|
Service Design
Service design is the activity of planning and arranging people, infrastructure, communication and material components of a service in order to improve its quality, and the interaction between the service provider and its users. Service design may function as a way to inform changes to an existing service or create a new service entirely. The purpose of service design methodologies is to establish the most effective practices for designing services, according to both the needs of users and the competencies and capabilities of service providers. If a successful method of service design is adapted then the service will be user-friendly and relevant to the users, while being sustainable and competitive for the service provider. For this purpose, service design uses methods and tools derived from different disciplines, ranging from ethnography to information and management science to interaction design. Service design concepts and ideas are typically portrayed visually, using differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Provider
A service provider (SP) is an organization that provides services, such as consulting, legal, real estate, communications, storage, and processing services, to other organizations. Although a service provider can be a sub-unit of the organization that it serves, it is usually a third-party or outsourced supplier. Examples include telecommunications service providers (TSPs), application service providers (ASPs), storage service providers (SSPs), and internet service providers (ISPs). A more traditional term is service bureau. IT professionals sometimes differentiate between service providers by categorizing them as type I, II, or III. The three service types are recognized by the IT industry although specifically defined by ITIL and the U.S. Telecommunications Act of 1996. *Type I: internal service provider *Type II: shared service provider *Type III: external service provider Type III SPs provide IT services to external customers and subsequently can be referred to as external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
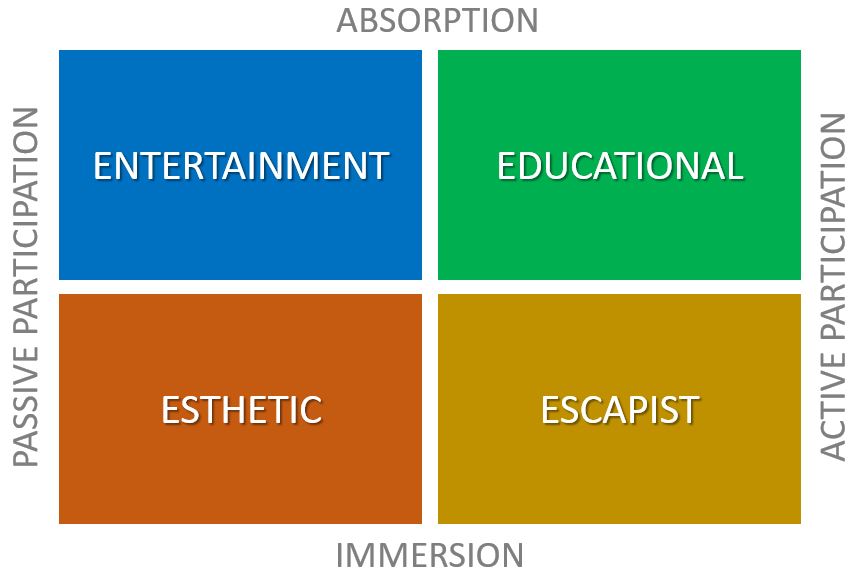
Customer Experience
Customer experience (CX) is a totality of cognitive, affective, sensory, and behavioral consumer responses during all stages of the consumption process including pre-purchase, consumption, and post-purchase stages. Pine and Gilmore described the experience economy as the next level after commodities, goods, and services with memorable events as the final business product. Four realms of experience include esthetic, escapist, entertainment, and educational components. Different dimensions of customer experience include senses, emotions, feelings, perceptions, cognitive evaluations, involvement, memories, as well as spiritual components, and behavioral intentions. The pre-consumption anticipation experience can be described as the amount of pleasure or displeasure received from savoring future events, while the remembered experience is related to a recollection of memories about previous events and experiences of a product or service. Definitions Forbes describes the customer e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service System
A service system (or customer service system, CSS) is a configuration of technology and organizational networks designed to deliver services that satisfy the needs, wants, or aspirations of customers. "Service system" is a term used in the service management, service operations, services marketing, service engineering, and service design literature. While the term frequently appears, it is rarely defined. One definition of a service system is a value coproduction configuration of people, technology, internal and external service systems connected via value propositions, and shared information (language, laws, measures, etc.). The smallest service system is a single person and the largest service system is the world economy. The external service system of the global economy is considered to be ecosystem services. Service systems can be characterized by the value that results from interaction between service systems, whether the interactions are between people, businesses, or n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Just In Time (business)
Lean manufacturing is a production method aimed primarily at reducing times within the production system as well as response times from suppliers and to customers. It is closely related to another concept called just-in-time manufacturing (JIT manufacturing in short). Just-in-time manufacturing tries to match production to demand by only supplying goods which have been ordered and focuses on efficiency, productivity (with a commitment to continuous improvement) and reduction of "wastes" for the producer and supplier of goods. Lean manufacturing adopts the just-in-time approach and additionally focuses on reducing cycle, flow and throughput times by further eliminating activities which do not add any value for the customer. Lean manufacturing also involves people who work outside of the manufacturing process, such as in marketing and customer service. Lean manufacturing is particularly related to the operational model implemented in the post-war 1950s and 1960s by the Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IDEF0
IDEF0, a compound acronym ("Icam DEFinition for Function Modeling", where ICAM is an acronym for "Integrated Computer Aided Manufacturing"), is a function modeling methodology for describing manufacturing functions, which offers a functional modeling language for the analysis, development, reengineering and integration of information systems, business processes or software engineering analysis.''Systems Engineering Fundamentals.'' Defense Acquisition University Press, 2001. IDEF0 is part of the IDEF family of modeling languages in the field of |
Functional Requirements
In software engineering and systems engineering, a functional requirement defines a function of a system or its component, where a function is described as a specification of behavior between inputs and outputs. Functional requirements may involve calculations, technical details, data manipulation and processing, and other specific functionality that define what a system is supposed to accomplish. Behavioral requirements describe all the cases where the system uses the functional requirements, these are captured in use cases. Functional requirements are supported by non-functional requirements (also known as "quality requirements"), which impose constraints on the design or implementation (such as performance requirements, security, or reliability). Generally, functional requirements are expressed in the form "system must do ," while non-functional requirements take the form "system shall be ." The plan for implementing functional requirements is detailed in the system design, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their life cycles. At its core, systems engineering utilizes systems thinking principles to organize this body of knowledge. The individual outcome of such efforts, an engineered system, can be defined as a combination of components that work in synergy to collectively perform a useful function. Issues such as requirements engineering, reliability, logistics, coordination of different teams, testing and evaluation, maintainability and many other disciplines necessary for successful system design, development, implementation, and ultimate decommission become more difficult when dealing with large or complex projects. Systems engineering deals with work-processes, optimization methods, and risk management tools in such projects. It overlaps technical and human-centered disciplines such as industrial engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated software documentation, documentation and data (computing), data. This is in contrast to Computer hardware, hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the low level language, lowest programming level, executable code consists of Machine code, machine language instructions supported by an individual Microprocessor, processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of Binary number, binary values signifying Instruction set architecture, processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction System call, may also invoke one of many Input/output, input or output operations, for example displaying some text on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blueprint
A blueprint is a reproduction of a technical drawing or engineering drawing using a contact print process on light-sensitive sheets. Introduced by Sir John Herschel in 1842, the process allowed rapid and accurate production of an unlimited number of copies. It was widely used for over a century for the reproduction of specification drawings used in construction and industry. The blueprint process was characterized by white lines on a blue background, a negative of the original. The process was not able to reproduce color or shades of grey. The process is now obsolete. It was first largely displaced by the diazo whiteprint process, and later by large-format xerographic photocopiers. The term '' blueprint'' continues to be used less formally to refer to any floor plan (and even less formally, any type of plan). Practicing engineers, architects, and drafters often call them "drawings", “prints”, or “plans”. It has almost entirely been replaced with digital computer-aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Construction Of Technology
Social construction of technology (SCOT) is a theory within the field of science and technology studies. Advocates of SCOT—that is, social constructivists—argue that technology does not determine human action, but that rather, human action shapes technology. They also argue that the ways a technology is used cannot be understood without understanding how that technology is embedded in its social context. SCOT is a response to technological determinism and is sometimes known as technological constructivism. SCOT draws on work done in the constructivist school of the sociology of scientific knowledge, and its subtopics include actor-network theory (a branch of the sociology of science and technology) and historical analysis of sociotechnical systems, such as the work of historian Thomas P. Hughes. Its empirical methods are an adaptation of the Empirical Programme of Relativism (EPOR), which outlines a method of analysis to demonstrate the ways in which scientific findings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |