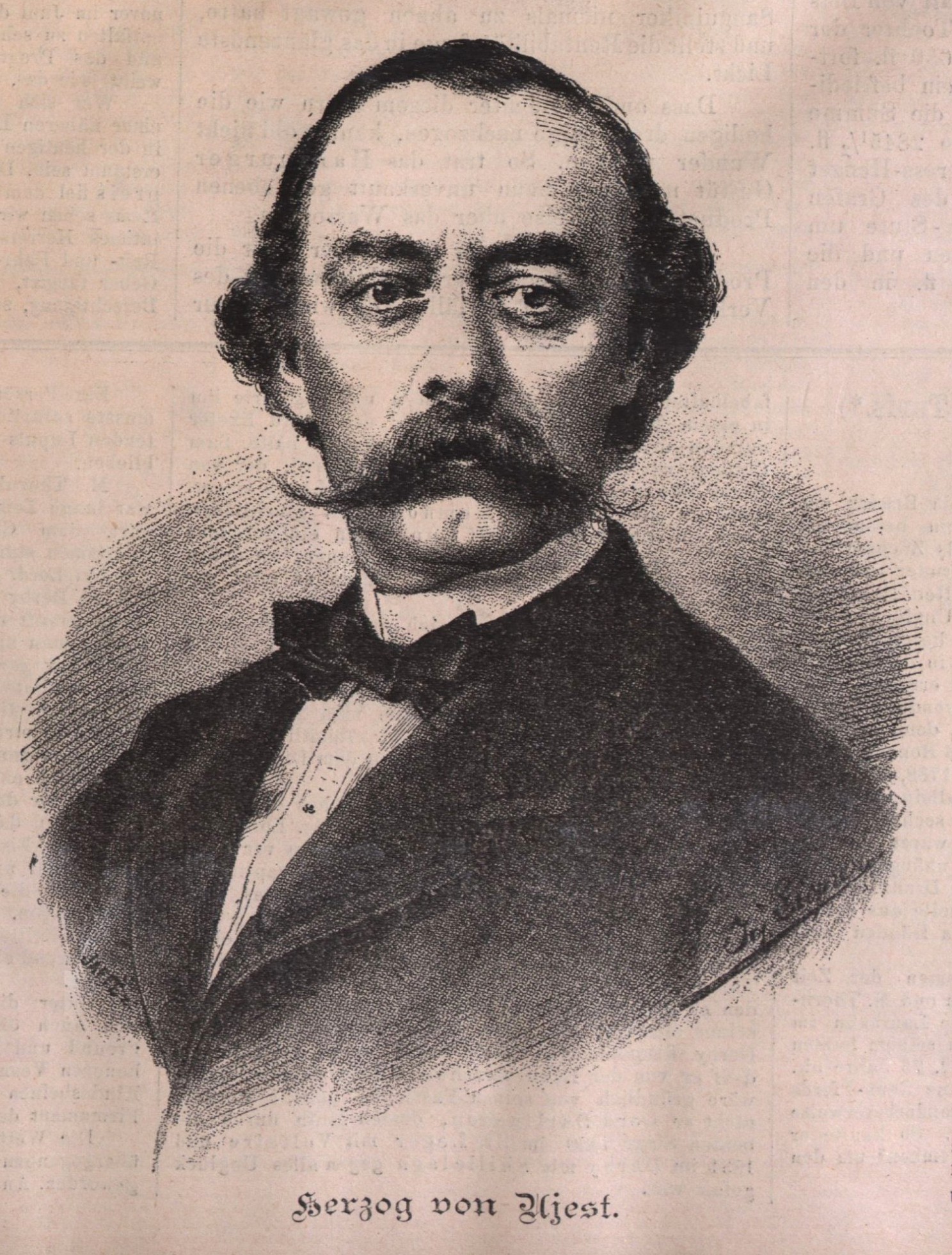|
Sławięcice Palace (Schloss Slawentzitz)
Sławięcice Palace (, ) is fragmentarily preserved palace in Sławięcice (part of Kędzierzyn-Koźle), in the historic Upper Silesia region in Poland. It served as the main residence of the princes of Hohenlohe-Öhringen, a branche of the House of Hohenlohe. It was heavily damaged in the Second World War and has subsequently been demolished. Only a portico remains. History Flemming and Hoym families In the 15th century, the first castle was built in Sławięcice, owned by the dukes of Duchy of Opole, Opole and later the Bohemian crown. In the 17th century, the castle was owned by various families: Bohussin von Zwolle und Güldenstein, who purchased it from emperor Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II in 1600, and later the barons of Sießwohl. In 1678, Countess Henkel came into possession of the estate, who was succeeded by counts Carl Maximillian and Leo Ferdinand Henkel. Subsequently, in 1702, their heirs sold the castle to the Electorate of Saxony, Saxon General officer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schloss Slawentzitz Sammlung Duncker
''Schloss'' (; pl. ''Schlösser''), formerly written ''Schloß'', is the German language, German term for a building similar to a château, palace, or manor house. Related terms appear in several Germanic languages. In the Scandinavian languages, the cognate word ''slot''/''slott'' is normally used for what in English could be either a palace or a castle (instead of words in rarer use such as ''palats''/''palæ'', ''kastell'', or ''borg''). In Dutch, the word ''slot'' is considered to be more archaic. Nowadays, one commonly uses ''paleis'' or ''kasteel''. But in English, the term does not appear; for instance, in the United Kingdom, this type of structure would be known as a stately home or English country house, country house. Most ''Schlösser'' were built after the Middle Ages as residences for the nobility, not as true fortresses, although originally, they often were fortified. The usual German term for a true castle is ''Burg'', while that for a fortress is ''Festung'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Louis, Prince Of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen
Frederick Louis, Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen () (31 January 1746 – 15 February 1818) was a Prussian general. Early life Frederick Louis was the eldest son of Henry August, Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen (1715-1796) and his wife, Wilhelmine Eleonore of Hohenlohe-Neuenstein-Öhringen (1717-1794). His grandfather, Christian Kraft, was a younger son of Henry Frederick, Count of Hohenlohe-Langenburg Biography He began his military career as a boy, serving against the Prussians in the last years of the Seven Years' War. Entering the Prussian army after the peace, he was, as a result of his princely rank, at once made a major; and in 1775 he was elevated to lieutenant-colonel. In 1778 Frederick Louis took part in the War of the Bavarian Succession and at about the same time was made a colonel. Shortly before the death of King Frederick the Great, he was promoted to the rank of major general and appointed Chief of a Regiment. For some years the prince did garrison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart. Together with Baden and Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württemberg now forms the Federal State of Baden-Württemberg. Württemberg was formerly also spelled Würtemberg and Wirtemberg Castle, Wirtemberg. History Originally part of the old Duchy of Swabia, its history can be summarized in the following periods: *County of Württemberg (1083–1495) *Duchy of Württemberg (1495–1803) *Electorate of Württemberg (1803–1806) *Kingdom of Württemberg (1806–1918) *Free People's State of Württemberg (1918–1945) After World War II, it was split into Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern owing to the different Allied Occupation Zones in Germany, occupation zones of the United States and France. Finally, in 1952, it was integrated into Baden-Württemberg. Stutt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William I, German Emperor
Wilhelm I (Wilhelm Friedrich Ludwig; 22 March 1797 – 9 March 1888) was King of Prussia from 1861 and German Emperor from 1871 until his death in 1888. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he was the first head of state of a united Germany. He was regent of Prussia from 1858 to 1861 for his brother Frederick William IV. During the reign of his grandson Wilhelm II, he was known as Emperor Wilhelm the Great (German: ''Kaiser Wilhelm der Große''). The second son of Frederick William III of Prussia, Prince Frederick William and Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Wilhelm was not expected to ascend to the throne. His grandfather, King Frederick William II of Prussia, Frederick William II died the year he was born, and his father was crowned Frederick William III of Prussia, Frederick William III. Wilhelm fought with distinction during the War of the Sixth Coalition, and afterwards became a prominent figure within the Prussian Army. In 1840, his childless elder brother became King of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujazd, Opole Voivodeship
Ujazd () is a town in Strzelce County in the Opole Voivodeship in southern Poland. Population 1,647. The town lies on bank of the river Kłodnica. Tourist attractions in the town include the Ujazd Castle (formerly used by bishops of Wrocław) and two churches: 17th-century Baroque Saint Andrew church and 19th-century Gothic Revival Visitation church. History The oldest known mention of Ujazd dates back to a document of Pope Adrian IV from 1155, when it was part of the Piast-ruled Kingdom of Poland. It was granted town rights in 1223 by Bishop of Wrocław Wawrzyniec. Already in the 13th century, a Catholic parish and municipal council existed in the town. Its name is of Polish origin. The town suffered during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and the Silesian Wars (1740–1763) and in 1666, 1676, 1770 it was hit by fires. It was captured by Prussia in 1740 and annexed afterwards. In 1838 the town passed to the family of Hohenlohe–Öhringen, a branch (1823) of that o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Ujest
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below grand dukes and above or below princes, depending on the country or specific title. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin ''dux'', 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic or Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''doux'', survived in the Eastern Roman Empire where it continued in sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Zu Hohenlohe-Öhringen
Friedrich Wilhelm Eugen Karl ''Hugo'', Prince of Hohenlohe-Öhringen, Duke of Ujest (title in German: ''Fürst zu Hohenlohe-Öhringen, Herzog von Ujest''; 27 May 1816 – 23 August 1897) was a German nobleman, politician, mining industrialist and general in the armies of the kingdom of Württemberg and the kingdom of Prussia. Early life A hereditary prince of the House of Hohenlohe, he was born in Stuttgart on 27 May 1816. He was the son of August, Prince of Hohenlohe-Öhringen. His paternal grandparents were Frederick Louis, Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen, and Countess Maria Amalie von Hoym. His uncle was Prince Adolf zu Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen (who briefly served as Minister-President of Prussia in 1862 and was succeeded by Otto von Bismarck), and his cousin was Prince Kraft zu Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen. Career His paternal grandfather, Frederick Louis, had acquired the estates of Slawentzitz, Ujest and Bitschin in Silesia by marriage in 1782, an area of 108 square mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Smelting
Zinc smelting is the process of converting zinc concentrates ( ores that contain zinc) into pure zinc. Zinc smelting has historically been more difficult than the smelting of other metals, e.g. iron, because in contrast, zinc has a low boiling point. At temperatures typically used for smelting metals, zinc is a gas that will escape from a furnace with the flue gas and be lost, unless specific measures are taken to prevent it. The most common zinc concentrate processed is zinc sulfide,. which is obtained by concentrating sphalerite via froth flotation. Secondary (recycled) zinc material, such as zinc oxide, is also processed with the zinc sulfide.. Approximately 30% of all zinc produced is from recycled sources. Methods There are two methods of smelting zinc: the pyrometallurgical process and the electrolysis process. Both methods are still used. Both of these processes share the same first step: roasting. Roasting Roasting is a process of oxidizing zinc sulfide concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August, Prince Of Hohenlohe-Öhringen
Frederick ''August'' Charles, Prince of Hohenlohe-Öhringen (27 November 1784 – 15 February 1853) was a German general of the Napoleonic Wars and nobleman of the house of Hohenlohe. Early life August was born on 27 November 1784 in Breslau. His parents were Frederick Louis, Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen (1748–1818) and Countess Maria Amalie von Hoym and his younger brother was Prince Adolf zu Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen who briefly served as Minister-President of Prussia in 1862 and was succeeded by Otto von Bismarck. His father was the eldest son of Heinrich August, 1st Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen and Wilhelmine Eleonora von Hohenlohe-Öhringen. His nephew was Prince Kraft zu Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen. His maternal grandparents were Count Julius Gebhard von Hoym and Christiane Charlotte Sophie von Dieskau. Career He was a German general during the Napoleonic Wars. Upon his parents' marriage in 1782, his father acquired the estates of Slawentzitz, Ujest and Bitschin in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon, a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French First Republic, French Republic as French Consulate, First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the First French Empire, French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy, King of Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Italy from 1805 to 1814 and Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813. Born on the island of Corsica to a family of Italian origin, Napoleon moved to mainland France in 1779 and was commissioned as an officer in the French Royal Army in 1785. He supported the French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Jena
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |