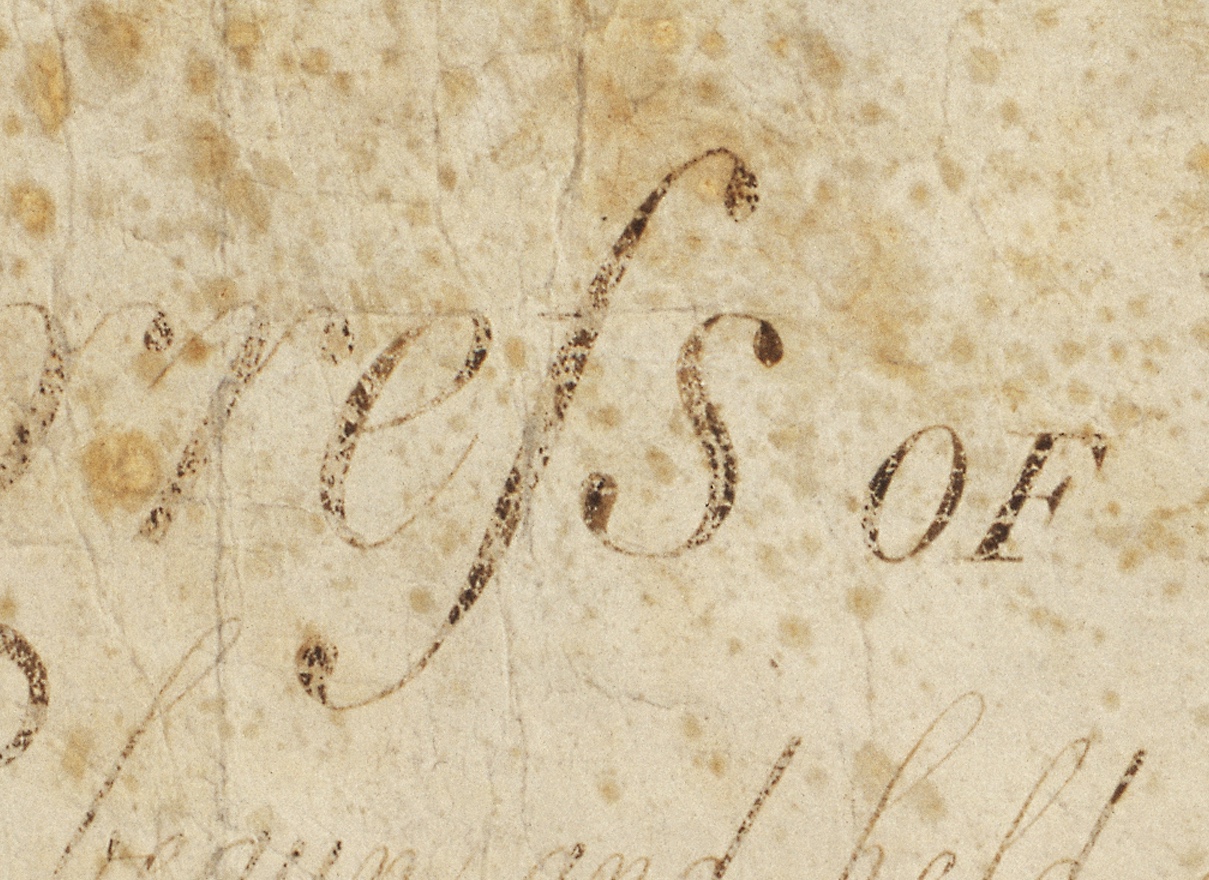|
S̩
S̩ (minuscule: s̩) is a letter of the Latin alphabet, formed from S with the addition of a vertical line below it. It is used in Yoruba when written in Nigeria to represent the sound (like English "sh"). The line is sometimes replaced by a dot, i.e. Ṣ ṣ. is also the International Phonetic Alphabet symbol for a syllabic "s" sound. Computer encoding Unicode does not include precomposed characters for S̩ s̩ — they should be represented with a combining character, which may not align properly or may display as squares in some fonts In movable type, metal typesetting, a font is a particular #Characteristics, size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design. For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) inclu .... Nevertheless, the sequence of base character + combining diacritic is given a unique name. In Unicode: * S̩: + * s̩: + References {{DEFAULTSORT:S Latin letters with diacrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Case
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing systems that distinguish between the upper- and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters: each in the majuscule set has a counterpart in the minuscule set. Some counterpart letters have the same shape, and differ only in size (e.g. ), but for others the shapes are different (e.g., ). The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are typically treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order. Letter case is generally applied in a mixed-case fashion, with both upper and lowercase letters appearing in a given piece of text for legibility. The choice of case is often denoted by the grammar of a language or by the conventions of a particular discipline. In ortho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combining Character
In digital typography, combining characters are Character (computing), characters that are intended to modify other characters. The most common combining characters in the Latin script are the combining diacritic, diacritical marks (including combining accents). Unicode also contains many precomposed characters, so that in many cases it is possible to use both combining diacritics and precomposed characters, at the user's or application's choice. This leads to a requirement to perform Unicode normalization before comparing two Unicode strings and to carefully design encoding converters to correctly map all of the valid ways to represent a character in Unicode to a legacy encoding to avoid data loss. In Unicode, the main block of combining diacritics for European languages and the International Phonetic Alphabet is U+0300–U+036F. Combining diacritical marks are also present in many other blocks of Unicode characters. In Unicode, diacritics are always added after the main char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precomposed Character
A precomposed character (alternatively composite character or decomposable character) is a Unicode entity that can also be defined as a sequence of one or more other characters. A precomposed character may typically represent a letter with a diacritical mark, such as ''é'' (Latin small letter ''e'' with acute accent). Technically, ''é'' (U+00E9) is a character that can be decomposed into an equivalent string of the base letter ''e'' (U+0065) and combining acute accent (U+0301). Similarly, ligatures are precompositions of their constituent letters or graphemes. Precomposed characters are the legacy solution for representing many special letters in various character sets. In Unicode, they are included primarily to aid computer systems with incomplete Unicode support, where equivalent decomposed characters may render incorrectly. Comparing precomposed and decomposed characters In the following example, there is a common Swedish surname Åström written in the two alterna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Character (computing), characters and 168 script (Unicode), scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Unicode has largely supplanted the previous environment of a myriad of incompatible character sets used within different locales and on different computer architectures. The entire repertoire of these sets, plus many additional characters, were merged into the single Unicode set. Unicode is used to encode the vast majority of text on the Internet, including most web pages, and relevant Unicode support has become a common consideration in contemporary software development. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllabic Consonant
A syllabic consonant or vocalic consonant is a consonant that forms the nucleus of a syllable on its own, like the ''m'', ''n'' and ''l'' in some pronunciations of the English words ''rhythm'', ''button'' and ''awful'', respectively. To represent it, the understroke diacritic in the International Phonetic Alphabet is used, . It may be instead represented by an overstroke, if the symbol that it modifies has a descender, such as in . Syllabic consonants in most languages are sonorants, such as nasals and liquids. Very few have syllabic obstruents (i.e., stops, fricatives, and affricates) in normal words, but English has syllabic fricatives in paralinguistic words like ''shh!'' and ''zzz''. Examples Germanic languages In many varieties of High and Low German, pronouncing syllabic consonants may be considered a shibboleth. In High German and Tweants (a Low Saxon dialect spoken in the Netherlands; more Low Saxon dialects have the syllabic consonant), all word-final syllab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dot (diacritic)
When used as a diacritic mark, the term dot refers to the glyphs "combining dot above" (, and "combining dot below" ( which may be combined with some letters of the extended Latin alphabets in use in a variety of languages. Similar marks are used with other scripts. Overdot Language scripts or transcription schemes that use the dot above a letter as a diacritical mark: * In some forms of Arabic romanization, stands for '' ghayn'' (غ). * The Latin orthography for Chechen includes ''ċ'', ''ç̇'', ''ġ'', ''q̇'' and ''ẋ'', corresponding to Cyrillic ''цӏ'', ''чӏ'', ''гӏ'', ''къ'' and ''хь'' and representing , , , and respectively. * Traditional Irish typography, where the dot denotes lenition, and is called a or "dot of lenition": ''ḃ ċ ḋ ḟ ġ ṁ ṗ ṡ ṫ''. Alternatively, lenition may be represented by a following letter ''h'', thus: ''bh ch dh fh gh mh ph sh th''. In Old Irish orthography, the dot was used only for ''ḟ ṡ'', while the fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered except several letters splitting—i.e. from , and from —additions such as , and extensions such as letters with diacritics, it forms the Latin script that is used to write most languages of modern Languages of Europe, Europe, languages of Africa, Africa, languages of the Americas, the Americas, and Languages of Oceania, Oceania. Its basic modern inventory is standardized as the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Etymology The term ''Latin alphabet'' may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s'' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess", but never "poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the "short", "terminal", or "round" ''s''. In typography, the long ''s'' is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash ''s''". The long ''s'' is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , ( or , 'sharp ''s'''). As with other letters, the long ''s'' may have a variant appearance depending on typeface: , , , . Rules English This list of rules for the long ''s'' is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th to early 19th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Language
Yoruba (, ; Yor. ) is a Niger–Congo languages, Niger-Congo language that is spoken in West Africa, primarily in South West (Nigeria), Southwestern and Middle Belt, Central Nigeria, Benin, and parts of Togo. It is spoken by the Yoruba people. Yoruba speakers number roughly 50 million, including around 2 million second-language or L2 speakers. As a pluricentric language, it is primarily spoken in a dialectal area spanning Nigeria, Benin, and Togo with smaller migrated communities in Côte d'Ivoire, Sierra Leone and The Gambia. Yoruba vocabulary is also used in African diaspora religions such as the Afro-Brazilian religion of Candomblé, the Caribbean religion of Santería in the form of the liturgical Lucumí language, and various Afro-American religions of North America. Most modern practitioners of these religions in the Americas are not fluent in the Yoruba language, yet they still use Yoruba words and phrases for songs or chants—rooted in cultural traditions. For such pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
𐌔
The Old Italic scripts are a family of ancient writing systems used in the Italian Peninsula between about 700 and 100 BC, for various languages spoken in that time and place. The most notable member is the Etruscan alphabet, which was the immediate ancestor of the Latin alphabet used by more than 100 languages today, including English. The runic alphabets used in Northern Europe are believed to have been separately derived from one of these alphabets by the 2nd century AD. Origins The Old Italic alphabets ultimately derive from the Phoenician alphabet, but the general consensus is that the Etruscan alphabet was imported from the Euboean Greek colonies of Cumae and Ischia (Pithekoūsai) situated in the Gulf of Naples in the 8th century BC; this Euboean alphabet is also called 'Cumaean' (after Cumae), or 'Chalcidian' (after its metropolis Chalcis). The Cumaean hypothesis is supported by the 1957–58 excavations of Veii by the British School at Rome, which found pieces of Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma
Sigma ( ; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; ) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used as an operator (mathematics), operator for summation. When used at the end of a Letter case, letter-case word (one that does not use all caps), the final form (ς) is used. In ' (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end. The Latin alphabet, Latin letter S derives from sigma while the Cyrillic script, Cyrillic letter Es (Cyrillic), Es derives from a #Lunate sigma, lunate form of this letter. History The shape (Σς) and alphabetic position of sigma is derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter (Shin (letter), ''shin''). Sigma's original name may have been ''san'', but due to the complicated early history of the Greek Archaic Greek alphabets, epich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |