|
System Management
Systems management is enterprise-wide administration of distributed systems including (and commonly in practice) computer systems. Systems management is strongly influenced by network management initiatives in telecommunications. The application performance management (APM) technologies are now a subset of Systems management. Maximum productivity can be achieved more efficiently through event correlation, system automation and predictive analysis which is now all part of APM. Discussion Centralized management has a time and effort trade-off that is related to the size of the company, the expertise of the IT staff, and the amount of technology being used: * For a small business startup with ten computers, automated centralized processes may take more time to learn how to use and implement than just doing the management work manually on each computer. * A very large business with thousands of similar employee computers may clearly be able to save time and money, by having IT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Administration
An IT administrator, system administrator, sysadmin, or admin is a person who is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and reliable operation of computer systems, especially multi-user computers, such as servers. The system administrator seeks to ensure that the uptime, performance, resources, and security of the computers they manage meet the needs of the users, without exceeding a set budget when doing so. To meet these needs, a system administrator may acquire, install, or upgrade computer components and software; provide routine automation; maintain security policies; troubleshoot; train or supervise staff; or offer technical support for projects. Related fields Many organizations staff offer jobs related to system administration. In a larger company, these may all be separate positions within a computer support or Information Services (IS) department. In a smaller group they may be shared by a few sysadmins, or even a single person. * A database administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Deployment
Software deployment is all of the activities that make a software system available for use. Deployment can involve activities on the producer (software developer) side or on the consumer ( user) side or both. Deployment to consumers is a hard task because the target systems are diverse and unpredictable. Software as a service avoids these difficulties by deploying only to dedicated servers that are typically under the producer's control. Because every software system is unique, the precise processes or procedures within each activity can hardly be defined. Therefore, "deployment" should be interpreted as a ''general process'' that has to be customized according to specific requirements or characteristics. History When computers were extremely large, expensive, and bulky (mainframes and minicomputers), the software was often bundled together with the hardware by manufacturers. If business software needed to be installed on an existing computer, this might require an expens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operational Intelligence
An operational definition specifies concrete, replicable procedures designed to represent a construct. In the words of American psychologist S.S. Stevens (1935), "An operation is the performance which we execute in order to make known a concept." For example, an operational definition of "fear" (the construct) often includes measurable physiologic responses that occur in response to a perceived threat. Thus, "fear" might be operationally defined as specified changes in heart rate, electrodermal activity, pupil dilation, and blood pressure. Overview An operational definition is designed to model or represent a concept or theoretical definition, also known as a construct. Scientists should describe the operations (procedures, actions, or processes) that define the concept with enough specificity such that other investigators can replicate their research. Operational definitions are also used to define system states in terms of a specific, publicly accessible process of preparation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IT Infrastructure
Information technology infrastructure is defined broadly as a set of information technology (IT) components that are the foundation of an IT service; typically physical components (Computer hardware, computer and networking hardware and facilities), but also various software and Computer network, network components. According to the ITIL Foundation Course Glossary, IT Infrastructure can also be termed as “All of the hardware, software, networks, facilities, etc., that are required to develop, test, deliver, monitor, control or support IT services. The term IT infrastructure includes all of the Information Technology but not the associated People, Processes and documentation.” Overview In IT Infrastructure, the above technological components contribute to and drive business functions. Leaders and managers within the IT field are responsible for ensuring that both the physical hardware and software networks and resources are working optimally. IT infrastructure can be looked at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
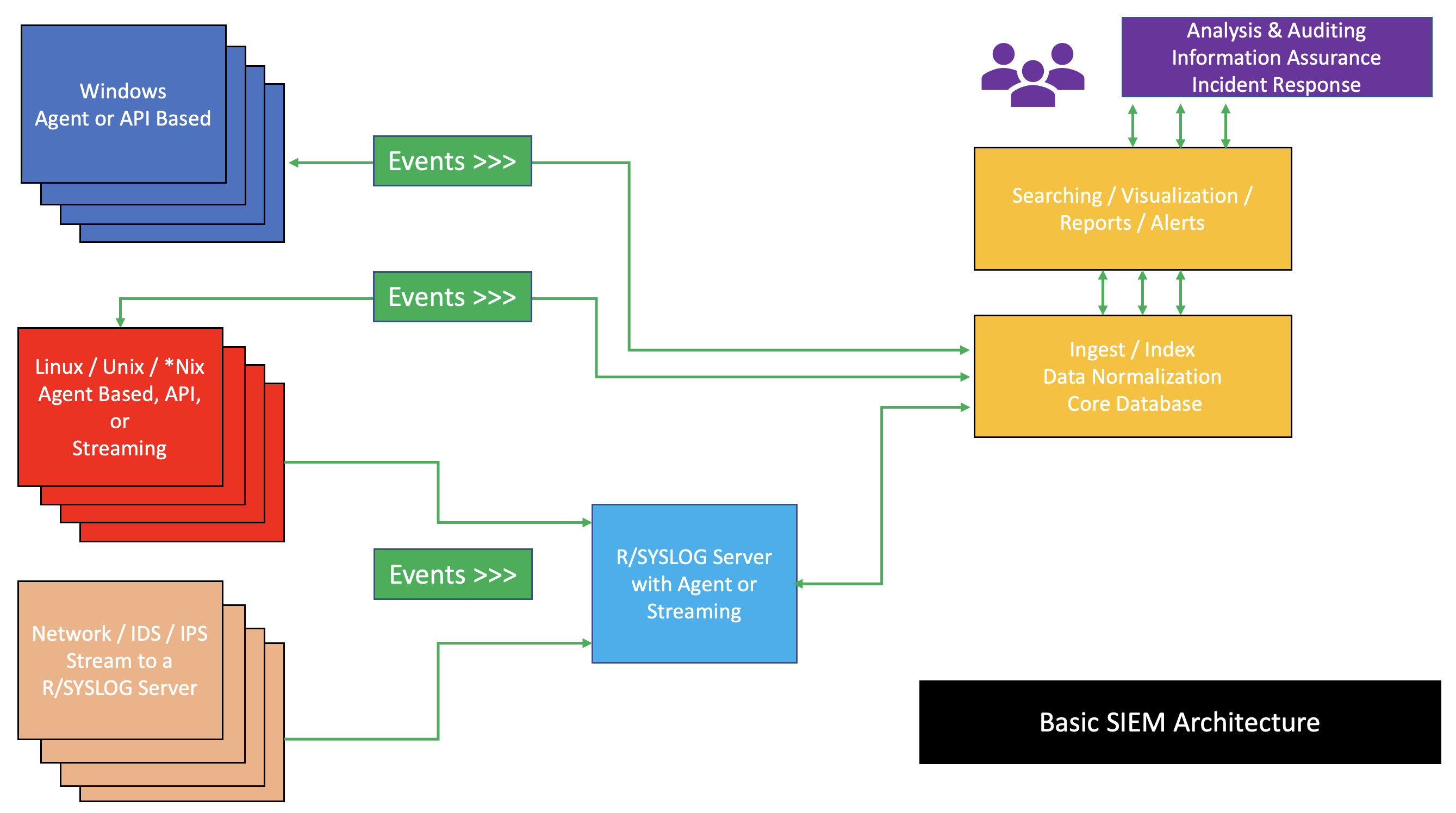
Security Information And Event Management
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a field within computer security that combines security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM) to enable real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. SIEM systems are central to Security operations center, security operations centers (SOCs), where they are employed to detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents. SIEM technology collects and aggregates data from various systems, allowing organizations to meet compliance requirements while safeguarding against Cyberattack, threats. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) definition for SIEM tool is application that provides the ability to gather security data from information system components and present that data as actionable information via a single interface. SIEM tools can be implemented as software, hardware, or managed services. SIEM systems log security events and generating reports to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacity Management
Capacity management's goal is to ensure that information technology resources are sufficient to meet upcoming business requirements cost-effectively. One common interpretation of capacity management is described in the ITIL framework. ITIL version 3 views capacity management as comprising three sub-processes: business capacity management, service capacity management, and component capacity management. As the usage of IT services change and functionality evolves, the amount of central processing units (CPUs), memory and storage to a physical or virtual server etc. also changes. If there are spikes in, for example, processing power at a particular time of the day, it proposes analyzing what is happening at that time and making changes to maximize the existing IT infrastructure; for example, tuning the application, or moving a batch cycle to a quieter period. This capacity planning identifies any potential capacity related issues likely to arise, and justifies any necessary inves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Systems Management
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." A business entity is not necessarily separate from the owner and the creditors can hold the owner liable for debts the business has acquired except for limited liability company. The taxation system for businesses is different from that of the corporates. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. A distinction is made in law and public offices between the term business and a company (such as a corporation or cooperative). Colloquially, the terms are used interchangeably. Corporations are distinct from sole proprietors and partnerships. Corporations are separate and unique legal entities from their shareholders; as such they provide limited liability for their owners and members. Corporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Policy Appliances
Middleware is a type of computer software program that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue". Middleware makes it easier for software developers to implement communication and input/output, so they can focus on the specific purpose of their application. It gained popularity in the 1980s as a solution to the problem of how to link newer applications to older legacy systems, although the term had been in use since 1968. In distributed applications The term is most commonly used for software that enables communication and management of data in distributed applications. An IETF workshop in 2000 defined middleware as "those services found above the transport (i.e. over TCP/IP) layer set of services but below the application environment" (i.e. below application-level APIs). In this more specific sense ''middleware'' can be described as the hyphen ("-") in '' client-server'', or the ''-to-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity Management
Identity and access management (IAM or IdAM) or Identity management (IdM), is a framework of policies and technologies to ensure that the right users (that are part of the ecosystem connected to or within an enterprise) have the appropriate access to technology resources. IAM systems fall under the overarching umbrellas of IT security and data management. Identity and access management systems not only identify, authenticate, and control access for individuals who will be utilizing IT resources but also the hardware and applications employees need to access. The terms "identity management" (IdM) and "identity and access management" are used interchangeably in the area of identity access management. Identity-management systems, products, applications and platforms manage identifying and ancillary data about entities that include individuals, computer-related hardware, and software applications. IdM covers issues such as how users gain an identity, the roles, and sometimes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Management
Security management is the identification of an organization's assets i.e. including people, buildings, machines, systems and information assets, followed by the development, documentation, and implementation of policies and procedures for protecting assets. An organization uses such security management procedures for information classification, threat assessment, risk assessment, and risk analysis to identify threats, categorize assets, and rate system vulnerabilities. Loss prevention Loss prevention focuses on what one's critical assets are and how they are going to protect them. A key component to loss prevention is assessing the potential threats to the successful achievement of the goal. This must include the potential opportunities that further the object (why take the risk unless there's an upside?) Balance probability and impact determine and implement measures to minimize or eliminate those threats. Security management includes the theories, concepts, ideas, met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Metering
Software metering is the monitoring and controlling of software for analytics and enforcing of agreements. It can be either passive data collection, or active restriction. Types Software metering can take different forms: * Tracking and maintaining software licenses. Making sure that the number of concurrent users of the software do not exceed the terms of the license. This can include monitoring of concurrent usage of software for real-time enforcement of license limits. * Real-time monitoring of all (or selected) applications running on the computers within the organization in order to detect unregistered or unlicensed software and prevent their execution, or limit their execution to within certain hours. The system administrator can configure the software metering agent on each computer in the organization. * Fixed planning to allocate software usage to computers according to the policies a company specifies and to maintain a record of usage and attempted usage. A company can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Performance Management
Business performance management (BPM) (also known as corporate performance management (CPM) enterprise performance management (EPM),) is a management approach which encompasses a set of processes and analytical tools to ensure that a business organization's activities and output are aligned with its goals. BPM is associated with business process management, a larger framework managing organizational processes. It aims to measure and optimize the overall performance of an organization, specific departments, individual employees, or processes to manage particular tasks. Performance standards are set by senior leadership and task owners which may include expectations for job duties, timely feedback and coaching, evaluating employee performance and behavior against desired outcomes, and implementing reward systems. BPM can involve outlining the role of each individual in an organization in terms of functions and responsibilities. History By 2017, Gartner had reclassified CPM as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |