|
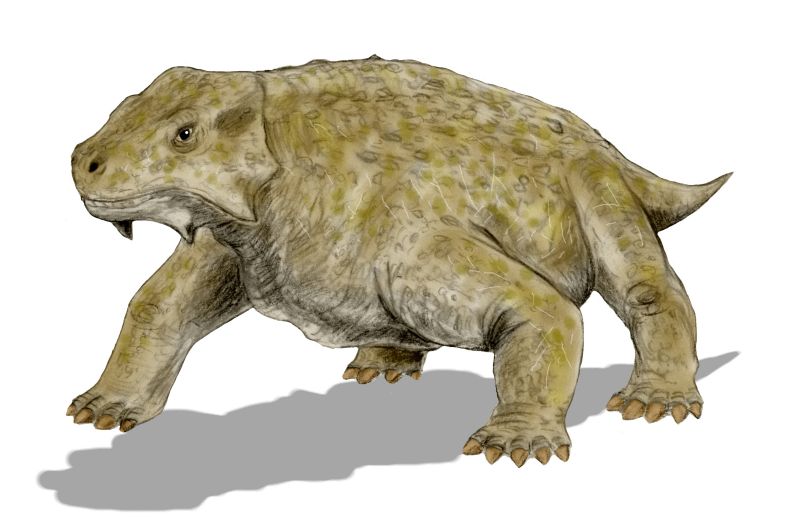
Shansisaurus
''Shihtienfenia'' was a pareiasaurid parareptile from the Late Permian of China. Species Lee (1997) refers to ''S. xuecunensis'' as a metaspecies lacking the autapomorphies of ''Shihtienfenia''. Tsuji & Müller (2009) seem to consider it a valid taxon for cladistic analysis, and like Lee 1997 place the two Chinese species close to '' Pareiasuchus''. ''S. permica'' (Young and Yeh, 1963); The skull of this pareiasaur is unknown. It is known originally from a number of isolated vertebrae, jaws, and limb-bones and an incomplete skeleton, all from the Shiqianfeng locality near Baode, Shanxi Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ..., part of the Sunjiagou Formation. ''Shanshisaurus xuecunensis'' Cheng, 1980 and ''Huanghesaurus liuliensis'' Gao, 1983 are synonyms. ''S. comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurs
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species ''Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honania
''Shihtienfenia'' was a pareiasaurid parareptile from the Late Permian of China. Species Lee (1997) refers to ''S. xuecunensis'' as a metaspecies lacking the autapomorphies of ''Shihtienfenia''. Tsuji & Müller (2009) seem to consider it a valid taxon for cladistic analysis, and like Lee 1997 place the two Chinese species close to '' Pareiasuchus''. ''S. permica'' (Young and Yeh, 1963); The skull of this pareiasaur is unknown. It is known originally from a number of isolated vertebrae, jaws, and limb-bones and an incomplete skeleton, all from the Shiqianfeng locality near Baode, Shanxi Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ..., part of the Sunjiagou Formation. ''Shanshisaurus xuecunensis'' Cheng, 1980 and ''Huanghesaurus liuliensis'' Gao, 1983 are synonyms. ''S. comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changhsingian
In the geologic time scale, the Changhsingian or Changxingian is the latest age or uppermost stage of the Permian. It is also the upper or latest of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch or Series. The Changhsingian lasted from to 251.902 million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Wuchiapingian and followed by the Induan. The greatest mass extinction in the Phanerozoic eon, the Permian–Triassic extinction event, occurred during this age. The extinction rate peaked about a million years before the end of this stage. Stratigraphic definitions The Changhsingian is named after Changxing () in northern Zhejiang, China. The stage was named for the Changhsing Limestone. The name was first used for a stage in 1970; 1973: ''Permian stages names'', in: : ''The Permian and Triassic systems and their mutual boundary'', Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists Memoir 2, pp 522–548. and was anchored in the international timescale in 1981.; 2006: ''The Global Boundary Stratotype Sect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi and Datong. Its one-character abbreviation is "" (), after the state of Jin that existed there during the Spring and Autumn period. The name ''Shanxi'' means "West of the Mountains", a reference to the province's location west of the Taihang Mountains. Shanxi borders Hebei to the east, Henan to the south, Shaanxi to the west and Inner Mongolia to the north. Shanxi's terrain is characterised by a plateau bounded partly by mountain ranges. Shanxi's culture is largely dominated by the ethnic Han majority, who make up over 99% of its population. Jin Chinese is considered by some linguists to be a distinct language from Mandarin and its geographical range covers most of Shanxi. Both Jin and Mandarin are spoken in Shanx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1963
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Animals Of China
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian China
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphibian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |