|
São Paulo Constitutional Revolution
The Constitutionalist Revolution of 1932 (sometimes also referred to as Paulista War or Brazilian Civil War) is the name given to the uprising of the population of the Brazilian state of São Paulo against the Brazilian Revolution of 1930 when Getúlio Vargas assumed the nation's presidency; Vargas was supported by the people, the military and the political elites of Minas Gerais, Rio Grande do Sul and Paraíba. The movement grew out of local resentment over the fact that Vargas ruled by decree, unbound by a Constitution, in a provisional government. The 1930 Revolution also affected São Paulo by eroding the autonomy that states enjoyed during the term of the 1891 Constitution and preventing the inauguration of the governor of São Paulo, Júlio Prestes, who had been elected president of Brazil in 1930, while simultaneously overthrowing President Washington Luís, who was governor of São Paulo from 1920 to 1924. These events marked the end of the First Brazilian Republic. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
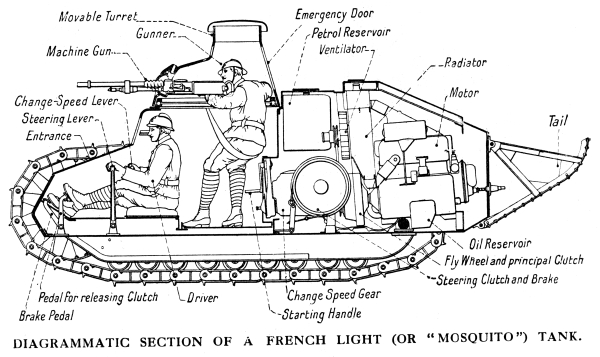
Renault FT
The Renault FT (frequently referred to in post-World War I literature as the FT-17, FT17, or similar) is a French light tank that was among the most revolutionary and influential tank designs in history. The FT was the first production tank to have its armament within a fully rotating turret.Although a rotating turret had been a feature of some earlier tank designs or prototypes, and had been incorporated in Armored car (military), armoured cars for several years, no tank with a turret had entered service. The Renault FT's configuration (crew compartment at the front, engine compartment at the back, and main armament in a revolving turret) became and remains the standard tank layout. Consequently, some armoured warfare historians have called the Renault FT the world's first modern tank. Over 3,000 Renault FT tanks were manufactured by France, most of them in 1918. After World War I, FT tanks were exported in large numbers. Copies and derivative designs were manufactured in the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazilian Marine Corps
The Brazilian Marine Corps (, CFN; or 'Corps of Naval Riflemen') is the Brazilian Navy's naval infantry component. It relies on the fleet and Brazilian Naval Aviation, Naval Aviation and fields its own artillery, amphibious and land armor, COMANF, special operations forces and other support elements. Its operational components are the Fleet Marine Force (''Força de Fuzileiros da Esquadra'', FFE), under the Naval Operations Command, in Rio de Janeiro (state), Rio de Janeiro, and Marine Groups and Riverine Operations Battalions, under the Naval Districts in the coast and the Amazon basin, Amazon and Río de la Plata Basin, Platine basins. The FFE, with a core of three infantry battalions, is its seagoing component. Tracing their origins to the Portuguese Navy's Royal Brigade of the Navy, Brazilian marines served across the 19th century aboard and landed from the Imperial Brazilian Navy, Imperial Navy's ships. By the next century, they were relegated to guard duty and largely infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vespasiano Martins
Vespasiano is a municipality in the Belo Horizonte metropolitan region in the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais, located north of Belo Horizonte. Vespasiano is home to Cidade do Galo, the training grounds of Campeonato Brasileiro Série A team Atlético Mineiro. FASEH, a higher learning institution, is also located in the city. See also * List of municipalities in Minas Gerais This is a list of the municipalities in the States of Brazil, state of Minas Gerais, Minas Gerais (MG), located in the Southeast Region, Brazil, Southeast Region of Brazil. Minas Gerais is divided into 853 Municipalities of Brazil, municipalities, ... References External links Official site Municipalities in Minas Gerais {{MinasGerais-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artur Bernardes
Artur da Silva Bernardes (8 August 1875 – 23 March 1955) was a Brazilian lawyer and politician who served as the 12th president of Brazil from 1922 to 1926. Bernades' presidency was marked by the crisis of the First Brazilian Republic and the almost uninterrupted duration of a state of emergency. During his long political career, from 1905 until his death, he was the main leader of the Republican Party of Minas Gerais (PRM) from 1918–1922 until the party's closure in 1937, and founder and leader of the Republican Party (PR). Before his presidency, Bernardes served as president (governor) of Minas Gerais from 1918 to 1922, during which time he founded the current Federal University of Viçosa and prevented American investor Percival Farquhar from exploiting the iron ore deposits in Itabira, cultivating an image of a nationalist and municipalist leader. A ''status quo'' and " milk coffee" candidate in the 1922 presidential election, Bernardes was the target of fake letter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Júlio Marcondes Salgado
Júlio Marcondes César Salgado (1 July 1890 — 23 July 1932) was a Brazilian general and commander of the São Paulo State Public Force, currently the Military Police of São Paulo State, Military Police of the State of São Paulo, during the Constitutionalist Revolution of 1932, Constitutionalist Revolution. Biography Early life Salgado was born on 1 July 1890 in the city of Pindamonhangaba to Victoriano Clementino Salgado and Anna Euphrosina Marcondes do Amaral Salgado. He was the brother of Sérgio, Luiz, Joaquim, Francisco, Euclydia, Francisco Marcondes Salgado and Eneas Marcondes Salgado. The Marcondes family had a tradition in public and military service. Among the most outstanding people in that family was colonel Manuel Marcondes de Oliveira Melo, the 1st Baron of Pindamonhangaba and commander of the Guard of Honour of Pedro I of Brazil, Prince Pedro on the occasion of the ''Grito do Ipiranga'' (Cry of Ipiranga) that culminated in the independence of Brazil. Another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Júlio De Mesquita Filho
Júlio is a Portuguese masculine given name. The equivalent in Spanish is Julio (given name), Julio. The diminutive form is Julinho (other), Julinho, as in Júlio César Teixeira known as Julinho, a Brazilian footballer. Notable people with the given name include: *Júlio Afrânio Peixoto (18761947), Brazilian physician, writer, politician, historian, university president and eugenicist *Júlio Almeida (born 1969), Brazilian sport shooter *Júlio Alves (born 1991), Portuguese footballer *Júlio Alves (born 1994), Brazilian footballer *Júlio Andrade (born 1976), Brazilian actor and director See also *Julio (other) *Julio (surname) {{given name Portuguese masculine given names Masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclides Figueiredo
Euclid generally refers to the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid of Alexandria (3rd century BC), who wrote a work on geometry called the ''Elements''. Euclid, Euclides, or Eucleides may also refer to: People * Euclid of Megara (c. 435 BC–c. 365 BC), ancient Greek philosopher * Eucleides, archon of Athens (5th century BC) * Euclid Bertrand (born 1974), Dominican former footballer * Euclides da Cunha (1866–1909), Brazilian sociologist * Euclid James Sherwood (1942–2011), American musician * Euclid Kyurdzidis (born 1968), Russian actor * Euclid Tsakalotos (born 1960), Greek economist and Minister of Finance * Nicholas Euclid (1932–2007), Australian rugby league player, coach, and official Mathematics, science, and technology * Euclid (computer program) * Euclid (programming language) * ''Euclid'', a space telescope built by ESA, launched in 2023 * Euclid, a computer system used by Euroclear * Euclid Contest, a maths competition held by the Centre for Education in Math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertoldo Klinger
Bertoldo Ritter Klinger (1 January 1884 — 31 January 1969) was a Brazilian divisional general in the Brazilian Army and commander in the Constitutionalist Revolution of 1932. Biography Early years Klinger was born in the city of Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul, Rio Grande, on 1 January 1884, to Antônio Klinger, an Austrian immigrant, and Suzana Ritter Klinger, a descendant of Germans who migrated to Brazil.Bertoldo Klinger , FGV CPDOC . de Abreu, Alzira Alvez (2015). ''Dicionário histórico-biográfico da Primeira República (1889-1930)''. Rio de Janeiro: Fundação Getúlio Vargas. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidoro Dias Lopes
Isidoro Dias Lopes (30 June 1865 – 27 May 1949) was a brigadier general of the Brazilian army, often styled the "Marshal of the Revolution of 1924". Early life Lopes was born in the city of Dom Pedrito, Rio Grande do Sul, on 30 June 1865, son of José Tavares Bastos Rios and Jacinta Barros Lopes. He joined the army in 1883 through the Military School of Porto Alegre, completed a course in artillery and was promoted to lieutenant in 1891.SPALDING, Walter. Construtores do Rio Grande. Livraria Sulina, Porto Alegre, 1969, 3 vol., 840pp. He supported the movement to bring the Empire of Brazil to an end. In 1893, he left the army and took part in the Federalist Revolution in Rio Grande do Sul, against the government of president Floriano Peixoto. After the defeat of the federalists, in 1895, he went into exile in Paris. In 1896, he benefited from an amnesty and returned to Brazil, resuming his position in the army in Rio de Janeiro. 1924 São Paulo revolt Dias Lopes was one of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Manuel De Toledo
Pedro Manuel de Toledo (1860–1935) was a Brazilian politician. He was born in São Paulo. He served in the Cabinet of President Hermes da Fonseca. He died in Rio de Janeiro. Toledo also served as the Governor of São Paulo from March 1932 to October 1932. See also *Constitutionalist Revolution The Constitutionalist Revolution of 1932 (sometimes also referred to as Paulista War or Brazilian Civil War) is the name given to the uprising of the population of the Brazilian state of São Paulo against the Brazilian Revolution of 1930 wh ... References External linksGaleria dos Governadores de São Paulo 1860 births 1935 deaths [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Police Of Paraná State
The Military Police (Brazil), Military Police are Military reserve force, reserve and ancillary forces of the Brazilian Army, and part of the System of Public Security and Brazilian Social Protection. Its members are called Military's States. The primary mission of PMPR is the ostensible and preventive Police, policing for the maintenance of public order in the State (administrative division), State of Paraná (state), Paraná. History The Military Police of Paraná was created as a unit of Skirmishers on August 10, 1854, under the name of the Police Force, like a military Company (military unit), company. This origin is due to military necessity of the Empire of Brazil in reinforcing the troops of the Army in emergency situations. With the Proclamation of the Republic of Brazil has adopted a Constitution based on the United States where the states have a large autonomy. With that the police have become small regional armies. The history of PMPR shows an honorable participation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Police Of Rio De Janeiro State
The Military Police of Rio de Janeiro State () (PMERJ) like other military polices in Brazil is a reserve and ancillary force of the Brazilian Army, and part of the System of Public Security and Brazilian Social Protection. Its members are called "state military" personnel. The primary mission of PMERJ is ostensively preventive policing for the maintenance of public order in the State of Rio de Janeiro. History The first militarized police in Portugal (when Brazil was still a colony) was the '' Royal Police Guard of Lisbon'' (), established in 1801, which followed the model of the National Gendarmerie () of France, created in 1791. When the Portuguese Royal Family was transferred to Brazil, the Royal Police Guard of Lisbon remained in Portugal, and another equivalent guard was created in Rio de Janeiro under the name of ''Military Division of the Royal Police Guard of Rio de Janeiro'', in 1809. With the abdication of Emperor Pedro I in 1831, the Regency restructured the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |