|
Synne Strand
Saint Sunniva (10th century; Old Norse ''Sunnifa'', from Old English ''Sunngifu'') is the patron saint of the Norwegian Church of Norway Diocese of Bjørgvin, as well as all of Western Norway. Sunniva was venerated alongside her brother Alban, who in Norwegian tradition was identified with Saint Alban, the Roman-era British saint. Legend ''Acta sanctorum in Selio'' is a Latin hagiography of saints Alban and Sunniva and their companions. It is believed to have been composed shortly after 1170. Oddr Snorrason made use of it in his ''Óláfs saga Tryggvasonar'', in a section known as ''Albani þáttr ok Sunnifu'' ("tale of Alban and Sunniva") and also as ''Seljumanna þáttr''. Oddr's original work was composed in Latin but only survives in an Old Icelandic translation. The legend was also included in the later compilation ''Óláfs saga Tryggvasonar en mesta''. The tale is directly based on that in ''Acta sanctorum in Selio'', and thus slightly younger, although likely still b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albani þáttr Ok Sunnifu
''Albani þáttr ok Sunnifu'', also known as ''Seljumanna þáttr'', is a short tale (þáttr) about the Irish princess Sunniva who, not wishing to marry a heathen king, flees to the Norwegian island of Selje with her brother Albanus and a number of followers. The residents of the island suspect Sunniva and her companions of killing their livestock and ask Jarl Hákon to kill these ‘bandits’. On seeing Jarl Hákon and his men approach, Sunniva and her companions retreat to their caves and pray that God will not allow them to be killed by the evil men. In answer to their prayers, the caves collapse on the group. Their bodies stay buried until discovered by Olaf Tryggvason, who has them exhumed and has a church built in dedication to them. Together with '' Sörla þáttr'', '' Tóka þáttr Tókasonar,'' '' Norna-gests þáttr '' and '' Þorsteins þáttr uxafóts'', the tale is part of a subgenre of "pagan-contact þættir". The tale is recorded in Oddr Snorrason’s ''Ólá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incorruptibility
Incorruptibility is a Catholic and Orthodox belief that divine intervention allows some human bodies (specifically saints and beati) to completely or partially avoid the normal process of decomposition after death as a sign of their holiness. Incorruptibility is thought to occur even in the presence of factors which normally hasten decomposition, as in the cases of saints Catherine of Genoa, Julie Billiart and Francis Xavier. Catholicism In Catholicism, if a body is judged as incorruptible after death, this is most often seen as a sign that the individual is a saint. Canon law allows inspection of the body so that relics can be taken and sent to Rome. The relics must be sealed with wax and the body must be replaced after inspection. These ritual inspections are performed very rarely and can only be performed by a bishop according to the requirements of canon law. A pontifical commission can authorize inspection of the relics and demand a written report. After solemn inspectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
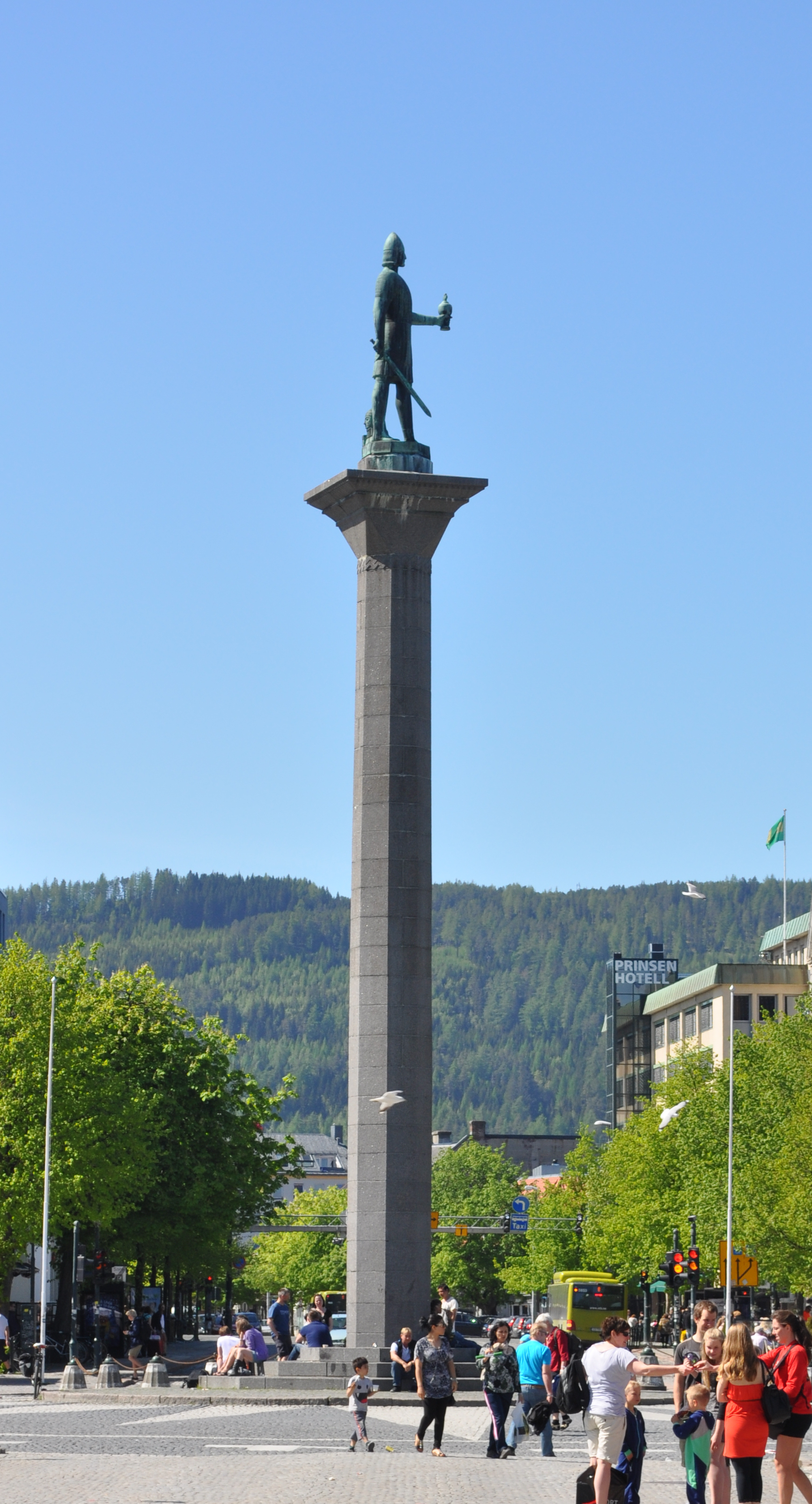
Olaf Tryggvason
Olaf Tryggvason (960s – 9 September 1000) was King of Norway from 995 to 1000. He was the son of Tryggvi Olafsson, king of Viken ( Vingulmark, and Rånrike), and, according to later sagas, the great-grandson of Harald Fairhair, first King of Norway. He is numbered as Olaf I. Olaf was important in the conversion of the Norse to Christianity, but he did so forcibly within his own kingdom. He is said to have built the first Christian church in Norway in 995, and to have founded the city of Trondheim in 997. A statue dedicated to him is located in the city's central plaza. Historical information on Olaf is sparse. He is mentioned in some contemporary English sources, and some skaldic poems. The oldest narrative source mentioning him briefly is Adam of Bremen's '' Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' of ''circa'' 1070. In the 1190s, two Latin versions of ''" Óláfs saga Tryggvasonar"'' were written in Iceland, by Oddr Snorrason and Gunnlaugr Leifsson – these are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hákon Sigurðarson
Haakon Sigurdsson ( , ; 937–995), known as Haakon Jarl (Old Norse: ''Hákon jarl''), was the '' de facto'' ruler of Norway from about 975 to 995. Sometimes he is styled as Haakon the Powerful (), though the '' Ágrip'' and ''Historia Norwegiæ'' give the less flattering name ''Hákon Illi'', that is, Haakon the Bad. Background Haakon was the son of Sigurd Haakonsson, Jarl of Lade and ruler of Trøndelag and Hålogaland. His mother was Bergljot Toresdatter, daughter of Tore Ragnvaldsson, Jarl of Møre. Adam of Bremen wrote that he was "of the stock of Ivar (either Ivar the Boneless or Ivar Vidfamne) and descended from a race of giants". In the sagas, Haakon claimed descent from the divine lineage of Sæming, son of Odin. The Hakon Jarl Runestones in Sweden may refer to him. Reign Haakon became ''jarl'' after his father was killed by King Harald Greycloak's men in 961. Haakon Jarl warred with King Harald for some time, until he was forced to flee to Denmark, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarl (title)
Jarl was a rank of the nobility in Scandinavia during the Viking Age and Early Middle Ages. The institution evolved over time and varied by region. In Old Norse, it meant "chieftain", specifically one appointed to rule a territory in a king's stead. It could also denote a sovereign prince. For example, during the Viking age, the rulers of several of the petty kingdoms of Norway held the title of ''jarl'', often wielding no less power than their neighboring kings. In later medieval Sweden and Norway, there was typically only one jarl in the kingdom, second in authority only to the king. The title became obsolete in the Middle Ages and was replaced by the rank of duke (''hertig''/''hertug''/''hertog''). The word is etymologically related to the English ''earl''. Etymology The term ''jarl'' (, Old Swedish: ''iarl'', ''iærl'', Old Danish: ''jærl'') has been connected to various similar words across Germanic languages, such as Proto-Norse ''eril,'' Old English ''eorl'' (meaning warr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Paganism
Old Norse religion, also known as Norse paganism, is a branch of Germanic paganism, Germanic religion which developed during the Proto-Norse language, Proto-Norse period, when the North Germanic peoples separated into Germanic peoples, distinct branches. It was replaced by Christianity and forgotten during the Christianisation of Scandinavia. Scholars reconstruct aspects of North Germanic Religion by historical linguistics, archaeology, toponymy, and records left by North Germanic peoples, such as runic alphabet, runic inscriptions in the Younger Futhark, a distinctly North Germanic extension of the runic alphabet. Numerous Old Norse works dated to the 13th-century record Norse mythology, a component of North Germanic religion. Old Norse religion was polytheistic, entailing a belief in Pantheon (religion), various gods and goddesses. These deities in Norse mythology were divided into two groups, the Æsir and the Vanir, who in some sources were said to have engaged in war until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a Dependencies of Norway, dependency, and not a part of the Kingdom; Norway also Territorial claims in Antarctica, claims the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. Norway has a population of 5.6 million. Its capital and largest city is Oslo. The country has a total area of . The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden, and is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast. Norway has an extensive coastline facing the Skagerrak strait, the North Atlantic Ocean, and the Barents Sea. The unified kingdom of Norway was established in 872 as a merger of Petty kingdoms of Norway, petty kingdoms and has existed continuously for years. From 1537 to 1814, Norway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinn
Kinn is a municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It was established on 1 January 2020. It is in the traditional districts of Nordfjord and Sunnfjord. The municipality is the only non-contiguous municipality in Norway since the municipality of Bremanger lies in between the north and south parts of Kinn. The administrative centres of the municipality is the two cities of Florø and Måløy. Some villages in the municipality include Rognaldsvåg, Stavang, Grov, Norddalsfjord, Nyttingnes, Steinhovden, Brandsøy, Deknepollen, Holvika, Kvalheim, Langeneset, Raudeberg, Refvika, Silda, Tennebø, Vedvika, and Vågsvåg. Historically, there was another municipality of Kinn in Norway that existed from 1838 until 1964. The "old" Kinn roughly corresponded to the southern part of the "new" municipality of Kinn. The municipality is the 142nd largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. Kinn is the 75th most populous municipality in Norway with a population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Invasions
Viking expansion was the historical movement which led Norse explorers, traders and warriors, the latter known in modern scholarship as Vikings, to sail most of the North Atlantic, reaching south as far as North Africa and east as far as Russia, and through the Mediterranean as far as Constantinople and the Middle East, acting as looters, traders, colonists and mercenaries. To the west, Vikings under Leif Erikson, the heir to Erik the Red, reached North America and set up a short-lived settlement in present-day L'Anse aux Meadows, Newfoundland, Canada. Longer lasting and more established Norse settlements were formed in Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Russia, Ukraine, Great Britain, Ireland, Normandy and Sicily. Motivation for expansion There is much debate among historians about what drove the Viking expansion. Researchers have suggested that Vikings may have originally started sailing and raiding due to a need to seek out women from foreign lands. The concept was ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
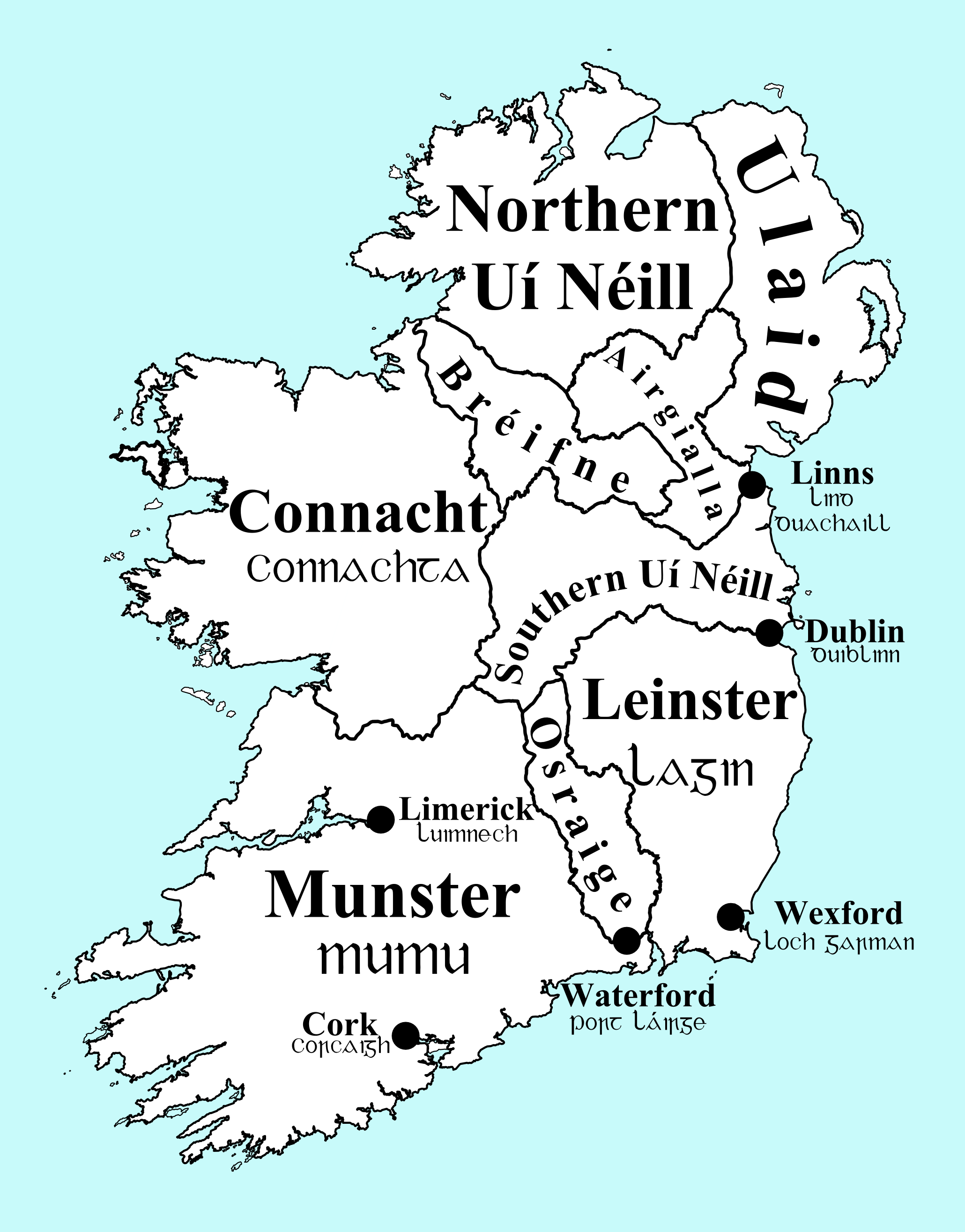
Gaelic Kingdoms Of Ireland
This article lists some of the attested Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic kingdoms of early medieval Ireland prior to the Norman invasion of Ireland, Norman invasion of 1169-72. For much of this period, the island was divided into numerous Irish clans, clan territories and kingdoms (known as ''túatha''). These túatha often competed for control of resources and thus they continually grew and shrank (in both size and number). In addition to kingdoms or túatha, Gaelic Ireland was also divided into Provinces of Ireland, five prime overkingdoms (Old Irish ''cóiceda'', Modern Irish ''cúige''). These were Ulster, Ulaid (in the north), Connacht (in the west), Leinster, Laighin (in the southeast), Munster, Mumhan (in the south) and Kingdom of Mide, Mide (in the centre). After the Norman invasion, much of the island came under the control of the Lordship of Ireland, although some parts remained under the control of Gaelic dynasties. After 1350, Norman control began to weaken, and a "History o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norna-Gests þáttr
''Nornagests þáttr'' or the ''Story of Norna-Gest'' is a legendary saga about the Norse hero Nornagestr, sometimes called Gestr, and here anglicized as Norna-Gest. ''Nornagests þáttr'' is as an episode of the '' Saga of Óláfr Tryggvason'' in the medieval Icelandic manuscript ''Flateyjarbók''. Summary Norna-Gest is the son of a Danish man named Thord Thingbiter, who once dwelt on the estate of Grøning in . As he relates in the tale, when he was born, three |