|
Saqqarah
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around . Saqqara contains the oldest complete stone building complex known in history, the Pyramid of Djoser, built during the Third Dynasty. Another sixteen Egyptian kings built pyramids at Saqqara, which are now in various states of preservation. High officials added private funeral monuments to this necropolis during the entire Pharaonic period. It remained an important complex for non-royal burials and cult ceremonies for more than 3,000 years, well into Ptolemaic and Roman times. North of the area known as Saqqara lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Userkaf
The pyramid complex of Userkaf was built c. 2490 BC for the pharaoh Userkaf (reigned 2494–2487 BC), founder of the 5th Dynasty of Egypt (c. 2494–2345 BC). It is located in the pyramid field at Saqqara, on the north-east of the step pyramid of Djoser (reigned c. 2670 BC). Constructed in dressed stone with a core of rubble, the pyramid is now ruined and resembles a conical hill in the sands of Saqqara.Mark Lehner, ''The Complete Pyramids'', Thames & Hudson, , p. 140 For this reason, it is known locally as ''El-Haram el-Maharbish'', the "Heap of Stone",Jean-Phillipe Lauer (in French): ''Saqqarah, Une vie, Entretiens avec Phillipe Flandrin'', Petite Bibliotheque Payot 107, 1988, and was recognized as a royal pyramid by western archaeologists in the 19th century. Userkaf's pyramid is part of a larger mortuary complex comprising a mortuary temple, an offering chapel and a cult pyramid as well as separate pyramid and mortuary temple for Userkaf's wife, queen Neferhet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
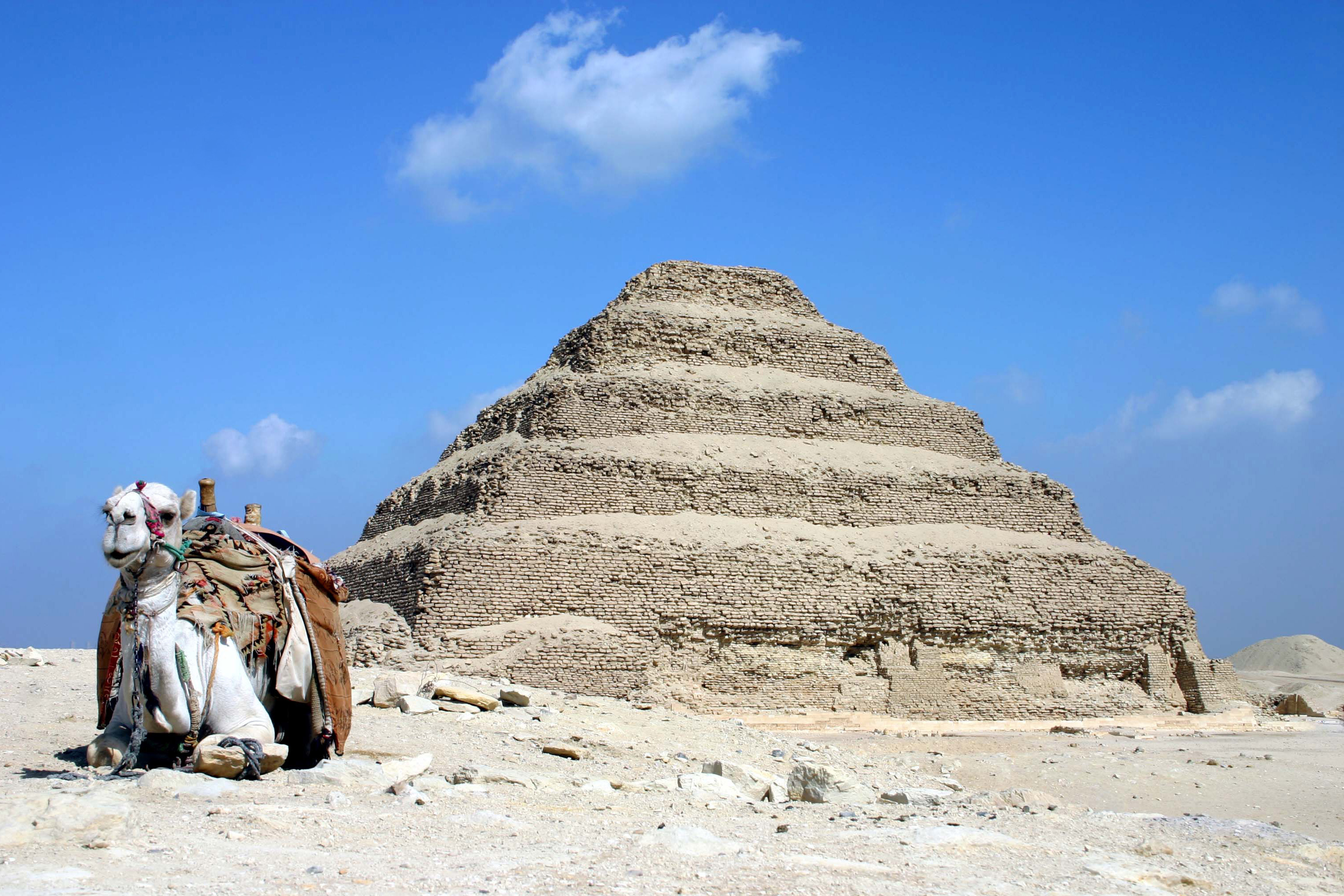
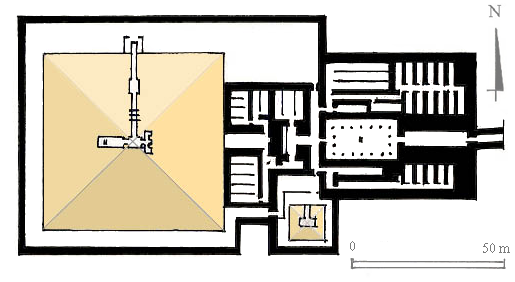
Pyramid Of Djoser
The pyramid of Djoser (or Djeser and Zoser), sometimes called the Step Pyramid of Djoser, is an archaeological site in the Saqqara necropolis, Egypt, northwest of the ruins of Memphis. The 6-tier, 4-sided structure is the earliest colossal stone building in Egypt. It was built in the 27th century BC during the Third Dynasty for the burial of Pharaoh Djoser. The pyramid is the central feature of a vast mortuary complex in an enormous courtyard surrounded by ceremonial structures and decoration. Its architect was Imhotep, chancellor of the pharaoh and high priest of the god Ra. The pyramid went through several revisions and redevelopments of the original plan. The pyramid originally stood tall, with a base of and was clad in polished white limestone. The step pyramid (or proto-pyramid) was considered to be the earliest large-scale cut stone construction made by man as of 1997, although the nearby enclosure wall "Gisr el-Mudir" is suggested by some Egyptologists to predate the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Akhethetep
The Tomb of Akhethetep, also known as Mastaba of Akhethetep (french: Mastaba d'Akhethétep), is a tomb complex in Saqqarah, Egypt. It was built for Akhethetep, a royal official, near the western part of the Pyramid of Djoser. Akhethetep was an official with several, mainly religious titles. including ''priest of Heka'', ''priest of Khnum'' and ''priest of Horus''. The tomb's decorated chapel was removed in 1903 and reassembled at the Louvre in Paris, where it is also known as the "Mastaba of Akhethetep" or simply "". History The tomb was discovered in 1903 by a team of Georges Aaron Bénédite, Curator of the Louvre's Egyptian Department, Hilda Petrie, and Margaret Murray. In line with Egypt's policy at the time, the Louvre was allowed to buy the entire chapel, and relocate and reassemble it to Paris. The chapel was initially displayed in 1905 in the ground floor of the in the Denon (South) Wing of the Louvre Palace, which the museum had recently taken over from non-museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortuary Complex Of Pepi I
The pyramid of Pepi I (in ancient Egyptian Men-nefer-Pepi meaning Pepi's splendour is enduring) is the pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Pepi I of the Sixth Dynasty in the 24th or 23rd century BC. The complex gave its name to the capital city of Egypt, Memphis. As in the pyramids of his predecessors, Pepi I's substructure was filled with vertical columns of hieroglyphic texts, Pyramid Texts. It was in Pepi I's pyramid that these texts were initially discovered in 1880 by Gaston Maspero, though they originated in the pyramid of Unas. The corpus of Pepi I's texts is also the largest from the Old Kingdom, comprising 2,263 columns and lines of hieroglyphs. Pepi I sited his pyramid complex in South Saqqara an approximate north of Djedkare Isesi's pyramid. It is unclear why Pepi I relocated to South Saqqara. Perhaps Pepi I had moved the royal palace south and away from the city, or perhaps no viable sites were left in North and Central Saqqara after Teti built his pyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Unas
The pyramid of Unas (Egyptian: ''Nfr swt Wnjs'' "Beautiful are the places of Unas") is a smooth-sided pyramid built in the 24th century BC for the Egyptian pharaoh Unas, the ninth and final king of the Fifth Dynasty. It is the smallest Old Kingdom pyramid, but significant due to the discovery of Pyramid Texts, spells for the king's afterlife incised into the walls of its subterranean chambers. Inscribed for the first time in Unas's pyramid, the tradition of funerary texts carried on in the pyramids of subsequent rulers, through to the end of the Old Kingdom, and into the Middle Kingdom through the Coffin Texts that form the basis of the ''Book of the Dead''. Unas built his pyramid between the complexes of Sekhemket and Djoser, in North Saqqara. Anchored to the valley temple at a nearby lake, a long causeway was constructed to provide access to the pyramid site. The causeway had elaborately decorated walls covered with a roof which had a slit in one section allowing light to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Teti
The pyramid of Teti is a smooth-sided pyramid situated in the pyramid field at Saqqara in Egypt. It is the second known pyramid containing pyramid texts. Excavations have revealed a satellite pyramid, two pyramids of queens accompanied by cult structures, and a funerary temple. The pyramid was opened by Gaston Maspero in 1882 and the complex explored during several campaigns ranging from 1907 to 1965. It was originally called ''Teti's Places Are Enduring''. The preservation above ground is very poor, and it now resembles a small hill. Below ground the chambers and corridors are very well preserved. The funerary complex The pyramid complex of Teti follows a model established during the reign of Djedkare Isesi, the arrangement of which is inherited from the funerary complexes of Abusir. A valley temple, now lost, was probably destroyed in antiquity due to the place of an Old Kingdom temple dedicated to Anubis constructed there. A better known funerary temple, revealed by Jame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Perneb
The Tomb of Perneb is a mastaba-style tomb from ancient Egypt, built during the reigns of Djedkare Isesi and Unas (ca. 2381 BC to 2323 BC), in the necropolis of Saqqara, north of Pharaoh Djoser's Step Pyramid and about 30 kilometers south of Giza, Egypt. It was the tomb of Perneb, and from the size and placement of the tomb he might have been a court official or royal family member. The tomb was erected during the 5th Dynasty in the Old Kingdom. It was discovered in 1907, purchased from the Egyptian government in 1913 and given to the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, by Edward S. Harkness. Perneb was a court official in the royal household who had a role in the robing and crowning of the king. His name means "my Lord has come forth to me". His tomb was attached to the larger tomb of the vizier Shepsesre, who may have been Perneb's father. Description The tomb consists of an underground burial chamber and a limestone mastaba above ground. The mastaba is div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemaic Dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Ancient Egypt during the Hellenistic period. Their rule lasted for 275 years, from 305 to 30 BC. The Ptolemaic was the last dynasty of ancient Egypt. Ptolemy, one of the seven somatophylakes (bodyguard companions), a general and possible half-brother of Alexander the Great, was appointed satrap of Egypt after Alexander's death in 323 BC. In 305 BC, he declared himself Pharaoh Ptolemy I, later known as ''Sōter'' "Saviour". The Egyptians soon accepted the Ptolemies as the successors to the pharaohs of independent Egypt. Ptolemy's family ruled Egypt until the Roman conquest of 30 BC. Like the earlier dynasties of ancient Egypt, the Ptolemaic dynasty practiced inbreeding including sibling marriage, but this did not start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ancient Egypt
The history of ancient Egypt spans the period from the early prehistoric settlements of the northern Nile valley to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC. The pharaonic period, the period in which Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, is dated from the 32nd century BC, when Upper and Lower Egypt were unified, until the country fell under Macedonian rule in 332 BC. Chronology ;Note: For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, see Egyptian chronology. Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty of each pharaoh. The dating of events is still a subject of research. The conservative dates are not supported by any reliable absolute date for a span of about three millennia. The following is the list according to conventional Egyptian chronology. * Prehistoric Egypt (prior to 3100 BC) * Naqada III ("the protodynastic period", approximately 3100–3000 BC; sometimes referred to as "Dynasty 0") * Early Dynastic Period (First– Second D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Dynasty Of Egypt
The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis. Overview After the turbulent last years of the Second Dynasty, which might have included civil war, Egypt came under the rule of Djoser, marking the beginning of the Third Dynasty.Dodson, Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', 2004 Both the Turin King List and the Abydos King List record five kings,Toby A.H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge, 2001 while the Saqqara Tablet only records four, and Manetho records nine,Aidan Dodson: ''The Layer Pyramid of Zawiyet el-Aryan: Its Layout and Context.'' In: ''Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt (JARCE)'', No. 37 (2000). American Research Center (Hg.), Eisenbrauns, Winona Lake/Bristol 2000, , pp. 81–90. many of whom did not exist or are simply the same king unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metropolitan area, with a population of 21.9 million, is the 12th-largest in the world by population. Cairo is associated with ancient Egypt, as the Giza pyramid complex and the ancient cities of Memphis and Heliopolis are located in its geographical area. Located near the Nile Delta, the city first developed as Fustat, a settlement founded after the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 640 next to an existing ancient Roman fortress, Babylon. Under the Fatimid dynasty a new city, ''al-Qāhirah'', was founded nearby in 969. It later superseded Fustat as the main urban centre during the Ayyubid and Mamluk periods (12th–16th centuries). Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life, and is titled "the city of a thousand m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |