|
Sólheimar Ecovillage
Sólheimar () is an eco-village in Iceland and is renowned for its ecological, artistic, and international community ethics. Its current population size is about 100 people. The village of Sólheimar lies in the south-western part of Iceland, the municipality of Grímsnes- og Grafningshreppur. It is a community where people with or without special needs live and work together. Sólheimar is a pioneer of practising organic farming. In Sólheimar there are an organically certified greenhouse, forestry, arboretum and egg production. Other environmentally friendly projects in Sólheimar include geothermal energy and recycling. History Sólheimar (Sunworlds) was founded on July 5, 1930 by a pioneering woman: Sesselja Sigmundsdóttir Sesselja (Hreindís) Sigmundsdóttir (5 July 1902 - 8 November 1974) was a noted Icelandic pioneer in the fields of pedagogy and the care for the mentally disabled and founder of the Sólheimar community. After her training in education in Germa ... ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the region's westernmost and most list of countries and dependencies by population density, sparsely populated country. Its Capital city, capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which is home to about 36% of the country's roughly 380,000 residents (excluding nearby towns/suburbs, which are separate municipalities). The official language of the country is Icelandic language, Icelandic. Iceland is on a rift between Plate tectonics, tectonic plates, and its geologic activity includes geysers and frequent Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions. The interior consists of a volcanic plateau with sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, and many Glacial stream, glacial rivers flow to the sea through the Upland and lowland, lowlands. Iceland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grímsnes- Og Grafningshreppur
Grímsnes- og Grafningshreppur () is a municipality in the south-western part of Iceland Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ..., in the Southern Region. It was formed in 1998 by the merger of Grímsneshreppur and Grafningshreppur. The main settlement is Sólheimar with 80 inhabitants (2006). The settlement Írafoss og Ljósafoss , which still had 15 inhabitants in 1997, has been abandoned since then. References External links Municipalities of Iceland {{Iceland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; ) are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe, as well as the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic oceans. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden; the autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland; and the autonomous region of Åland. The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, History of Scandinavia, history, religion and Nordic model, social and economic model. They have a long history of political unions and other close relations but do not form a singular state or federation today. The Scandinavism, Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century. With the dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden (Norwegian independence), the independence of Finland in the early 20th century and the 1944 Icelandic constitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for millennia. Geothermal heating, using water from hot springs, for example, has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since Roman times. Geothermal power (generation of electricity from geothermal energy), has been used since the 20th century. Unlike wind and solar energy, geothermal plants produce power at a constant rate, without regard to weather conditions. Geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs. Most extraction occurs in areas near tectonic plate boundaries. The cost of generating geothermal power decreased by 25% during the 1980s and 1990s. Technological advances continued to reduce costs and thereby expand the amount of viable resources. In 2021, the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. This concept often includes the recovery of energy from waste materials. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the properties it had in its original state. It is an alternative to "conventional" waste disposal that can save material and help lower greenhouse gas emissions. It can also prevent the waste of potentially useful materials and reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reducing energy use, air pollution (from incineration) and water pollution (from landfilling). Recycling is a key component of modern waste reduction and represents the third step in the "Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle" waste hierarchy, contributing to environmental sustainability and resource conservation. It promotes environmental sustainability by removing raw material input and redirecting waste output in the economic system. There are some ISO standards related to recycling, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesselja Sigmundsdóttir
Sesselja (Hreindís) Sigmundsdóttir (5 July 1902 - 8 November 1974) was a noted Icelandic pioneer in the fields of pedagogy and the care for the mentally disabled and founder of the Sólheimar community. After her training in education in Germany and Switzerland, where she was inspired by Rudolf Steiner Rudolf Joseph Lorenz Steiner (; 27 or 25 February 1861 – 30 March 1925) was an Austrian occultist, social reformer, architect, esotericist, and claimed clairvoyant. Steiner gained initial recognition at the end of the nineteenth century ..., Sesselja returned to Iceland with the plan of establishing a self-sustaining community based on the anthroposophist philosophy. Here she would offer shelter and education to disabled and neglected children. At the age of 28, she acquire some land in a remote valley with its own hot spring and with the help of her family and friends built a farmhouse and named it Sólheimar - ''home of the sun''. The 2002 stamp She has been rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Horticulture
Organic horticulture is the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture in soil building and conservation, pest management, and heirloom variety preservation. The Latin words ''hortus'' (garden plant) and ''cultura'' (culture) together form ''horticulture'', classically defined as the culture or growing of garden plants. ''Horticulture'' is also sometimes defined simply as "agriculture minus the plough". Instead of the plough, horticulture makes use of human labour and gardener's hand tools, although some small machine tools like rotary tillers are commonly employed now. General Mulches, cover crops, compost, manures, vermicompost, and mineral supplements are soil-building mainstays that distinguish this type of farming from its conventional counterpart. Through attention to good healthy soil condition, it is expected that insect, fungal, or other problems that sometimes plague pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Steiner
Rudolf Joseph Lorenz Steiner (; 27 or 25 February 1861 – 30 March 1925) was an Austrian occultist, social reformer, architect, esotericist, and claimed clairvoyant. Steiner gained initial recognition at the end of the nineteenth century as a literary critic and published works including '' The Philosophy of Freedom''. At the beginning of the twentieth century he founded an esoteric spiritual movement, anthroposophy, with roots in German idealist philosophy and theosophy. His teachings are influenced by Christian Gnosticism or neognosticism.Sources for 'Christian Gnosticism': Many of his ideas are pseudoscientific. He was also prone to pseudohistory.Sources for 'pseudohistory': In the first, more philosophically oriented phase of this movement, Steiner attempted to find a synthesis between science and spirituality. His philosophical work of these years, which he termed " spiritual science", sought to apply what he saw as the clarity of thinking characteristic of West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
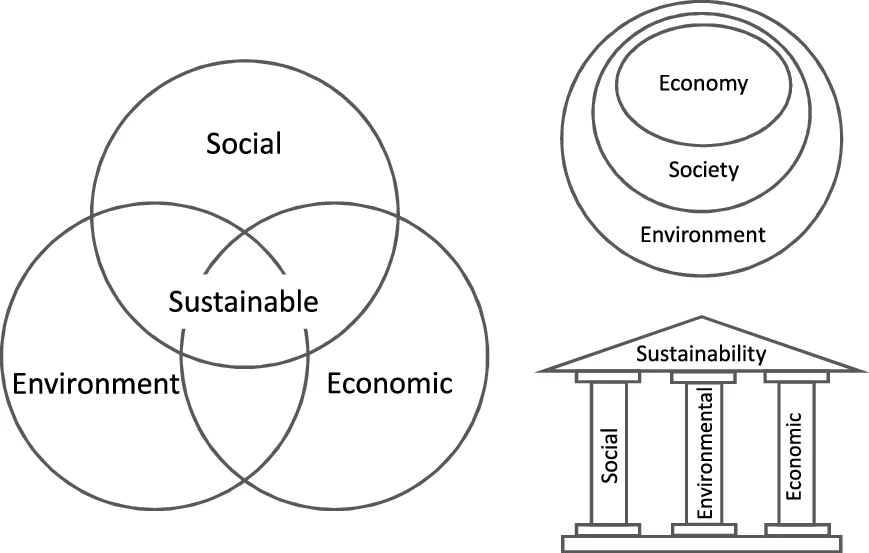
Environmental Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental issues, environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |