|
Schistosomatidae
Schistosomatidae is a family (biology), family of digenetic trematodes with Parasitic life cycles, complex parasitic life cycles. Immature developmental stages of schistosomes are found in molluscs and adults occur in vertebrates. The best studied group, the blood flukes of the genus ''Schistosoma'', infect and cause disease in humans. Other genus, genera which are infective to non-human vertebrates can cause swimmer's itch, mild rashes in humans. Schistosomatids are dioecious (individuals are of separate sexes) which is exceptional with regards to their phylum, flatworm, Platyhelminthes, in which most species are hermaphroditic (individuals possess both male and female reproductive systems). History The eggs of these parasites were first described by Theodor Bilharz, a German pathologist working in Egypt in 1851 who found the eggs during the course of an autopsy. He wrote two letters to his former teacher Karl Theodor Ernst von Siebold in May and August 1851 describing his findi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Fluke
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed '' schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease (after malaria), with hundreds of millions infected worldwide. Adult flatworms parasitize blood capillaries of either the mesenteries or plexus of the bladder, depending on the infecting species. They are unique among trematodes and any other flatworms in that they are dioecious with distinct sexual dimorphism between male and female. Thousands of eggs are released and reach either the bladder or the intestine (according to the infecting species), and these are then excreted in urine or feces to fresh water. Larvae must then pass through an intermediate snail host, before the next larval stage of the parasite emerges that can infect a new mammalian host by direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed '' schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease (after malaria), with hundreds of millions infected worldwide. Adult flatworms parasitize blood capillaries of either the mesenteries or plexus of the bladder, depending on the infecting species. They are unique among trematodes and any other flatworms in that they are dioecious with distinct sexual dimorphism between male and female. Thousands of eggs are released and reach either the bladder or the intestine (according to the infecting species), and these are then excreted in urine or feces to fresh water. Larvae must then pass through an intermediate snail host, before the next larval stage of the parasite emerges that can infect a new mammalian host by directl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
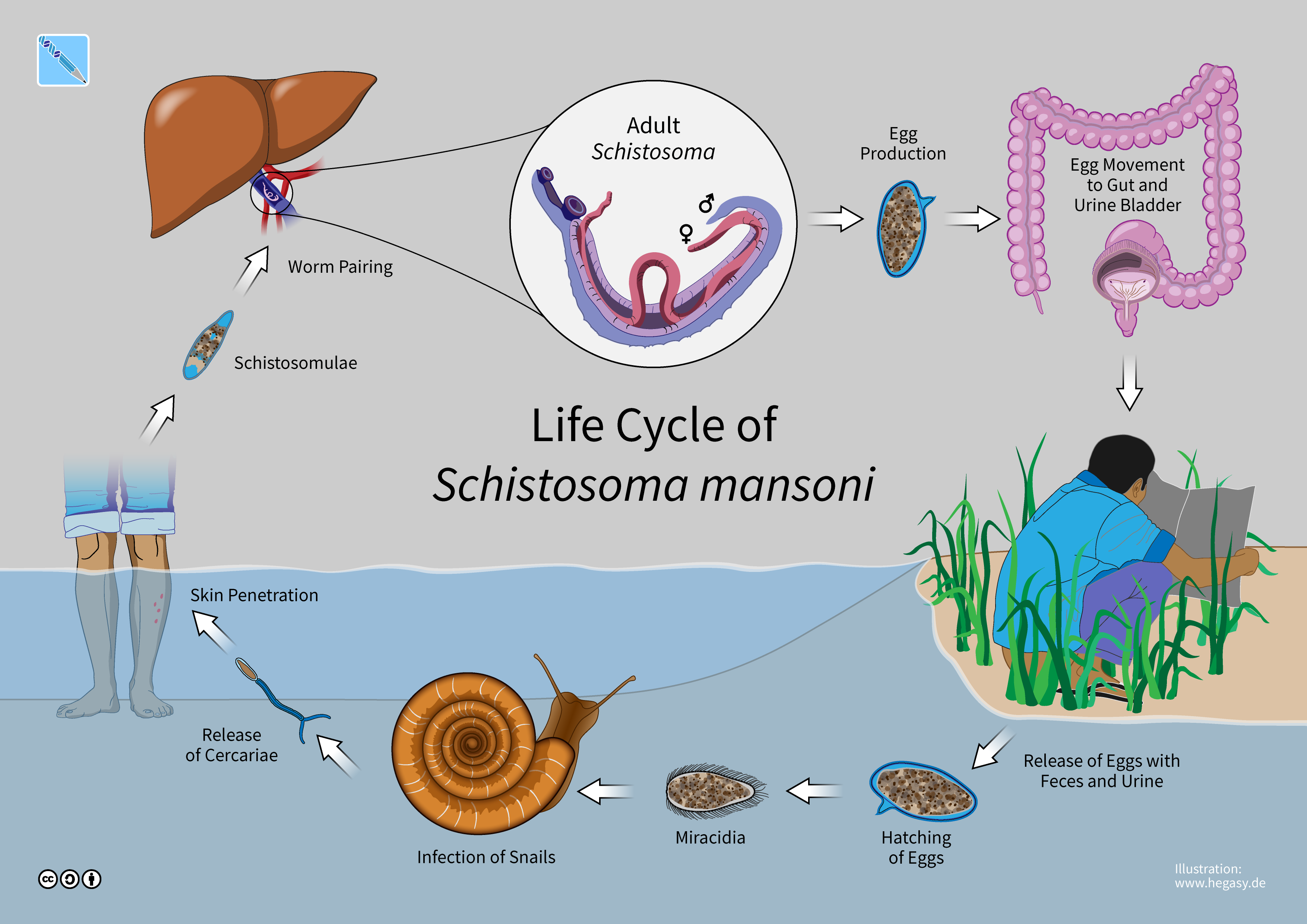
Schistosoma Mansoni
A paired couple of ''Schistosoma mansoni''. ''Schistosoma mansoni'' is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes (''Schistosoma''). The adult lives in the blood vessels ( mesenteric veins) near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis (similar to '' S. japonicum'', '' S. mekongi'', ''S. guineensis'', and '' S. intercalatum''). Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 236.6 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to ''S. mansoni''. It is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Caribbean, Brazil, Venezuela and Suriname. Unlike other flukes (trematodes) in which sexes are not separate ( monoecious), schistosomes are unique in that adults are divided into males and females, thus, gonochoric. However, a permanent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griphobilharzia Amoena
''Griphobilharzia amoena'' is a significant trematode that infect crocodiles such as the Australian freshwater crocodile, ''Crocodylus johnstoni'', located in Darwin, Australia with reported illness in Irian Jaya as well. Platt TR, Blair D, et al. 1991. ''Griphobilharzia amoena'' n. gen., n. sp. (Digenea: Schistosomatidae), a parasite of the freshwater crocodile ''Crocodylus johnstoni'' (Reptilia: Crocodylia) from Australia, with the erection of a new subfamily, Griphobilharziinae. ''Journal of Parasitology'' 77:65–68. They possess a distinctive tegument that is composed of two lipid bilayers instead of a single bilayer. The double bilayer may be an adaptation to survive the host's immune response. Description The life cycle remains unknown but cercariae probably develop in mollusks, most likely gastropods. Its intermediate host could be freshwater snails from family Planorbidae.Brant S.V., Loker E.S. 2005''Can Specialized Pathogens Colonize Distantly Related Hosts? Schisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griphobilharzia
''Griphobilharzia amoena'' is a significant trematode that infect crocodiles such as the Australian freshwater crocodile, ''Crocodylus johnstoni'', located in Darwin, Australia with reported illness in Irian Jaya as well. Platt TR, Blair D, et al. 1991. ''Griphobilharzia amoena'' n. gen., n. sp. (Digenea: Schistosomatidae), a parasite of the freshwater crocodile ''Crocodylus johnstoni'' (Reptilia: Crocodylia) from Australia, with the erection of a new subfamily, Griphobilharziinae. ''Journal of Parasitology'' 77:65–68. They possess a distinctive tegument that is composed of two lipid bilayers instead of a single bilayer. The double bilayer may be an adaptation to survive the host's immune response. Description The life cycle remains unknown but cercariae probably develop in mollusks, most likely gastropods. Its intermediate host could be freshwater snails from family Planorbidae.Brant S.V., Loker E.S. 2005''Can Specialized Pathogens Colonize Distantly Related Hosts? Schisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swimmer's Itch
Swimmer's itch, cercarial dermatitis or schistosome dermatitis is a short-term allergic contact dermatitis occurring in the skin of humans that have been infected by water-borne schistosomes, a type of flatworm. It is common in freshwater, brackish and marine habitats worldwide. The incidence of this condition may be increasing, although this may be attributed to better monitoring and reporting. Nevertheless, the condition is considered to be an emerging infectious disease. The main symptom is itchy papules (raised skin) that commonly occur within 2 days of infection. Initially, wheals develop quickly, then turn into maculae in about half an hour. Within 10–12 hours these turn into very itchy papules that reach their worst by the second or third day. The papules disappear in 1–2 weeks but secondary effects from scratching can continue longer. The intense itching, which peaks after 48–72 hours, is associated with pain and swelling of the affected areas. People repeatedly expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digenetic Trematode
Digenea (Gr. ''Dis'' – double, ''Genos'' – race) is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms (known as ''flukes'') with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date. Morphology Key features Characteristic features of the Digenea include a syncytial tegument; that is, a tegument where the junctions between cells are broken down and a single continuous cytoplasm surrounds the entire animal. A similar tegument is found in other members of the Neodermata; a group of platyhelminths comprising the Digenea, Aspidogastrea, Monogenea and Cestoda. Digeneans possess a vermifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylus Johnstoni
The freshwater crocodile (''Crocodylus johnstoni''), also known as the Australian freshwater crocodile, Johnstone's crocodile or the freshie, is a species of crocodile endemic to the northern regions of Australia. Unlike their much larger Australian relative, the saltwater crocodile, freshwater crocodiles are not known as man-eaters, although they bite in self-defence, and brief, nonfatal attacks have occurred, apparently the result of mistaken identity. Taxonomy and etymology When Gerard Krefft named the species in 1873, he intended to commemorate the man who first reported it to him, Australian native police officer and amateur naturalist Robert Arthur Johnstone (1843–1905). However, Krefft made an error in writing the name, and for many years, the species has been known as ''C. johnsoni''. Recent studies of Krefft's papers have determined the correct spelling of the name, and much of the literature has been updated to the correct usage, but both versions still exist. Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirorchiidae
Spirorchiidae is a family of digenetic trematodes. Infestation by these trematodes leads to the disease spirorchiidiosis. Spirorchiids are mainly parasites of turtles. It has been synonymised with Proparorchiidae Ward, 1921, Spirorchidae Stunkard, 1921, and Spirorchiidae MacCallum, 1921. Genera *'' Amphiorchis'' Price, 1934 *'' Baracktrema'' Roberts, Platt & Bullard in Roberts, Platt, Orélis-Ribeiro & Bullard, 2016 *'' Cardiotrema'' Dwivedi, 1967 *'' Carettacola'' Manter & Larson, 1950 *'' Cheloneotrema'' Simha & Chattopadhyaya, 1980 *'' Coeuritrema'' Mehra, 1933 *'' Enterohaematotrema'' Mehra, 1940 *'' Hapalorhynchus'' Stunkard, 1922 *'' Hapalotrema'' Looss, 1899 *'' Learedius'' Price, 1934 *'' Monticellius'' Mehra, 1939 *'' Neocaballerotrema'' Simha, 1977 *'' Neospirorchis'' Price, 1934 *'' Plasmiorchis'' Mehra, 1934 *'' Platt'' Roberts & Bullard in Roberts, Arias, Halanych, Dang & Bullard, 2018 *'' Satyanarayanotrema'' Simha & Chattopadhyaya, 1980 *'' Shobanatrema'' Simha & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana (and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanguinicolidae
Aporocotylidae is a family of trematodes within the order Diplostomida, which contains species commonly known as fish blood flukes. It contains more than 40 genera, the largest being '' Cardicola''. Species in this family parasite fish in both fresh and marine water. Genera * Acipensericola Bullard, Snyder, Jensen & Overstreet, 2008 * Adelomyllos Nolan & Cribb, 2004 * Ankistromeces Nolan & Cribb, 2004 * Aporocotyle Odhner, 1900 * Cardallagium Yong, Cutmore, Jones, Gauthier & Cribb, 2017 * Cardicola Short, 1953 * Chaulioleptos Nolan & Cribb, 2005 * Chimaerohemecus van der Land, 1967 * Cladocaecum Orelis-Ribeiro & Bullard, 2016 * Cruoricola Herbert, Shaharom-Harrison & Overstreet, 1994 * Deontacylix Linton, 1910 * Elaphrobates Bullard & Overstreet, 2003 * Elopicola Bullard, 2014 * Holocentricola ''Holocentricola'' is a genus of digeneans in the family Aporocotylidae or blood flukes, described in 2021. The name of the genus refers to the host fish, which are memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |