|
SORT1
Sortilin (SORT1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SORT1'' gene on chromosome 1. This protein is a type I membrane glycoprotein in the vacuolar protein sorting 10 protein (Vps10p) family of sorting receptors. While it is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues, sortilin is most abundant in the central nervous system. At the cellular level, sortilin functions in protein transport between the Golgi apparatus, endosome, lysosome, and plasma membrane, leading to its involvement in multiple biological processes such as glucose and lipid metabolism as well as neural development and cell death. Moreover, the function and role of sortilin is now emerging in several major human diseases such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. The ''SORT1'' gene also contains one of 27 loci associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease. Structure Gene The ''SORT1'' gene resides on chromosome 1 at the band 1p13.3 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
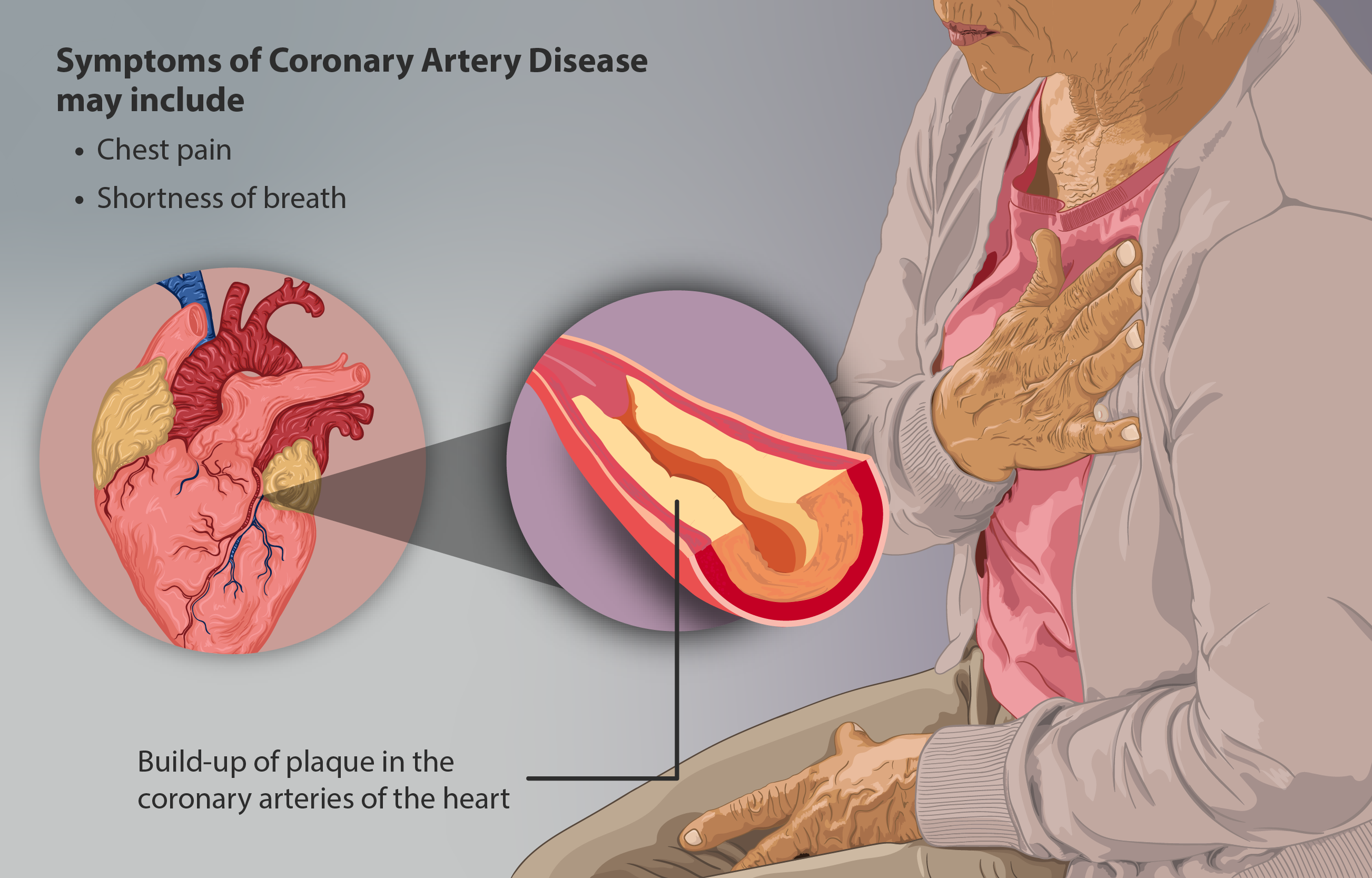
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood choles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Precursor
A protein precursor, also called a pro-protein or pro-peptide, is an inactive protein (or peptide) that can be turned into an active form by post-translational modification, such as breaking off a piece of the molecule or adding on another molecule. The name of the precursor for a protein is often prefixed by ''pro-''. Examples include proinsulin and proopiomelanocortin, which are both prohormones. Protein precursors are often used by an organism when the subsequent protein is potentially harmful, but needs to be available on short notice and/or in large quantities. Enzyme precursors are called zymogens or proenzymes. Examples are enzymes of the digestive tract in humans. Some protein precursors are secreted from the cell. Many of these are synthesized with an N-terminal signal peptide that targets them for secretion. Like other proteins that contain a signal peptide, their name is prefixed by ''pre''. They are thus called pre-pro-proteins or pre-pro-peptides. The signal peptide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences. Protein synthesis can be divided broadly into two phases - transcription and translation. During transcription, a section of DNA encoding a protein, known as a gene, is converted into a template molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out by enzymes, known as RNA polymerases, in the nucleus of the cell. In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form ( pre-mRNA) which undergoes post-transcriptional modifications to produce mature mRNA. The mature mRNA is exported from the cell nucleus via nuclear pores to the cytoplasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding Site
In biochemistry and molecular biology, a binding site is a region on a macromolecule such as a protein that binds to another molecule with specificity. The binding partner of the macromolecule is often referred to as a ligand. Ligands may include other proteins (resulting in a protein-protein interaction), enzyme substrates, second messengers, hormones, or allosteric modulators. The binding event is often, but not always, accompanied by a conformational change that alters the protein's function. Binding to protein binding sites is most often reversible (transient and non-covalent), but can also be covalent reversible or irreversible. Function Binding of a ligand to a binding site on protein often triggers a change in conformation in the protein and results in altered cellular function. Hence binding site on protein are critical parts of signal transduction pathways. Types of ligands include neurotransmitters, toxins, neuropeptides, and steroid hormones. Binding sites incur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectodomain
An ectodomain is the domain of a membrane protein that extends into the extracellular space (the space outside a cell). Ectodomains are usually the parts of proteins that initiate contact with surfaces, which leads to signal transduction.A notable example of an ectodomain is the S protein, commonly known as the spike protein, of the viral particle responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi .... The ectodomain region of the spike protein (S) is essential for attachment and eventual entry of the viral protein into the host cell. Ectodomains play a crucial part in the signaling pathways of viruses. Recent findings have indicated that certain antibodies including the anti-receptor binding domain (anti-RBD) or anti-spike ectodomain (anti-ECD) I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotensin
Neurotensin is a 13 amino acid neuropeptide that is implicated in the regulation of luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and has significant interaction with the dopaminergic system. Neurotensin was first isolated from extracts of bovine hypothalamus based on its ability to cause a visible vasodilation in the exposed cutaneous regions of anesthetized rats. Neurotensin is distributed throughout the central nervous system, with highest levels in the hypothalamus, amygdala and nucleus accumbens. It induces a variety of effects, including analgesia, hypothermia and increased locomotor activity. It is also involved in regulation of dopamine pathways. In the periphery, neurotensin is found in enteroendocrine cells of the small intestine, where it leads to secretion and smooth muscle contraction. Sequence and biosynthesis Neurotensin shares significant sequence similarity in its 6 C-terminal amino acids with several other neuropeptides, including neuromedin N (which is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, and in the case of liquid crystals, time of fluid evaporation. Crystallization occurs in two major steps. The first is nucleation, the appearance of a crystalline phase from either a supercooled liquid or a supersaturated solvent. The second step is known as crystal growth, which is the increase in the size of particles and leads to a crystal state. An important feature of this step is that loose particles form layers at the crystal's surface and lodge themselves into open inconsistencies such as pores, cracks, etc. The majority of minerals and organic molecules crystallize easily, and the resulting crystals are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
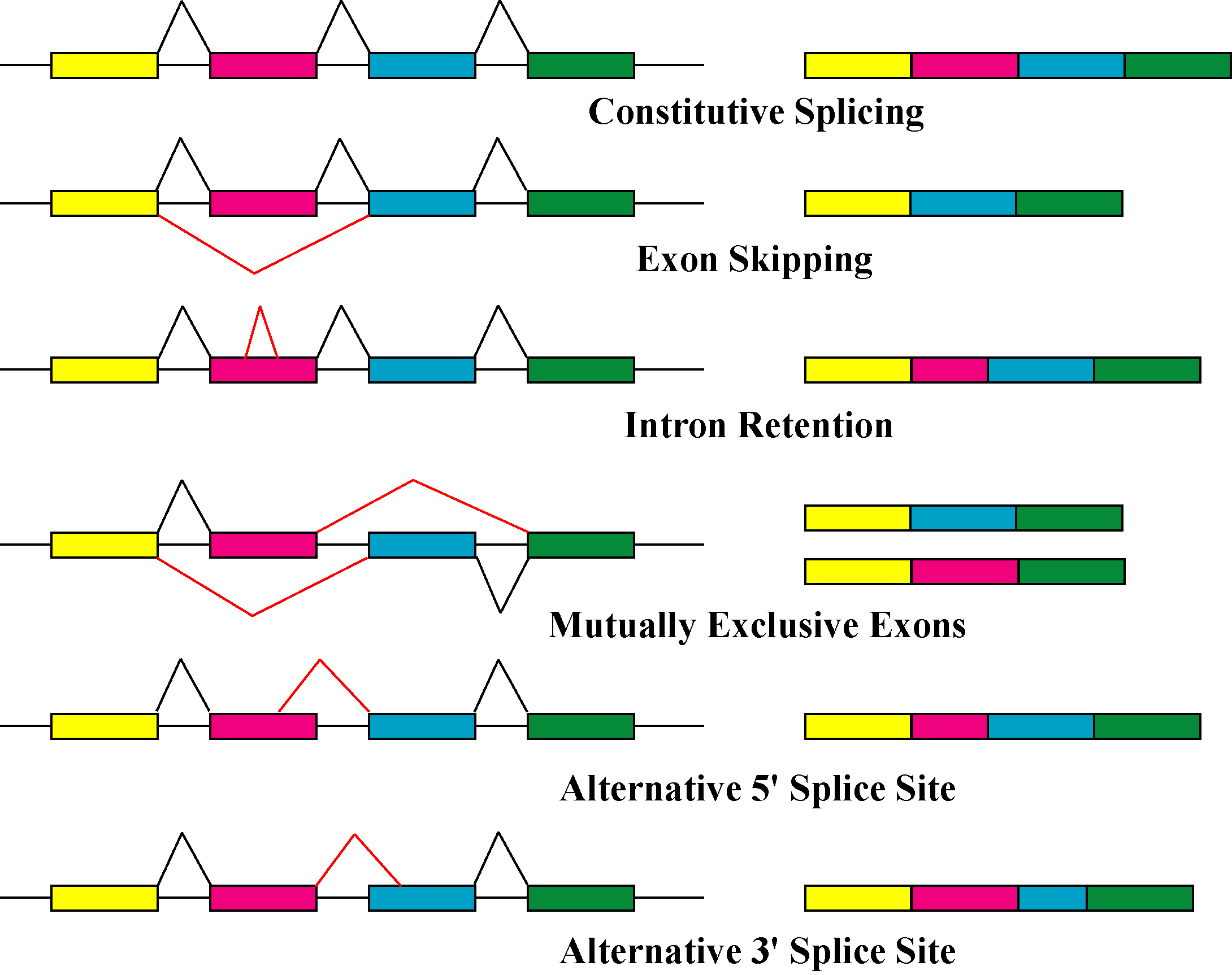
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome. History The term ''exon'' derives from the expressed region and was coined by American biochemist Walter Gilbert in 1978: "The notion of the cistron… must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messengerwhich I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions)alternating with regions which will be expressedexons." This definition was originally made for protein-coding transcripts that are spliced before being translate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



4-3D-balls.png)