|
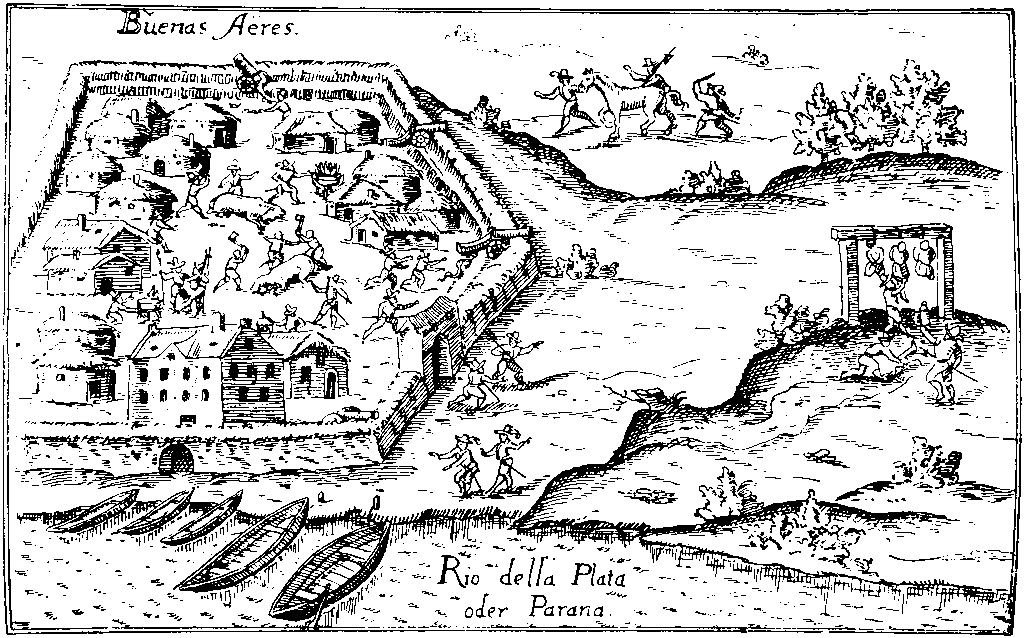
Sancti Spiritu (Argentina)
Sancti Spiritu was a fortification established in 1527 near the Paraná River by the explorer Sebastian Cabot. It was the first European settlement in the territory of modern Argentina and was destroyed by Amerindians (Native Argentines) two years later. Antecedents The voyage of Juan Díaz de Solís explored the Río de la Plata, along the coast of Uruguay. In 1516, Solís disembarked on the Uruguay coast shortly after entering the Uruguay River, along with six other men. The local Charrúas saw them and killed them in a swift surprise attack. A boy, Francisco del Puerto, was spared because of his young age. The remaining sailors left and returned to Europe. Del Puerto, who was left behind, lived for ten years among the indigenous people. He was rescued by a subsequent European voyage led by Sebastian Cabot. Del Puerto told Cabot rumors of a "white king" and a mountain of silver that was located north of the Paraná River. Cabot considered the tale to be true, and dropped h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraná River
The Paraná River ( es, Río Paraná, links=no , pt, Rio Paraná, gn, Ysyry Parana) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. 26 May. 2012 . "Rio de la Plata". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. 26 May. 2012 Among South American rivers, it is second in length only to the Amazon River. It merges with the Paraguay River and then farther downstream with the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata and empties into the Atlantic Ocean. The first European to go up the Paraná River was the Venetian explorer Sebastian Cabot, in 1526, while working for Spain. A drought hit the river in 2021, causing a 77-year low. Etymology In eastern South America there is "an immense number of river names containing the element ''para-'' or ''parana-''", f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraguay River
The Paraguay River (Río Paraguay in Spanish, Rio Paraguai in Portuguese, Ysyry Paraguái in Guarani) is a major river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay and Argentina. It flows about from its headwaters in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso to its confluence with the Paraná River north of Corrientes and Resistencia. Course The Paraguay's source is south of Diamantino in the Mato Grosso state of Brazil. It follows a generally southwesterly course, passing through the Brazilian city of Cáceres. It then turns in a generally southward direction, flowing through the Pantanal wetlands, the city of Corumbá, then running close to the Brazil-Bolivia border for a short distance in the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul. From the city of Puerto Bahia Negra, Paraguay, the river forms the border between Paraguay and Brazil, flowing almost due south before the confluence with the Apa River. The Paraguay makes a long, gentle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Santa Fe Province
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortifications In Argentina
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Argentina
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Argentina
Colonial Argentina is designated as the period of the History of Argentina when it was an overseas territory of the Spanish Empire. It begins in the Precolumbian age of the indigenous peoples of Argentina, with the arrival of the first Spanish conqueror. European exploration When Spain and Portugal realized that the Americas were not the Indies but a new and unknown continent, they settled the portions with the Treaty of Tordesillas, dividing an eastern section of South America for Portugal and the rest for Spain. However, most of the geography of the Americas was still unknown, and many navigators sought a passage to the East Indies rather than exploring the Americas. The voyage of Ferdinand Magellan continued towards the south, passed the Strait of Magellan and eventually completed the first circumnavigation of the world. The first navigators of the Americas through unexplored territories, navigated into the wide Río de la Plata expecting to find a passage to the west and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Love Triangle
A love triangle or eternal triangle is a scenario or circumstance, usually depicted as a rivalry, in which two people are pursuing or involved in a romantic relationship with one person, or in which one person in a romantic relationship with someone is simultaneously pursuing or involved in a romantic relationship with someone else. A love triangle typically is not conceived of as a situation in which one person loves a second person, who loves a third person, who loves the first person, or variations thereof. Love triangles are a common narrative device in theater, literature, and film. Statistics suggest that, in Western society, "Willingly or not, most adults have been involved in a love triangle." The 1994 book ''Beliefs, Reasoning, and Decision Making'' states, "Although the romantic love triangle is formally identical to the friendship triad, as many have noted their actual implications are quite different ... Romantic love is typically viewed as an exclusive relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South America's southeastern coast. "Buenos Aires" can be translated as "fair winds" or "good airs", but the former was the meaning intended by the founders in the 16th century, by the use of the original name "Real de Nuestra Señora Santa María del Buen Ayre", named after the Madonna of Bonaria in Sardinia, Italy. Buenos Aires is classified as an alpha global city, according to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) 2020 ranking. The city of Buenos Aires is neither part of Buenos Aires Province nor the Province's capital; rather, it is an autonomous district. In 1880, after decades of political infighting, Buenos Aires was federalized and removed from Buenos Aires Province. The city limits were enlarged to include t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro De Mendoza
Pedro de Mendoza () (c. 1499 – June 23, 1537) was a Spanish ''conquistador'', soldier and explorer, and the first ''adelantado'' of New Andalusia. Setting sail Pedro de Mendoza was born in Guadix, Grenada, part of a large noble family that was preeminent in Spain. His family settled in Guadix after its reconquest by the Christians in 1489. He was a page at the Spanish court of Emperor Charles V and accompanied the sovereign on his trip to England. In 1524 he received the title of knight of the Order of Alcántara and later, through the influence of his father — the knight Fernando de Mendoza Guadix — entered the Order of Santiago. He later fought in the Italian Wars against the French, in which he participated in the Sack of Rome in 1527. In 1529, he offered to explore South America at his own expense and establish colonies. Thanks to the efforts of his mother María de Mendoza, in 1534 his offer was accepted: he was made ''adelantado'' governor, captain general, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punitive Expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong behavior by miscreants, as revenge or corrective action, or to apply strong diplomatic pressure without a formal declaration of war (e.g. surgical strike). In the 19th century, punitive expeditions were used more commonly as pretexts for colonial adventures that resulted in annexations, regime changes or changes in policies of the affected state to favour one or more colonial powers. Stowell (1921) provides the following definition: When the territorial sovereign is too weak or is unwilling to enforce respect for international law, a state which is wronged may find it necessary to invade the territory and to chastise the individuals who violate its rights and threaten its security. Historical examples *In the 5th century BC, the Achaemenid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacique
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a Spanish transliteration of the Taíno word ''kasike''. Cacique was initially translated as "king" or "prince" for the Spanish. In the colonial era the conquistadors and the administrators who followed them used the word generically, to refer to any leader of practically any indigenous group they encountered in the Western Hemisphere. In Hispanic and Lusophone countries, the term also has come to mean a political boss, similar to ''caudillo,'' exercising power in a system of ''caciquismo''. Spanish colonial-era caciques The Taíno word ''kasike'' descends from the Taíno word ''kassiquan'', which means "to keep house". In 1555 the word first entered the English language, defined as "prince". In Taíno culture, the ''kasike'' rank was her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples In Paraguay
Indigenous peoples in Paraguay, or Native Paraguayans, include 17 ethnic groups belonging to five language families."Paraguay." ''Pan-American Health Organization.'' (retrieved 12 July 2011) ''Countries and Their Cultures.'' (retrieved 12 July 2011) While only a 1.7% of 's population is fully indigenous, 75% of the population identifies as being partially of indigenous descent;"Paraguay: Ethnic Groups." ''CIA: The World Factbook.'' (retri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)