|
Seismic Attribute
In reflection seismology, a seismic attribute is a quantity extracted or derived from seismic data that can be analysed in order to enhance information that might be more subtle in a traditional seismic image, leading to a better geological or geophysical interpretation of the data. Examples of seismic attributes can include measured time, amplitude, frequency and attenuation, in addition to combinations of these. Most seismic attributes are post-stack, but those that use CMP gathers, such as amplitude versus offset (AVO), must be analysed pre-stack.Young, R. & LoPiccolo, R. 2005. AVO analysis demystified. E&P. http://www.e-seis.com/white_papers/AVO%20Analysis%20Demystified.pdf They can be measured along a single seismic trace or across multiple traces within a defined window. The first attributes developed were related to the 1D complex seismic trace and included: envelope amplitude, instantaneous phase, instantaneous frequency, and apparent polarity. Acoustic impedance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Seismology
Reflection seismology (or seismic reflection) is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic source of energy, such as dynamite or Tovex blast, a specialized air gun or a seismic vibrator. Reflection seismology is similar to sonar and echolocation. This article is about surface seismic surveys; for vertical seismic profiles, see VSP. History Reflections and refractions of seismic waves at geologic interfaces within the Earth were first observed on recordings of earthquake-generated seismic waves. The basic model of the Earth's deep interior is based on observations of earthquake-generated seismic waves transmitted through the Earth's interior (e.g., Mohorovičić, 1910). The use of human-generated seismic waves to map in detail the geology of the upper few kilometers of the Earth's crust followed shortly thereafter and ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Inversion
In geophysics (primarily in oil-and-gas exploration/development), seismic inversion is the process of transforming seismic reflection data into a quantitative rock-property description of a reservoir. Seismic inversion may be pre- or post- stack, deterministic, random or geostatistical; it typically includes other reservoir measurements such as well logs and cores. Introduction Geophysicists routinely perform seismic surveys to gather information about the geology of an oil or gas field. These surveys record sound waves which have traveled through the layers of rock and fluid in the earth. The amplitude and frequency of these waves can be estimated so that any side-lobe and tuning effects introduced by the wavelet may be removed. Seismic data may be inspected and interpreted on its own without inversion, but this does not provide the most detailed view of the subsurface and can be misleading under certain conditions. Because of its efficiency and quality, most oil and gas compani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bright Spot
In reflection seismology, a bright spot is a local high amplitude seismic attribute anomaly that can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons and is therefore known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator. It is used by geophysicists in hydrocarbon exploration. History Bright spots were not commonly identified until the early 1970s because of the extensive and industry-wide use of automatic gain control, which obscured the amplitude effects of hydrocarbon accumulations. Theory A bright spot primarily results from the increase in acoustic impedance Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The SI unit of acoustic impedance is the pascal-second per cu ... contrast when a hydrocarbon (with a lower acoustic impedance) replaces the brine-saturated zone (with a higher acoustic impedance) that underlies a shale (with a higher acoustic impedance sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
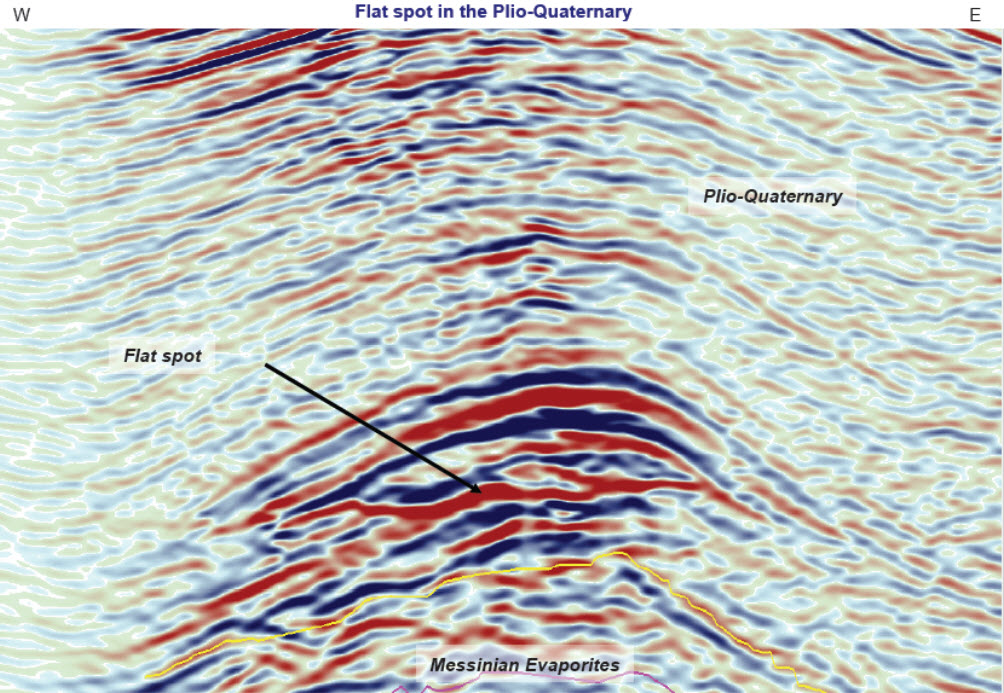
Direct Hydrocarbon Indicator
A hydrocarbon indicator (HCI) or direct hydrocarbon indicator (DHI), is an anomalous seismic attribute value or pattern that could be explained by the presence of hydrocarbons in an oil or gas reservoir. DHIs are particularly useful in hydrocarbon exploration for reducing the geological risk of exploration wells. Broadly, geophysicists recognize several types of DHI: * Bright spots: localized amplitudes of greater magnitude than background amplitude values. Equipment prior to the 1970s had the bright spots obscured due to the automatic gain control. * Flat spot A flat spot, or wheel flat, also called spalling or shelling, is a fault in railroad wheel shape. A flat spot occurs when a rail vehicle's wheelset is dragged along the rail after the wheel/axle has stopped rotating. Flat spots are usually cau ...s: nearly horizontal reflectors that cross existing stratigraphy, possibly indicating a hydrocarbon fluid level within an oil or gas reservoir. * Dim spots: low amplitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or exemplified by the odors of gasoline and lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to the naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, and to their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decomposition Of Spectrum (functional Analysis)
The spectrum of a linear operator T that operates on a Banach space X (a fundamental concept of functional analysis) consists of all scalars \lambda such that the operator T-\lambda does not have a bounded inverse on X. The spectrum has a standard decomposition into three parts: * a point spectrum, consisting of the eigenvalues of T; * a continuous spectrum, consisting of the scalars that are not eigenvalues but make the range of T-\lambda a proper dense subset of the space; * a residual spectrum, consisting of all other scalars in the spectrum. This decomposition is relevant to the study of differential equations, and has applications to many branches of science and engineering. A well-known example from quantum mechanics is the explanation for the discrete spectral lines and the continuous band in the light emitted by excited atoms of hydrogen. Decomposition into point spectrum, continuous spectrum, and residual spectrum For bounded Banach space operators Let ''X'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
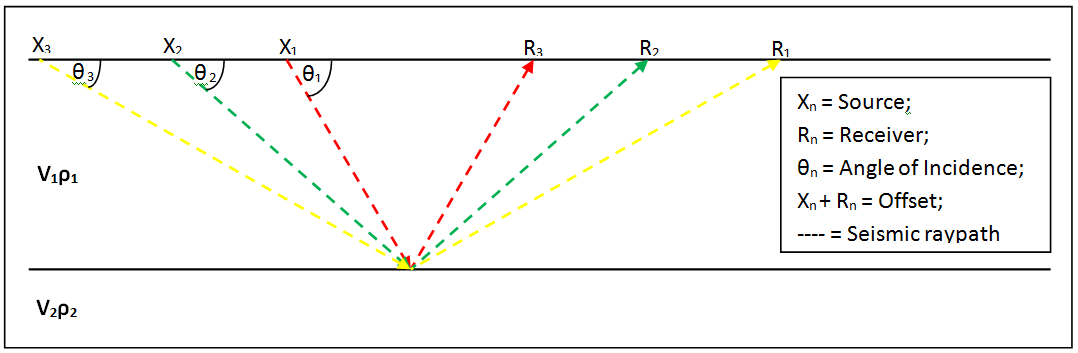
Amplitude Versus Offset
In geophysics and reflection seismology, amplitude versus offset (AVO) or amplitude variation with offset is the general term for referring to the dependency of the seismic attribute, amplitude, with the distance between the source and receiver (the offset). AVO analysis is a technique that geophysicists can execute on seismic data to determine a rock's fluid content, porosity, density or seismic velocity, shear wave information, fluid indicators (hydrocarbon indications). The phenomenon is based on the relationship between the reflection coefficient and the angle of incidence and has been understood since the early 20th century when Karl Zoeppritz wrote down the Zoeppritz equations. Due to its physical origin, AVO can also be known as amplitude versus angle (AVA), but AVO is the more commonly used term because the offset is what a geophysicist can vary in order to change the angle of incidence. (See diagram) Background and theory For a seismic wave reflecting off an inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instantaneous Bandwidth
In physics and the philosophy of science, instant refers to an infinitesimal interval in time, whose passage is instantaneous. In ordinary speech, an instant has been defined as "a point or very short space of time," a notion deriving from its etymological source, the Latin verb ''instare'', from ''in-'' + ''stare'' ('to stand'), meaning 'to stand upon or near.' The continuous nature of time and its infinite divisibility was addressed by Aristotle in his ''Physics'', where he wrote on Zeno's paradoxes. The philosopher and mathematician Bertrand Russell Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British mathematician, philosopher, logician, and public intellectual. He had a considerable influence on mathematics, logic, set theory, linguistics, ... was still seeking to define the exact nature of an instant thousands of years later. , the smallest time interval certify in regulated measurements is on the order of 397 zeptosecon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Response Phase
Response may refer to: *Call and response (music), musical structure *Reaction (other) * Request–response **Output or response, the result of telecommunications input *Response (liturgy), a line answering a versicle *Response (music) or antiphon, a response to a psalm or other part of a religious service *Response, a phase in emergency management * Response rate (survey) Proper names and titles *''Response'', a print and online magazine of Christian thought published by Seattle Pacific University * ''Response'' (album), a studio album by Phil Wickham *Response (company), a call centre company based in Scotland * ''The Response'' (film) *The National War Memorial (Canada), titled ''The Response'' *The Northumberland Fusiliers Memorial in Newcastle upon Tyne, titled "The Response" See also *Action (other) *Answer (other) * Reply (other) *Response variable, or the realization thereof *Responsions, an examination formerly required for a degree a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Response Amplitude
Response may refer to: *Call and response (music), musical structure *Reaction (other) * Request–response **Output or response, the result of telecommunications input *Response (liturgy), a line answering a versicle *Response (music) or antiphon, a response to a psalm or other part of a religious service *Response, a phase in emergency management * Response rate (survey) Proper names and titles *''Response'', a print and online magazine of Christian thought published by Seattle Pacific University * ''Response'' (album), a studio album by Phil Wickham *Response (company), a call centre company based in Scotland * ''The Response'' (film) *The National War Memorial (Canada), titled ''The Response'' *The Northumberland Fusiliers Memorial in Newcastle upon Tyne, titled "The Response" See also *Action (other) *Answer (other) * Reply (other) *Response variable, or the realization thereof *Responsions, an examination formerly required for a degree a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instantaneous Amplitude
In physics and engineering, the envelope of an oscillating signal is a smooth curve outlining its extremes. The envelope thus generalizes the concept of a constant amplitude into an instantaneous amplitude. The figure illustrates a modulated sine wave varying between an ''upper envelope'' and a ''lower envelope''. The envelope function may be a function of time, space, angle, or indeed of any variable. In beating waves A common situation resulting in an envelope function in both space ''x'' and time ''t'' is the superposition of two waves of almost the same wavelength and frequency: : \begin F(x, \ t) & = \sin \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f + \Delta f )t \right) \right+ \sin \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f - \Delta f )t \right) \right\\ pt& \approx 2\cos \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - \Delta f \ t \right) \right\ \sin \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - f \ t \right) \right\end which uses the trigonometric formula for the addition of two sine waves, and the approximation&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dip (geology)
Strike and dip is a measurement convention used to describe the orientation, or attitude, of a planar geologic feature. A feature's strike is the azimuth of an imagined horizontal line across the plane, and its dip is the angle of inclination measured downward from horizontal. They are used together to measure and document a structure's characteristics for study or for use on a geologic map. A feature's orientation can also be represented by dip and dip direction, using the azimuth of the dip rather than the strike value. Linear features are similarly measured with trend and plunge, where "trend" is analogous to dip direction and "plunge" is the dip angle. Strike and dip are measured using a compass and a clinometer. A compass is used to measure the feature's strike by holding the compass horizontally against the feature. A clinometer measures the features dip by recording the inclination perpendicular to the strike. These can be done separately, or together using a tool such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |