|
Sanriku
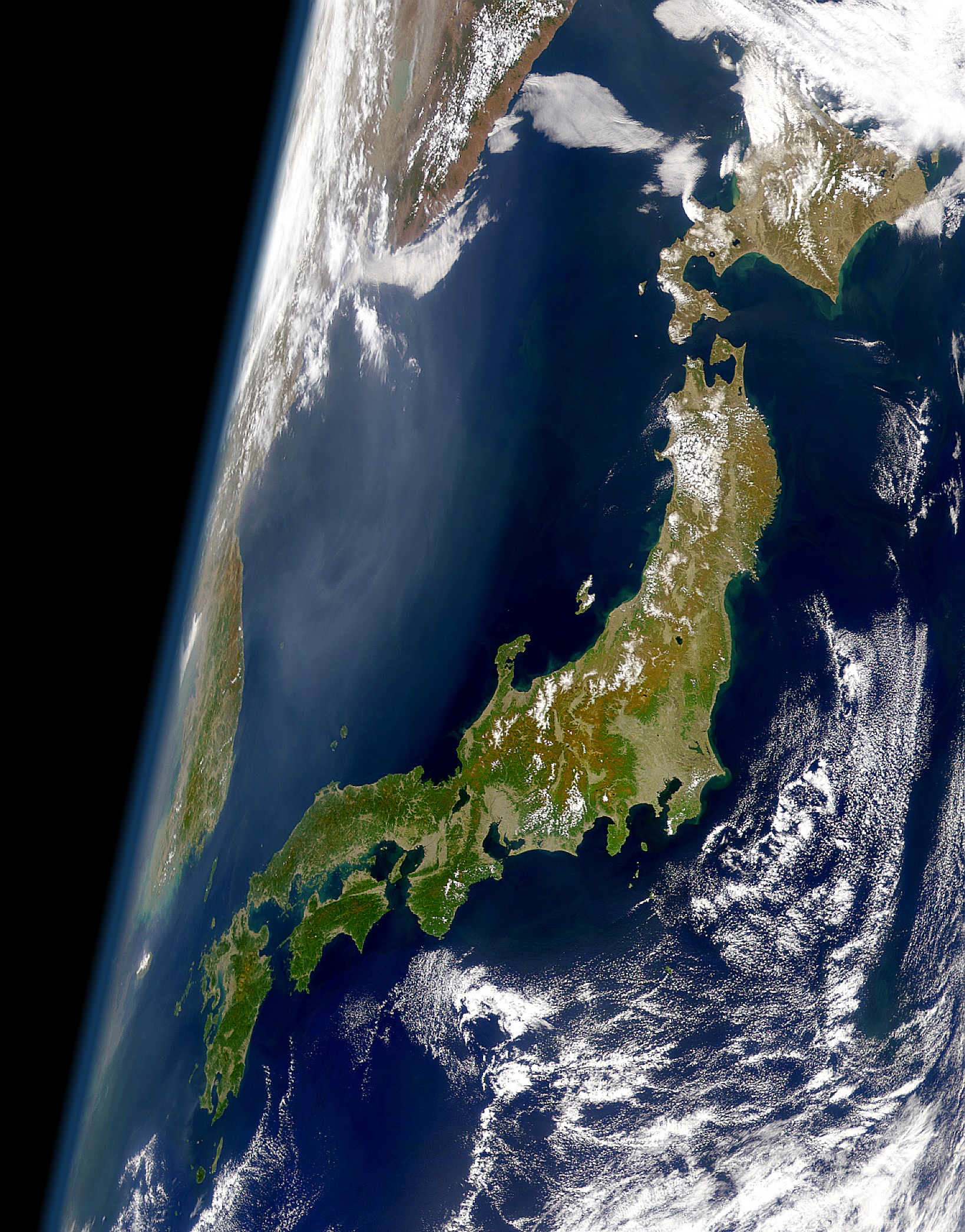
, sometimes known as , lies on the northeastern side of the island of Honshu, corresponding to today's Aomori, Iwate and parts of Miyagi Prefecture and has a long history. The 36 bays of this irregular coastline tend to amplify the destructiveness of tsunami waves which reach the shores of Sanriku, as demonstrated in the damage caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. Regions of Japan History On January 19, 1869, in the aftermath of the Boshin War, the provinces of Mutsu and Dewa were divided. Mutsu was split into new five provinces: Rikuō (also read ''Mutsu''), Rikuchū, Rikuzen, Iwashiro and Iwaki. The first three of these collectively known as the "Three Riku", or ''Sanriku'', with san (三) meaning "three." The new provinces became quickly obsolete in July 1871 when the abolition of the han system divided Japan into its present prefectures that became the sole divisions used by the government. However, the label lives on in common usages such as the Sanrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismicity Of The Sanriku Coast
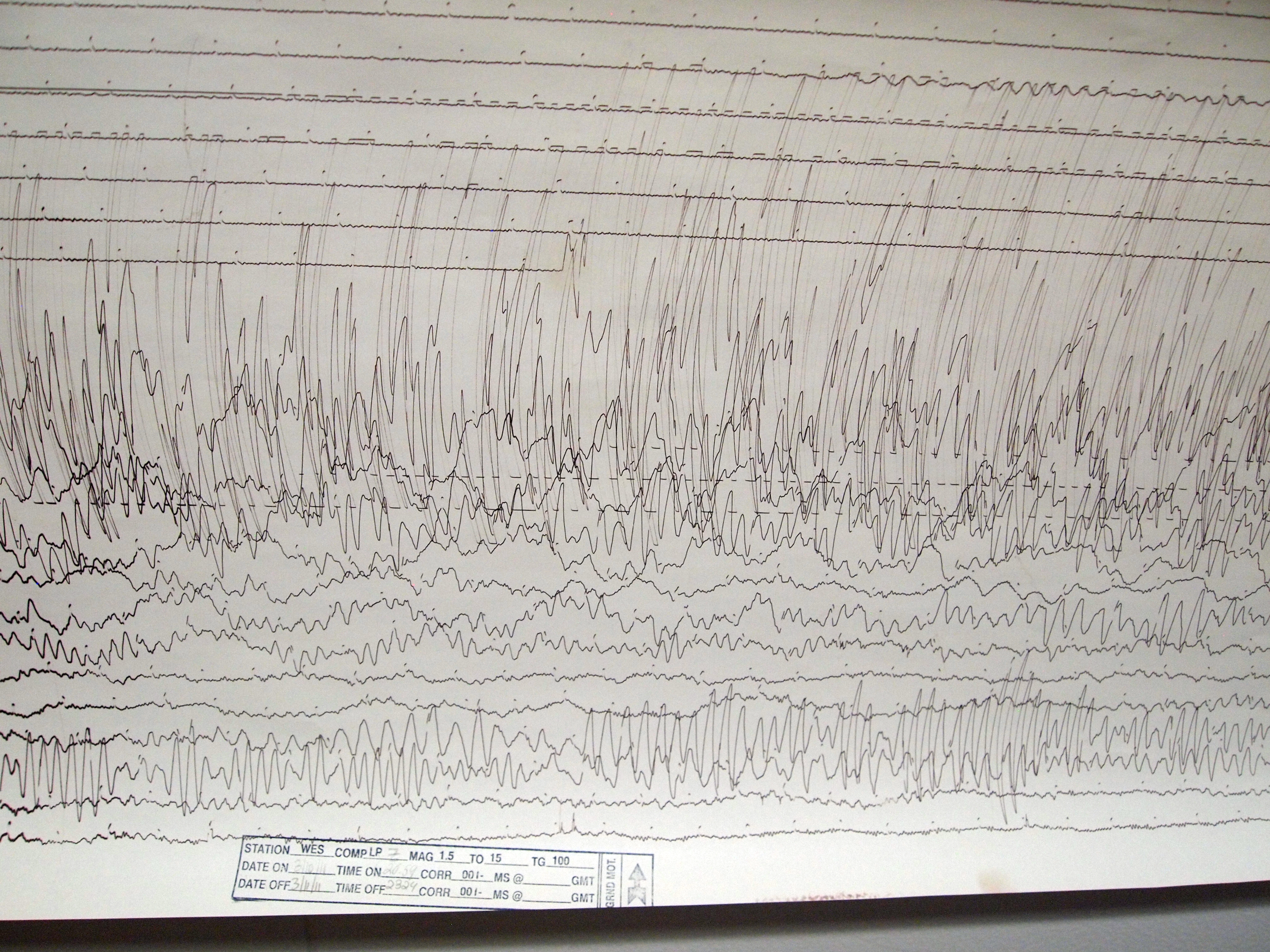
The seismicity of the Sanriku coast identifies and describes the seismic activity of an area of Japan. Seismicity refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time. The is a descriptive term referring to the coastal areas of the former provinces of Rikuō in Aomori, Rikuchū in Aomori, and Rikuzen in Miyagi. The irregular ria coastline and its many bays tend to amplify the destructiveness of tsunami waves which reach the shores of Sanriku, as demonstrated in the damage caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. History The Sanriku coast has a well-documented history of significant seismic activity. A major earthquake in the 19th century caused more than 20,000 deaths, and another in the 20th century caused thousands more. The recurrence of major seismic activity continues in the 21st century. Ancient There is geological evidence, uncovered after the latest tsunami event of 2011, of six catastrophic tsunamis hitting the Sanriku co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanriku Coast
The is a coastal region on the Pacific Ocean, extending from southern Aomori Prefecture, through Iwate Prefecture and northern Miyagi Prefecture in northeastern Honshū, which is Japan's main island. The name comes from the historical region of Sanriku (lit. "three ''riku''"), referring to the former provinces of Rikuō, Rikuchū and Rikuzen. Tourist destination There are the Tanesashi Coast, the Rikuchu Kaigan National Park and the Minami-Sanriku Kinkazan Quasi-National Park in the Sanriku Coast region. Earthquakes and tsunami The bays of this ria coastline tend to amplify the destructiveness of tsunami waves. Significant events which devastated coastal communities include: * 869 Jogan Sanriku earthquake * 1611 Keicho Sanriku earthquake * 1896 Meiji Sanriku earthquake * 1933 Showa Sanriku earthquake * 1960 Valdivia earthquake * 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami Prior to 2011, the tsunami history of Sanriku might have been interpreted as a story of progressively fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanriku Railway
The is a railway company in Iwate Prefecture in northern Japan. The company and its lines are also known as . The company was founded in 1981, as the first " third sector" (half public, half private) railway line in the country, excluding special cases such as freight railways in seaports. Its lines are former Japanese National Railways (JNR) lines, that were going to be closed. Santetsu acquired these lines in 1984. The company also operates a travel agency and other businesses. Lines * Rias Line ( リアス線) (163.0 km, - ) Rias Line Station list History Kita-Rias Line The Japanese National Railways (JNR) opened the Miyako to Taro section in 1972 and the Kuji to Fudai section in 1975. It constructed the Taro to Fudai section, and transferred the entire line to Sanriku on the day it opened in 1984. The line features 42 tunnels, including the Masaki (6,532 m) and Omoto (5,174 m) tunnels, both opened in 1984. Minami-Rias Line JNR opened the Sakari to Ryori sectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanriku Expressway
The is an incomplete expressway that exists in multiple segments in Miyagi Prefecture and Iwate Prefecture, Japan. The expressway connects Sendai, the capital and largest city in Miyagi Prefecture, to Miyako in Iwate Prefecture. It follows the coast of the Pacific Ocean in the northern parts of the Tōhoku region, otherwise known as the Sanriku Coast. It is owned and operated by East Nippon Expressway Company (NEXCO East Japan), the Miyagi Prefecture Road Corporation, and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT). The route is signed as an auxiliary route of National Route 45 as well as E6 and E45 under MLIT's "2016 Proposal for Realization of Expressway Numbering." It is one of three routes numbered E45, the other two are the Sanriku-kita Jūkan Road and the Hachinohe-Kuji Expressway, and one of many routes numbered E6, although the Sanriku Expressway only carries the number close to its southern terminus in Sendai. When completed, all of these routes wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanriku Tsunami (other)
, sometimes known as , lies on the northeastern side of the island of Honshu, corresponding to today's Aomori, Iwate and parts of Miyagi Prefecture and has a long history. The 36 bays of this irregular coastline tend to amplify the destructiveness of tsunami waves which reach the shores of Sanriku, as demonstrated in the damage caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. Regions of Japan History On January 19, 1869, in the aftermath of the Boshin War, the provinces of Mutsu and Dewa were divided. Mutsu was split into new five provinces: Rikuō (also read ''Mutsu''), Rikuchū, Rikuzen, Iwashiro and Iwaki. The first three of these collectively known as the "Three Riku", or ''Sanriku'', with san (三) meaning "three." The new provinces became quickly obsolete in July 1871 when the abolition of the han system divided Japan into its present prefectures that became the sole divisions used by the government. However, the label lives on in common usages such as the Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Tōhoku Earthquake And Tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the , among other names. The disaster is often referred to in both Japanese and English as simply 3.11 (read in Japanese). It was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan, and the fourth most powerful earthquake in the world since modern record-keeping began in 1900. The earthquake triggered powerful tsunami waves that may have reached heights of up to in Miyako in Tōhoku's Iwate Prefecture,Yomiuri Shimbun evening edition 2-11-04-15 page 15, nearby Aneyoshi fishery port (姉吉漁港)(Google map E39 31 57.8, N 142 3 7.6) 2011-04-15大震災の津波、宮古で38.9 m…明治三陸上回るby okayasu Akio (岡安 章夫) and which, in the Sendai area, traveled at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwate Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. It is the second-largest Japanese prefecture at , with a population of 1,210,534 (as of October 1, 2020). Iwate Prefecture borders Aomori Prefecture to the north, Akita Prefecture to the west, and Miyagi Prefecture to the south. Morioka is the capital and largest city of Iwate Prefecture; other major cities include Ichinoseki, Ōshū, and Hanamaki. Located on Japan's Pacific Ocean coast, Iwate Prefecture features the easternmost point of Honshu at Cape Todo, and shares the highest peaks of the Ōu Mountains—the longest mountain range in Japan—at the border with Akita Prefecture. Iwate Prefecture is home to famous attractions such as Morioka Castle, the Buddhist temples of Hiraizumi including Chūson-ji and Mōtsū-ji, the Fujiwara no Sato movie lot and theme park in Ōshū, and the Tenshochi park in Kitakami known for its huge, ancient cherry trees. Iwate has the lowest population density of any prefecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanriku Earthquake (other)
{{Disambiguation ...
Sanriku earthquake () may refer to: * 869 Sanriku earthquake * 1611 Sanriku earthquake * 1896 Sanriku earthquake * 1933 Sanriku earthquake * 1994 offshore Sanriku earthquake * 2012 Sanriku earthquake See also * Seismicity of the Sanriku coast * Sanriku tsunami (other) , sometimes known as , lies on the northeastern side of the island of Honshu, corresponding to today's Aomori, Iwate and parts of Miyagi Prefecture and has a long history. The 36 bays of this irregular coastline tend to amplify the destructiven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aomori Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan in the Tōhoku region. The prefecture's capital, largest city, and namesake is the city of Aomori. Aomori is the northernmost prefecture on Japan's main island, Honshu, and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the east, Iwate Prefecture to the southeast, Akita Prefecture to the southwest, the Sea of Japan to the west, and Hokkaido across the Tsugaru Strait to the north. Aomori Prefecture is the 8th-largest prefecture, with an area of , and the 31st-most populous prefecture, with more than 1.2 million people. Approximately 45 percent of Aomori Prefecture's residents live in its two core cities, Aomori and Hachinohe, which lie on coastal plains. The majority of the prefecture is covered in forested mountain ranges, with population centers occupying valleys and plains. Aomori is the third-most populous prefecture in the Tōhoku region, after Miyagi Prefecture and Fukushima Prefecture. Mount Iwaki, an active stratovolcano, is the prefecture's highest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miyagi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Miyagi Prefecture has a population of 2,305,596 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of . Miyagi Prefecture borders Iwate Prefecture to the north, Akita Prefecture to the northwest, Yamagata Prefecture to the west, and Fukushima Prefecture to the south. Sendai is the capital and largest city of Miyagi Prefecture, and the largest city in the Tōhoku region, with other major cities including Ishinomaki, Ōsaki, and Tome. Miyagi Prefecture is located on Japan's eastern Pacific coast and bounded to the west by the Ōu Mountains, the longest mountain range in Japan, with 24% of its total land area being designated as Natural Parks. Miyagi Prefecture is home to Matsushima Islands, a group of islands ranked as one of the Three Views of Japan, near the town of Matsushima. On 7 April, 2011 the biggest earthquake in Japan occurred. History Miyagi Prefecture was formerly part of the province of Mutsu. 2011 T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separates the Sea of Japan, which lies to its north and west, from the North Pacific Ocean to the south and east. It is the seventh-largest island in the world, and the second-most populous after the Indonesian island of Java. Honshu had a population of 104 million , constituting 81.3% of the entire population of Japan, and is mostly concentrated in the coastal areas and plains. Approximately 30% of the total population resides in the Greater Tokyo Area on the Kantō Plain. As the historical center of Japanese cultural and political power, the island includes several past Japanese capitals, including Kyōto, Nara and Kamakura. Much of the island's southern shore forms part of the Taiheiyō Belt, a megalopolis that spans several of the Japane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)