|
Socket 4
Socket 4, presented in 1993, was the first CPU socket designed for the early P5 Pentium microprocessors. Socket 4 was the only 5-volt socket for the Pentium. Socket 4 does support a special Pentium OverDrive, which allows running at 120 MHz (for the 60 MHz Pentium) or 133 MHz (for the 66 MHz Pentium). Socket 4 was superseded by the 3.3-volt-powered Socket 5 in 1994. See also * List of Intel microprocessors This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the pioneering 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 13th generation Cor ... References {{earlysock Socket 004 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 4
Socket 4, presented in 1993, was the first CPU socket designed for the early P5 Pentium microprocessors. Socket 4 was the only 5-volt socket for the Pentium. Socket 4 does support a special Pentium OverDrive, which allows running at 120 MHz (for the 60 MHz Pentium) or 133 MHz (for the 66 MHz Pentium). Socket 4 was superseded by the 3.3-volt-powered Socket 5 in 1994. See also * List of Intel microprocessors This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the pioneering 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 13th generation Cor ... References {{earlysock Socket 004 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
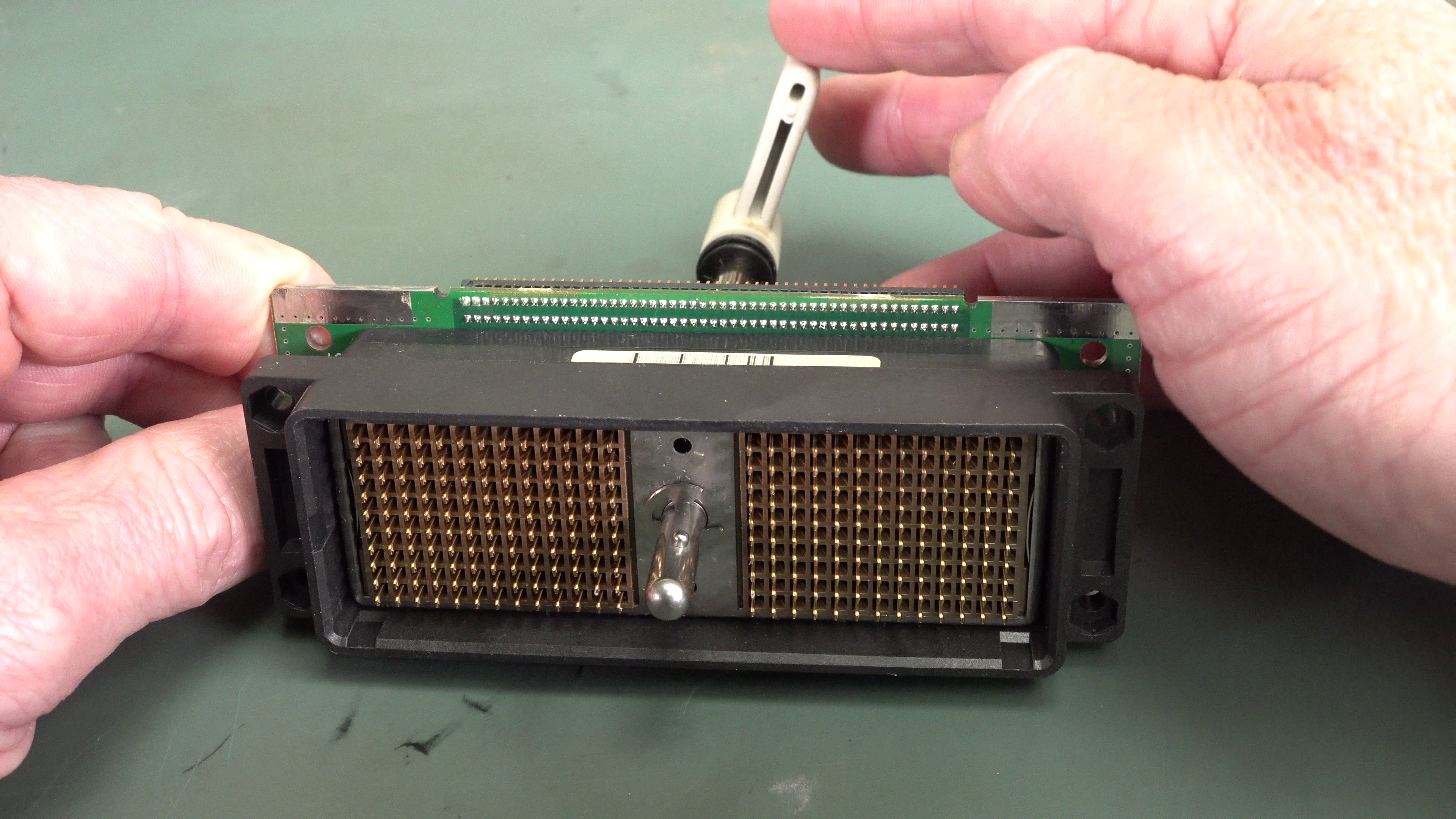
Zero Insertion Force
Zero insertion force (ZIF) is a type of IC socket or electrical connector that requires very little (but not literally zero) force for insertion. With a ZIF socket, before the IC is inserted, a lever or slider on the side of the socket is moved, pushing all the sprung contacts apart so that the IC can be inserted with very little force - generally the weight of the IC itself is sufficient and no external downward force is required. The lever is then moved back, allowing the contacts to close and grip the pins of the IC. ZIF sockets are much more expensive than standard IC sockets and also tend to take up a larger board area due to the space taken up by the lever mechanism. Typically, they are only used when there is a good reason to do so. Design A normal integrated circuit (IC) socket requires the IC to be pushed into sprung contacts which then grip by friction. For an IC with hundreds of pins, the total insertion force can be very large (hundreds of newtons), leading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P5 (microarchitecture)
The Pentium (also referred to as P5, its microarchitecture, or i586) is a fifth generation, 32-bit x86 microprocessor that was introduced by Intel on March 22, 1993, as the very first CPU in the Pentium brand. It was instruction set compatible with the 80486 but was a new and very different microarchitecture design from previous iterations. The P5 Pentium was the first superscalar x86 microarchitecture and the world's first superscalar microprocessor to be in mass productionmeaning it generally executes at least 2 instructions per clock mainly because of a design-first dual integer pipeline design previously thought impossible to implement on a CISC microarchitecture. Additional features include a faster floating-point unit, wider data bus, separate code and data caches, and many other techniques and features to enhance performance and support security, encryption, and multiprocessing, for workstations and servers when compared to the next best previous industry standard proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium (brand)
Pentium is a brand used for a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel. The original Pentium processor from which the brand took its name was first released on March 22, 1993. After that, the Pentium II and Pentium III were released. In their form , Pentium processors are considered entry-level products that Intel rates as "two stars", meaning that they are above the low-end Atom and Celeron series, but below the faster Intel Core lineup, and workstation/server Xeon series. , Pentium processors have little more than their name in common with earlier Pentiums, which were Intel's flagship processor for over a decade until the introduction of the Intel Core line in 2006. They are based on both the architecture used in Atom and that of Core processors. In the case of Atom architectures, Pentiums are the highest performance implementations of the architecture. Pentium processors with Core architectures prior to 2017 were distinguished from the fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
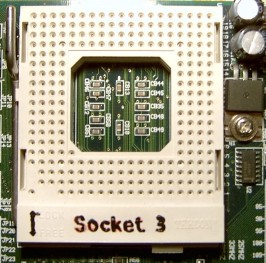
Socket 3
Socket 3 was a series of CPU sockets for various x86 microprocessors. It was sometimes found alongside a secondary socket designed for a math coprocessor chip, such as the 487. Socket 3 resulted from Intel's creation of lower voltage microprocessors. An upgrade to Socket 2, it rearranged the pin layout. Socket 3 is compatible with 168-pin socket CPUs. Socket 3 was a 237-pin low insertion force (LIF) or zero insertion force (ZIF) 19×19 pin grid array (PGA) socket suitable for the 3.3 V and 5 V, 25–50 MHz Intel 486 SX, 486 DX, 486 DX2, 486 DX4, 486 OverDrive and Pentium OverDrive processors as well as AMD Am486, Am5x86 and Cyrix Cx5x86 processors. See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of AMD microprocessors This article gives a list of AMD microprocessors, sorted by generation and release year. If applicable and openly known, the designation(s) of each processor's core (versions) is (are) listed in parentheses. For an overview over concrete prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 5
Socket 5 was created for the second generation of Intel P5 Pentium processors operating at speeds from 75 to 133 MHz as well as certain Pentium OverDrive and Pentium MMX processors with core voltage 3.3 V. It superseded the earlier Socket 4. It was released in March 1994. Consisting of 320 pins, this was the first socket to use a staggered pin grid array, or SPGA, which allowed the chip's pins to be spaced closer together than earlier sockets. Socket 5 was replaced by Socket 7 in 1995. External linksDifferences between Socket 5 and Socket 7(archived) See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of AMD microprocessors This article gives a list of AMD microprocessors, sorted by generation and release year. If applicable and openly known, the designation(s) of each processor's core (versions) is (are) listed in parentheses. For an overview over concrete product, y ... References {{earlysock Socket 005 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include Pin Grid Array (PGA) or Land Grid Array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) greatly reduced the cost of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium OverDrive
The Pentium OverDrive was a microprocessor marketing brand name used by Intel, to cover a variety of consumer upgrade products sold in the mid-1990s. It was originally released for 486 motherboards, and later some Pentium sockets. Intel dropped the brand, as it failed to appeal to corporate buyers, and discouraged new system sales. 486 sockets The Pentium OverDrive is a heavily modified, 3.3 volt Pentium P54 core manufactured on 0.6 micrometer technology. It is fitted with a 486-compatible bus unit (though with an increased pin-count), an integrated heatsink and fan, and 32 kB of level 1 cache, double the 16 kB offered on regular P54C chips. As the data bus was effectively reduced to 32-bit width, per-clock performance was much lower than that of a 'regular' Pentium, though still substantially faster compared to a similarly clocked 486 owing to the Pentium's architectural improvements, such as the much improved FPU. It was also equipped with an integrated 3.3 volt power regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |