|
Sándor Rosenberg
Alexander ándorRosenberg (1844 – 11 August 1909) was a Hungarian Neolog rabbi. Rosenberg was born in Makó; after studying at Vienna and Leipzig, and was trained in the Jewish Theological Seminary of Breslau, where he was made Doctor of Philosophy. He officiated at the opening ceremony of the Ujpest Synagogue in 1866. In 1868 he was elected preacher in Nagyvárad.Susanne Blumesberger. ''Handbuch österreichischer Autorinnen und Autoren jüdischer Herkunft 18. bis 20. Jahrhundert''. K.G. Saur (2002). . p. 1139. There, the progressive elements in the community seceded from the conservative majority in 1861, seeking to administer synagogue reforms. While the authorities forced reunification in 1863, they allowed the former to maintain a house of worship. In 1870, in the aftermath of the Schism in Hungarian Jewry, the dispute was institutionalized and they formed an independent Neolog congregation. Rosenberg was its first rabbi. In 1876 he was appointed Neolog rabbi of Kaposvár, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolog Judaism
Neologs (, "Neolog faction") are one of the two large communal organizations among Hungarian Jewry. Socially, the liberal and modernist Neologs had been more inclined toward integration into Hungarian society since the Era of Emancipation in the 19th century. This was their main feature, and they were largely the representative body of urban, assimilated middle- and upper-class Jews. Religiously, the Neolog rabbinate was influenced primarily by Zecharias Frankel's Positive-Historical School, from which Conservative Judaism evolved as well, although the formal rabbinical leadership had little sway over the largely assimilationist communal establishment and congregants. Their rift with the traditionalist and conservative Orthodox Jews was institutionalized following the 1868–1869 Hungarian Jewish Congress, and they became a separate communal organization. The Neologs remained organizationally independent in those territories ceded under the terms of the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dina D'Malkhutah Dina
Dina d'malkhuta dina (alternative spelling: dina de-malkhuta dina; , or "the law of the land is the law") is a principle in Jewish religious law that the civil law of the country is binding upon the Jewish inhabitants of that country, and, in certain cases, is to be preferred to Jewish law. The law of the land and its binding on Jewish citizens pertains, however, exclusively to monetary matters. The concept of ''dina de-malkhuta dina'' is similar to the concept of conflict of laws in other legal systems. It appears in at least twenty-five places in the '' Shulchan Arukh''. The principle of ''dina d'malkhuta dina'' means that, for Jews, obedience to the civil law of the country in which they live is viewed as a religiously mandated obligation and disobedience is a transgression, according to Jewish law. This general principle is subject, however, to the qualifications that the government enacting the law must be one which is recognized by Jewish law as having legitimacy; the law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Makó
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1910 Deaths
Events January * January 6 – Abé people in the French West Africa colony of Côte d'Ivoire rise against the colonial administration; the rebellion is brutally suppressed by the military. * January 8 – By the Treaty of Punakha, the Himalayan kingdom of Bhutan becomes a protectorate of the British Empire. * January 11 – Charcot Island is discovered by the Antarctic expedition led by French explorer Jean-Baptiste Charcot on the ship '' Pourquoi Pas?'' Charcot returns from his expedition on February 11. * January 12 – Great January Comet of 1910 first observed ( perihelion: January 17). * January 15 – Amidst the constitutional crisis caused by the House of Lords rejecting the People's Budget the January 1910 United Kingdom general election is held resulting in a hung parliament with neither Liberals nor Conservatives gaining a majority. * January 21 – The Great Flood of Paris begins when the Seine overflows its banks. * January 22 – Completion of cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1844 Births
In the Philippines, 1844 had only 365 days, when Tuesday, December 31 was skipped as Monday, December 30 was immediately followed by Wednesday, January 1, 1845, the next day after. The change also applied to Caroline Islands, Guam, Marianas Islands, Marshall Islands and Palau as part of the Captaincy General of the Philippines; these became the first places on Earth to redraw the International Date Line. Events January–March * January 4 – The first issue of the Swedish-languaged ''Saima'' newspaper founded by J. V. Snellman is published in Kuopio, Finland. * January 15 – The University of Notre Dame, based in the city of the same name, receives its charter from Indiana. * February 27 – The Dominican Republic gains independence from Haiti. * February 28 – A gun on the USS ''Princeton'' explodes while the boat is on a Potomac River cruise, killing U.S. Secretary of State Abel Upshur, U.S. Secretary of the Navy Thomas Walker Gilmer and four other people. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immanuel Löw
Immanuel Löw (January 20, 1854 in Szeged – July 19, 1944 in Budapest) was a Hungarian rabbi and scholar, botanist and politician. Life Löw was the son of Leopold Löw whom he succeeded in 1878 as rabbi of Szeged, Hungary, and whose collected works he published (5 vols., 1889–1900). He was educated in his native town and in Berlin, where he studied at the Hochschule für die Wissenschaft des Judentums, graduating as rabbi and receiving his Ph.D. from the University of Leipzig in 1878. The Szeged Synagogue built in 1903 was designed according to Löw's plans. In the 'White Terror (Hungary), White Terror' of 1920–21 he was imprisoned for 13 months for alleged statements against Admiral Miklós Horthy. While in prison, he worked on his four volume work ''Die Flora der Juden'' (“The Flora of the Jews”), on terminology of plants in Jewish sources. Like his father, Löw was a great preacher in the Hungarian language, and several hundred of his sermons were published in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nashim
__notoc__ Nashim ( "Women" or "Wives") is the third order of the Mishnah (also of the Tosefta and Talmud) containing family law. Of the six orders of the Mishnah, it is the shortest. Nashim consists of seven tractates: #'' Yevamot'' ( "Brothers-in-Law") deals with the Jewish law of yibbum (levirate marriage) () and other topics such as the status of minors. It consists of 16 chapters. #'' Ketubot'' (, "Prenuptial agreements") deals with the ketubah (Judaism's prenuptial agreement), as well as topics such as virginity Virginity is a social construct that denotes the state of a person who has never engaged in sexual intercourse. As it is not an objective term with an operational definition, social definitions of what constitutes virginity, or the lack thereo ..., and the obligations of a couple towards each other. It consists of 13 chapters. #''Nedarim (Talmud), Nedarim'' (, "Vows") deals with various types of vows often known as ''nedarim'' and their legal consequences. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish culture, Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The Talmud includes the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, Jewish philosophy, philosophy, Jewish customs, customs, Jewish history, history, and Jewish folklore, folklore, and many other topics. The Talmud is a commentary on the Mishnah. This text is made up of 63 Masekhet, tractates, each covering one subject area. The language of the Talmud is Jewish Babylonian Aramaic. Talmudic tradition emerged and was compiled between the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the Arab conquest in the early seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arad, Romania
Arad () is the capital city of Arad County, at the edge of Crișana and Banat. No villages are administered by the city. It is the third largest city in Western Romania, behind Timișoara and Oradea, and the List of cities and towns in Romania, 12th largest in Romania, with a population of 145,078. A busy transportation hub on the Mureș River and an important cultural and industrial center, Arad has hosted one of the first Music school, music conservatories in Europe, one of the earliest normal schools in Europe, and the first car factory in Hungary and present-day Romania. Today, it is the seat of a Romanian Orthodox Church, Romanian Orthodox archbishop and features a Romanian Orthodox theological seminary and two universities. The city's multicultural heritage is owed to the fact that it has been part of the Kingdom of Hungary, the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom, the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Temeşvar Eyalet, Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Principality of Transylvania, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makó
Makó (, , Makowe, or , ) is a town in Csongrád County, in southeastern Hungary, from the Romanian border. It lies on the Maros River. Makó is home to 21,913 people and it has an area of , of which is arable land. Makó is the fourth-largest town in Csongrád County after Szeged, Hódmezővásárhely and Szentes. The town is from Hódmezővásárhely, from Szeged, from Arad, Romania, Arad, from Gyula, Hungary, Gyula, from Timișoara (Temesvár), and from Budapest. The climate is warmer than anywhere else in Hungary, with hot, dry summers. The town is noted for its onion which is a hungarikum, the spa and the thermal bath. The Makó International Onion Festival, the largest of its kind, is held annually. Makó is a popular tourist destination in Hungary. The Makó gas field, located near the town, is the largest natural gas field in Central Europe. The gas volume is more than 600 billion cubic metres (21 trillion cubic feet), according to a report by the Scotia Group. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
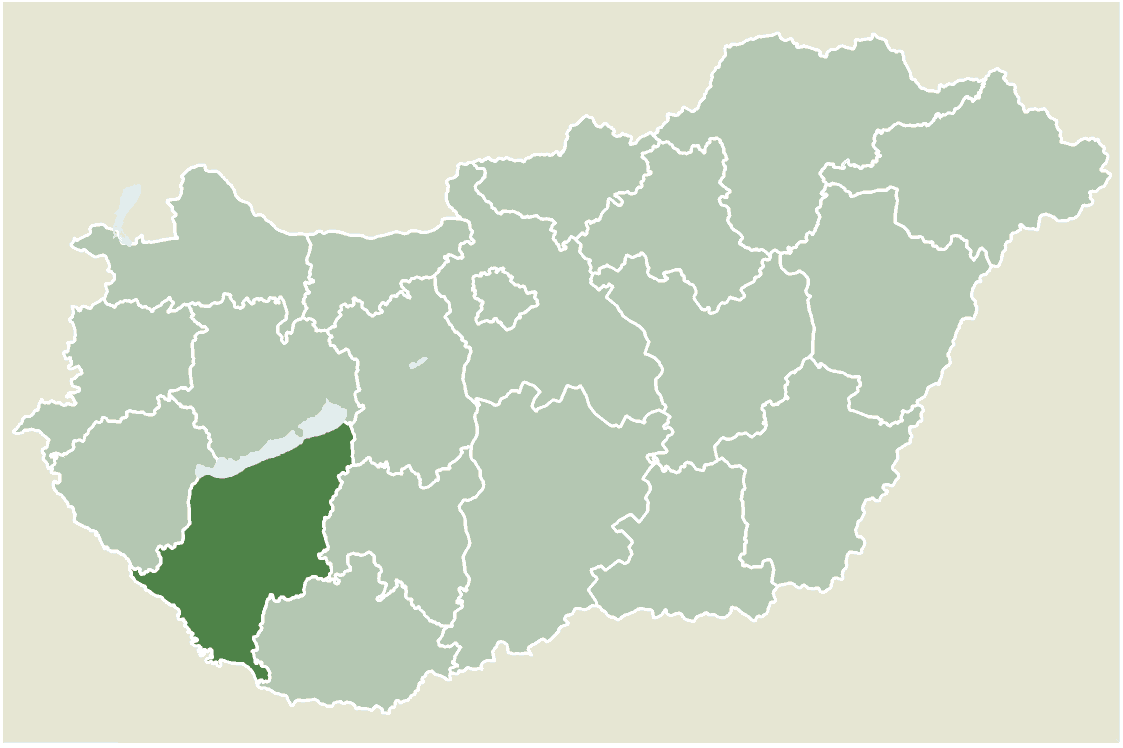
Kaposvár
Kaposvár (; also known by alternative names) is a city with county rights in southwestern Hungary, south of Lake Balaton. It is one of the leading cities of Transdanubia, the capital of Somogy County, and the seat of the Kaposvár District and the Roman Catholic Diocese of Kaposvár. Etymology and names The name ''Kaposvár'' is derived from the Hungarian words ''kapu'' (gate) and ''vár'' (castle). Variants of the city's name include ''Ruppertsburg'' / ''Ruppertsberg'' / ''Kopisch'' ( German), ''Kapoşvar'' ( Turkish), ''Rupertgrad'' ( Slovene), and ''Kapošvar'' ( Croatian). Symbols The shield of Kaposvár features a castle with a rounded arch port surmounted by three battlements with loopholes on a hill of green grass. The flag of Kaposvár consists of the coat of arms placed over a yellow background. Geography Kaposvár is surrounded by the hills of the outer Somogy area around the Kapos river and the forests of Zselic. It lies southwest of Budapest. Historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schism In Hungarian Jewry
The Schism in Hungarian Jewry (, "Orthodox-Neolog Schism"; , Transliteration, trans. ''Die Teilung in Ungarn'', "The Division in Hungary") was the institutional division of the History of the Jews in Hungary, Jewish community in the Kingdom of Hungary between 1869 and 1871, following a failed attempt to establish a national, united representative organization. The founding congress of the new body was held during an ongoing conflict between the traditionalist Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox party and its modernist Neolog Judaism, Neolog rivals, which had been raging for decades. The traditionalists, fearing their opponents would dominate the new body, seceded and then lobbied the government to allow the formation of an independent Orthodox supracommunal organization with a policy of strict separation from the Neologs. When faced with the need to choose between the two, a third faction of "Status Quo" congregations emerged, refusing to join either and remaining fully autonomous, without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |