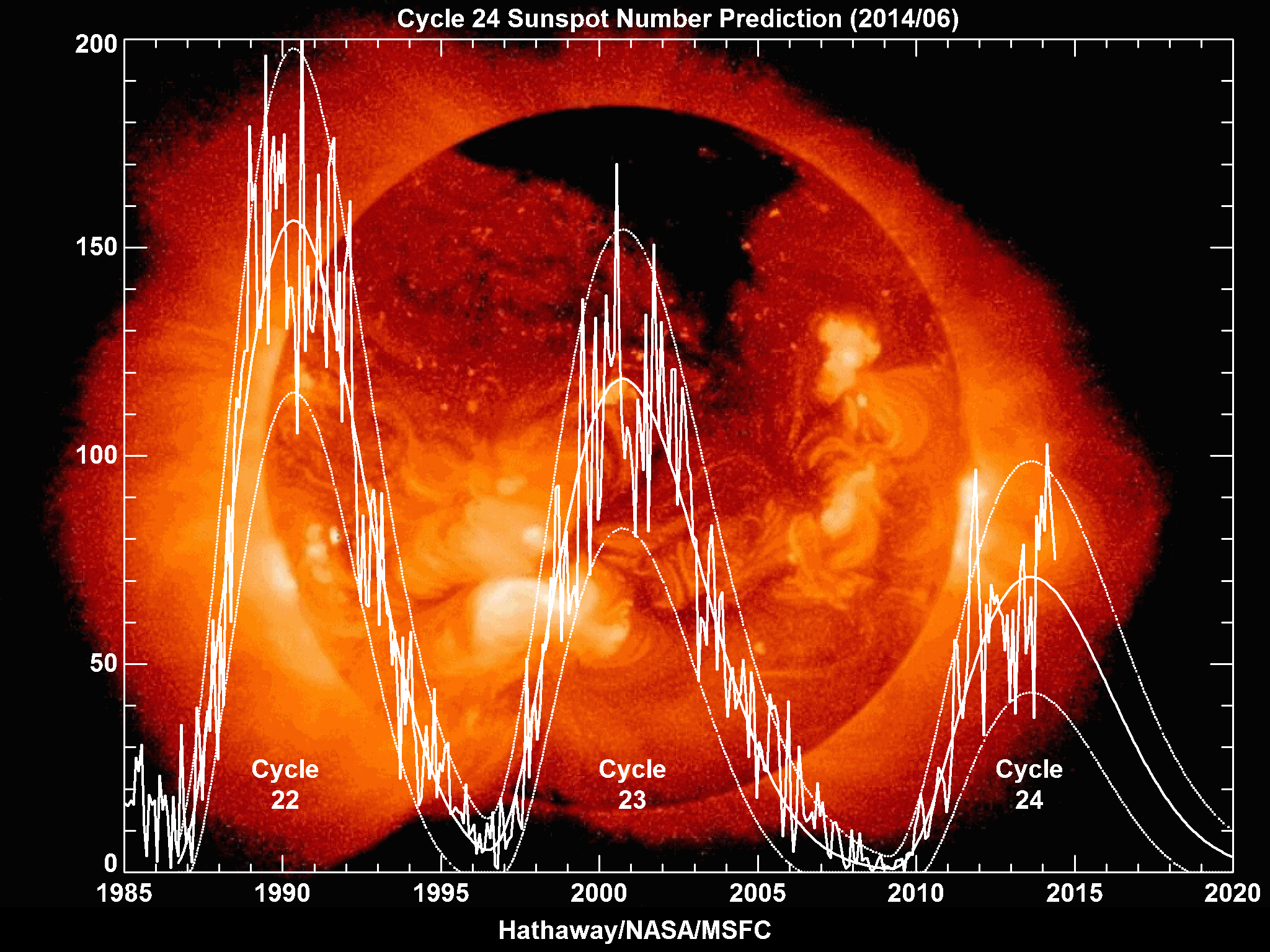
Solar Cycle 24
Solar cycle 24 is the most recently completed solar cycle, the 24th since 1755, when extensive recording of solar sunspot activity began.Kane, R.P. (2002).Some Implications Using the Group Sunspot Number Reconstruction. ''Solar Physics'' 205(2), 383-401. It began in December 2008 with a minimum smoothed sunspot number of 2.2, and ended in December 2019. Activity was minimal until early 2010. It reached its maximum in April 2014 with a 23 months smoothed sunspot number of 81.8. This maximum value was substantially lower than other recent solar cycles, down to a level which had not been seen since cycles 12 to 15 (1878-1923). Predictions Prior to the minimum between the end of Solar Cycle 23 and the beginning of Solar Cycle 24, two theories predicted how strong Solar Cycle 24 would be. One camp postulated that the Sun retained a long memory (Solar Cycle 24 would be active) while the other asserted that it had a short memory (quiet). Prior to 2006, the difference was substantial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Over the period of a solar cycle, levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material, the number and size of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal loops all exhibit a synchronized fluctuation from a period of minimum activity to a period of a maximum activity back to a period of minimum activity. The magnetic field of the Sun flips during each solar cycle, with the flip occurring when the solar cycle is near its maximum. After two solar cycles, the Sun's magnetic field returns to its original state, completing what is known as a Hale cycle. This cycle has been observed for centuries by changes in the Sun's appearance and by terrestrial phenomena such as aurora but was not clearly identified until 1843. Solar activity, driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Solar Cycles
Solar cycles are nearly periodic 11-year changes in the Sun's activity that are based on the number of sunspots present on the Sun's surface. The first solar cycle conventionally is said to start in 1755 when Rudolf Wolf began extensive reporting of sunspot activity. The source data are the revised International Sunspot Numbers (ISN v2.0), as available at SILSO. Sunspot counts exist since 1610 but the cycle numbering is not well defined during the Maunder minimum. It was proposed that one cycle might have been lost in the late 18th century, but this remains not fully confirmed. Solar cycles can be reconstructed indirectly, using the radiocarbon Carbon-14, C-14, or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and c ... 14C proxy, for the last millennium. The smoothing is done using the traditional SIDC s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Region
An active region is a temporary region in the Sun's atmosphere characterized by a strong and complex magnetic field. They are often associated with sunspots and are commonly the source of violent eruptions such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares. The number and location of active regions on the solar disk at any given time is dependent on the solar cycle. Region numbers Newly observed active regions on the solar disk are assigned 4-digit region numbers by the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) on the day following the initial observation. The region number assigned to a particular active region is one added to the previously assigned number. For example, the first observation of active region 8090, or AR8090, was followed by AR8091. According to the SWPC, a number is assigned to a region if it meets at least one of the following criteria: # It contains a sunspot group of class C or larger based on the Modified Zurich Class sunspot classification system. # It contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Maximum
The Modern Maximum, refers to the period of relatively high solar activity which began with solar cycle 15 in 1914. It reached a maximum in solar cycle 19 during the late 1950s and may have ended with the peak of solar cycle 23 in 2000, as solar cycle 24 is recording, at best, very muted solar activity. Another proposed end date for the maximum is 2007, with the decline phase of Cycle 23. In any case the low solar activity of solar cycle 24 in the 2010s marked a new period of reduced solar activity. This maximum period is a natural example of solar variation The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surfa ..., and one of many that are known from proxy records of past solar variability. The Modern Maximum reached a double peak once in the 1950s and again during the 1990s. Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton Minimum
The Dalton Minimum was a period of low sunspot count, representing low solar activity, named after the English meteorologist John Dalton, lasting from about 1790 to 1830 or 1796 to 1820, corresponding to the period solar cycle 4 to solar cycle 7. While the Dalton Minimum is often compared with the Maunder Minimum, its sunspot number was slightly higher and reported sunspots distributed in both solar hemispheres unlike the Maunder Minimum. The coronal streamers are visually confirmed in Ezra Ames and José Joaquin de Ferrer’s eclipse drawings in 1806 and indicates similarity of its magnetic field not with that of the Maunder Minimum but with that of the modern solar cycles. Temperature Like the Maunder Minimum and Spörer Minimum, the Dalton Minimum coincided with a period of lower-than-average global temperatures. During that period, there was a variation of temperature of about 1 °C in Germany. The cause of the lower-than-average temperatures and their possible r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spörer Minimum
The Spörer Minimum is a hypothesized 90-year span of low solar activity, from about 1460 until 1550, which was identified and named by John A. Eddy in a landmark 1976 paper published in ''Science'' titled '' "The Maunder Minimum"''.Eddy, J. A., "The Maunder Minimum", ''Science'' 18 June 1976: Vol. 192. no. 4245, pp. 1189–1202 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Minimum
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Over the period of a solar cycle, levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material, the number and size of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal loops all exhibit a synchronized fluctuation from a period of minimum activity to a period of a maximum activity back to a period of minimum activity. The magnetic field of the Sun flips during each solar cycle, with the flip occurring when the solar cycle is near its maximum. After two solar cycles, the Sun's magnetic field returns to its original state, completing what is known as a Hale cycle. This cycle has been observed for centuries by changes in the Sun's appearance and by terrestrial phenomena such as aurora but was not clearly identified until 1843. Solar activity, driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Warm Period
The Roman Warm Period, or Roman Climatic Optimum, was a period of unusually-warm weather in Europe and the North Atlantic that ran from approximately 250 BC to AD 400. Theophrastus (371 – c. 287 BC) wrote that date trees could grow in Greece if they were planted but that they could not set fruit there. That is still the case today, which implies that South Aegean mean summer temperatures in the 4th and the 5th centuries BC were within a degree of modern ones. That and other literary fragments from the time confirm that the Greek climate was basically the same then as around 2000. Tree rings from the Italian Peninsula in the late 3rd century BC indicate a time of mild conditions there around the time of Hannibal's crossing of the Alps with imported elephants in 218 BC. Dendrochronological evidence from wood found at the Parthenon shows variability of climate in the 5th century BC, which resembles the modern pattern of variation. Cooling at the end of the period is noted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |