|
Systems Science
Systems science, also referred to as systems research or simply systems, is a transdisciplinary field that is concerned with understanding simple and complex systems in nature and society, which leads to the advancements of formal, natural, social, and applied attributions throughout engineering, technology, and science itself. To systems scientists, the world can be understood as a system of systems. The field aims to develop transdisciplinary foundations that are applicable in a variety of areas, such as psychology, biology, medicine, communication, business, technology, computer science, engineering, and social sciences. Themes commonly stressed in system science are (a) holistic view, (b) interaction between a system and its embedding environment, and (c) complex (often subtle) trajectories of dynamic behavior that sometimes are stable (and thus reinforcing), while at various ' boundary conditions' can become wildly unstable (and thus destructive). Concerns about Earth-scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Thinking About The Society
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Cybernetics
Engineering cybernetics, also known as technical cybernetics or cybernetic engineering, is the branch of cybernetics concerned with applications in engineering, in fields such as control engineering and robotics. History Qian Xuesen (Hsue-Shen Tsien) defined engineering cybernetics as a theoretical field of "engineering science", the purpose of which is to "study those parts of the broad science of cybernetics which have direct engineering applications in designing controlled or guided systems". Published in 1954, Qian's published work "Engineering Cybernetics" describes the mathematical and engineering concepts of cybernetic ideas as understood at the time, breaking them down into granular scientific concepts for application. Qian's work is notable for going beyond model-based theories and arguing for the necessity of a new design principle for types of system the properties and characteristics of which are largely unknown. In the 2020s, concerns with the social consequences of cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTI System Theory
In system analysis, among other fields of study, a linear time-invariant (LTI) system is a system that produces an output signal from any input signal subject to the constraints of linearity and time-invariance; these terms are briefly defined in the overview below. These properties apply (exactly or approximately) to many important physical systems, in which case the response of the system to an arbitrary input can be found directly using convolution: where is called the system's impulse response and ∗ represents convolution (not to be confused with multiplication). What's more, there are systematic methods for solving any such system (determining ), whereas systems not meeting both properties are generally more difficult (or impossible) to solve analytically. A good example of an LTI system is any electrical circuit consisting of resistors, capacitors, inductors and linear amplifiers. Linear time-invariant system theory is also used in image processing, where the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
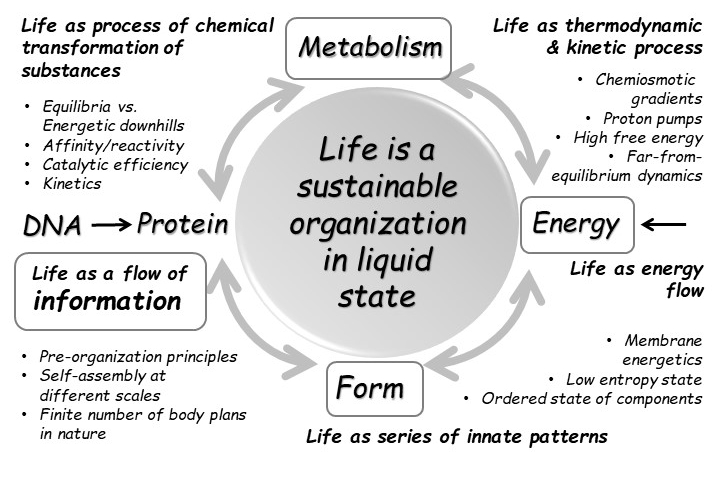
Living Systems Theory
Living systems are life forms (or, more colloquially known as living things) treated as a system. They are said to be open self-organizing and said to interact with their environment. These systems are maintained by flows of information, energy and matter. Multiple theories of living systems have been proposed. Such theories attempt to map general principles for how all living systems work. Context Some scientists have proposed in the last few decades that a general theory of living systems is required to explain the nature of life. Such a general theory would arise out of the ecological and biological sciences and attempt to map general principles for how all living systems work. Instead of examining phenomena by attempting to break things down into components, a general living systems theory explores phenomena in terms of dynamic patterns of the relationships of organisms with their environment. Theories Miller's open systems James Grier Miller's living systems theory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Systems Theory
Systems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems, i.e. cohesive groups of interrelated, interdependent components that can be natural or artificial. Every system has causal boundaries, is influenced by its context, defined by its structure, function and role, and expressed through its relations with other systems. A system is "more than the sum of its parts" when it expresses synergy or emergent behavior. Changing one component of a system may affect other components or the whole system. It may be possible to predict these changes in patterns of behavior. For systems that learn and adapt, the growth and the degree of adaptation depend upon how well the system is engaged with its environment and other contexts influencing its organization. Some systems support other systems, maintaining the other system to prevent failure. The goals of systems theory are to model a system's dynamics, constraints, conditions, and relations; and to elucidate principles (such as purpose, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Systems Theory
Developmental systems theory (DST) is an overarching theoretical perspective on biological development, heredity, and evolution. It emphasizes the shared contributions of genes, environment, and epigenetic factors on developmental processes. DST, unlike conventional scientific theories, is not directly used to help make predictions for testing experimental results; instead, it is seen as a collection of philosophical, psychological, and scientific models of development and evolution. As a whole, these models argue the inadequacy of the modern evolutionary synthesis on the roles of genes and natural selection as the principal explanation of living structures. Developmental systems theory embraces a large range of positions that expand biological explanations of organismal development and hold modern evolutionary theory as a misconception of the nature of living processes. Overview All versions of developmental systems theory espouse the view that: * All biological processes (incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Systems Theory
Ecological systems theory is a broad term used to capture the theoretical contributions of developmental psychologist Urie Bronfenbrenner. Bronfenbrenner developed the foundations of the theory throughout his career, published a major statement of the theory in American Psychologist, articulated it in a series of propositions and hypotheses in his most cited book, ''The Ecology of Human Development'' and further developing it in ''The Bioecological Model of Human Development'' and later writings.Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979).The ecology of human development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. A primary contribution of ecological systems theory was to systemically examine contextual variability in development processes. As the theory evolved, it placed increasing emphasis on the role of the developing person as an active agent in development and on understanding developmental process rather than "social addresses" (e.g., gender, ethnicity) as explanatory mechanisms. Overview Ecol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemical Systems Theory
Biochemical systems theory is a mathematical modelling framework for biochemical systems, based on ordinary differential equations (ODE), in which biochemical processes are represented using power-law expansions in the variables of the system. This framework, which became known as Biochemical Systems Theory, has been developed since the 1960s by Michael Savageau, Eberhard Voit and others for the systems analysis of biochemical processes. According to Cornish-Bowden (2007) they "regarded this as a general theory of metabolic control, which includes both metabolic control analysis and flux-oriented theory as special cases". Athel Cornish-BowdenMetabolic control analysis FAQ website 18 April 2007. Representation The dynamics of a species is represented by a differential equation with the structure: \frac=\sum_j \mu_ \cdot \gamma_j \prod_k X_k^\, where ''X''''i'' represents one of the ''n''''d'' variables of the model (metabolite concentrations, protein concentrations or levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Theory In Anthropology
Systems theory in anthropology is an interdisciplinary, non-representative, non-referential, and non-Cartesian approach that brings together natural and social sciences to understand society in its complexity. The basic idea of a system theory in social science is to solve the classical problem of duality; mind-body, subject-object, form-content, signifier-signified, and structure-agency. Systems theory suggests that instead of creating closed categories into binaries (subject-object), the system should stay open so as to allow free flow of process and interactions. In this way the binaries are dissolved. Complex systems in nature involve a dynamic interaction of many variables (e.g. animals, plants, insects and bacteria; predators and prey; climate, the seasons and the weather, etc.) These interactions can adapt to changing conditions but maintain a balance both between the various parts and as a whole; this balance is maintained through homeostasis. Human societies are also co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Intelligence
Synthetic intelligence (SI) is an alternative/opposite term for artificial intelligence emphasizing that the intelligence of machines need not be an imitation or in any way artificial; it can be a genuine form of intelligence. John Haugeland proposes an analogy with simulated diamonds and synthetic diamonds—only the synthetic diamond is truly a diamond. Synthetic means that which is produced by synthesis, combining parts to form a whole; colloquially, a human-made version of that which has arisen naturally. A "synthetic intelligence" would therefore be or appear human-made, but not a simulation. Definition The term was used by Haugeland in 1986 to describe artificial intelligence research up to that point, which he called " good old fashioned artificial intelligence" or "GOFAI". AI's first generation of researchers firmly believed their techniques would lead to real, human-like intelligence in machines. After the first AI winter, many AI researchers shifted their focus from ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyber–physical System
Cyber-physical systems (CPS) are mechanisms controlled and monitored by computer algorithms, tightly integrated with the internet and its users. In cyber-physical systems, physical and software components are deeply intertwined, able to operate on different spatial and temporal scales, exhibit multiple and distinct behavioral modalities, and interact with each other in ways that change with context.Hu, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Robust formation control for networked robotic systems using Negative Imaginary dynamics Automatica, 2022. CPS involves transdisciplinary approaches, merging theory of cybernetics, mechatronics, design and process science.Patil T., Rebaioli L., Fassi I.,Cyber-physical systems for end-of-life management of printed circuit boards and mechatronics products in home automation: A review Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2022.Suh, S.C., Carbone, J.N., Eroglu, A.E.: ''Applied Cyber-Physical Systems.'' Springer, 2014. The process control is often referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |