|
Sign Test
The sign test is a statistical method to test for consistent differences between pairs of observations, such as the weight of subjects before and after treatment. Given pairs of observations (such as weight pre- and post-treatment) for each subject, the sign test determines if one member of the pair (such as pre-treatment) tends to be greater than (or less than) the other member of the pair (such as post-treatment). The paired observations may be designated ''x'' and ''y''. For comparisons of paired observations (''x'',y), the sign test is most useful if comparisons can only be expressed as ''x'' > ''y'', ''x'' = ''y'', or ''x'' 0. Assuming that H0 is true, then ''W'' follows a binomial distribution ''W'' ~ b(''m'', 0.5). Assumptions Let ''Z''i = ''Y''i – ''X''i for ''i'' = 1, ... , ''n''. # The differences ''Zi'' are assumed to be independent. # Each ''Zi'' comes from the same continuous population. # The values ''X''''i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-test
A ''t''-test is any statistical hypothesis testing, statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t-distribution, Student's ''t''-distribution under the null hypothesis. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a Scale parameter, scaling term in the test statistic were known (typically, the scaling term is unknown and therefore a nuisance parameter). When the scaling term is estimated based on the data, the test statistic—under certain conditions—follows a Student's ''t'' distribution. The ''t''-test's most common application is to test whether the means of two populations are different. History The term "''t''-statistic" is abbreviated from "hypothesis test statistic". In statistics, the t-distribution was first derived as a Posterior probability, posterior distribution in 1876 by Friedrich Robert Helmert, Helmert and Jacob Lüroth, Lüroth. The t-distribution also appeared in a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-value
In null-hypothesis significance testing, the ''p''-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small ''p''-value means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis. Reporting ''p''-values of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields. Since the precise meaning of ''p''-value is hard to grasp, misuse is widespread and has been a major topic in metascience. Basic concepts In statistics, every conjecture concerning the unknown probability distribution of a collection of random variables representing the observed data X in some study is called a ''statistical hypothesis''. If we state one hypothesis only and the aim of the statistical test is to see whether this hypothesis is tenable, but not to investigate other specific hypotheses, then such a test is called a null ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
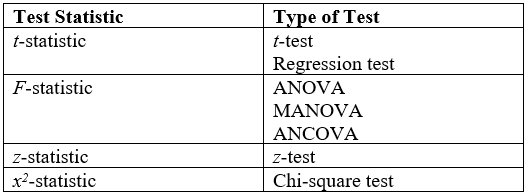
Statistical Tests
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, "significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean D
Jean may refer to: People * Jean (female given name) * Jean (male given name) * Jean (surname) Fictional characters * Jean Grey, a Marvel Comics character * Jean Valjean, fictional character in novel ''Les Misérables'' and its adaptations * Jean Pierre Polnareff, a fictional character from ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure'' Places * Jean, Nevada, USA; a town * Jean, Oregon, USA Entertainment * Jean (dog), a female collie in silent films * "Jean" (song) (1969), by Rod McKuen, also recorded by Oliver * ''Jean Seberg'' (musical), a 1983 musical by Marvin Hamlisch Other uses * JEAN (programming language) * USS ''Jean'' (ID-1308), American cargo ship c. 1918 * Sternwheeler Jean, a 1938 paddleboat of the Willamette River See also *Jehan * * Gene (other) * Jeanne (other) * Jehanne (other) * Jeans (other) * John (other) John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Test
In statistics, Mood's median test is a special case of Pearson's chi-squared test. It is a nonparametric test that tests the null hypothesis that the medians of the populations from which two or more samples are drawn are identical. The data in each sample are assigned to two groups, one consisting of data whose values are higher than the median value in the two groups combined, and the other consisting of data whose values are at the median or below. A Pearson's chi-squared test is then used to determine whether the observed frequencies in each sample differ from expected frequencies derived from a distribution combining the two groups. Relation to other tests The test has low power (efficiency) for moderate to large sample sizes. The Wilcoxon– Mann–Whitney U two-sample test or its generalisation for more samples, the Kruskal–Wallis test, can often be considered instead. The relevant aspect of the median test is that it only considers the position of each observation relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedman Test
The Friedman test is a non-parametric statistical test developed by Milton Friedman. Similar to the parametric repeated measures ANOVA, it is used to detect differences in treatments across multiple test attempts. The procedure involves ranking each row (or ''block'') together, then considering the values of ranks by columns. Applicable to complete block designs, it is thus a special case of the Durbin test. Classic examples of use are: * ''n'' wine judges each rate ''k'' different wines. Are any of the ''k'' wines ranked consistently higher or lower than the others? * ''n'' welders each use ''k'' welding torches, and the ensuing welds were rated on quality. Do any of the ''k'' torches produce consistently better or worse welds? The Friedman test is used for one-way repeated measures analysis of variance by ranks. In its use of ranks it is similar to the Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance by ranks. The Friedman test is widely supported by many statistical software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McNemar's Test
In statistics, McNemar's test is a statistical test used on paired nominal data. It is applied to 2 × 2 contingency tables with a dichotomous trait, with matched pairs of subjects, to determine whether the row and column marginal frequencies are equal (that is, whether there is "marginal homogeneity"). It is named after Quinn McNemar, who introduced it in 1947. An application of the test in genetics is the transmission disequilibrium test for detecting linkage disequilibrium. The commonly used parameters to assess a diagnostic test in medical sciences are sensitivity and specificity. Sensitivity (or recall) is the ability of a test to correctly identify the people with disease. Specificity is the ability of the test to correctly identify those without the disease. Now presume two tests are performed on the same group of patients. And also presume that these tests have identical sensitivity and specificity. In this situation one is carried away by these findings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platykurtic Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis (from el, κυρτός, ''kyrtos'' or ''kurtos'', meaning "curved, arching") is a measure of the "tailedness" of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. Like skewness, kurtosis describes a particular aspect of a probability distribution. There are different ways to quantify kurtosis for a theoretical distribution, and there are corresponding ways of estimating it using a sample from a population. Different measures of kurtosis may have different interpretations. The standard measure of a distribution's kurtosis, originating with Karl Pearson, is a scaled version of the fourth moment of the distribution. This number is related to the tails of the distribution, not its peak; hence, the sometimes-seen characterization of kurtosis as "peakedness" is incorrect. For this measure, higher kurtosis corresponds to greater extremity of deviations (or outliers), and not the configuration of data near the mean. It is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |