|
Synchronization Operations
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronous or ''in sync''—and those that are not are '' asynchronous''. Today, time synchronization can occur between systems around the world through satellite navigation signals and other time and frequency transfer techniques. Navigation and railways Time-keeping and synchronization of clocks is a critical problem in long-distance ocean navigation. Before radio navigation and satellite-based navigation, navigators required accurate time in conjunction with astronomical observations to determine how far east or west their vessel traveled. The invention of an accurate marine chronometer revolutionized marine navigation. By the end of the 19th century, important ports provided time signals in the form of a signal gun, flag, or dropping t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockettes 2239918515 96df95270e
Rockettes may refer to: * The Rockettes The Radio City Rockettes are an American precision dance company. Founded in 1925 in St. Louis, they have, since 1932, performed at Radio City Music Hall in New York City. Until 2015, they also had a touring company. They are best known for sta ..., a New York dance company famous for their kickline and eye-high kicks * Rockettes (synchronized skating team), a Finnish synchronized ice skating team * Rockette Morton (born 1949), U.S. musician See also * Can-can, a music hall dance * Rocket (other) * Rockett (other) * Roquette (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
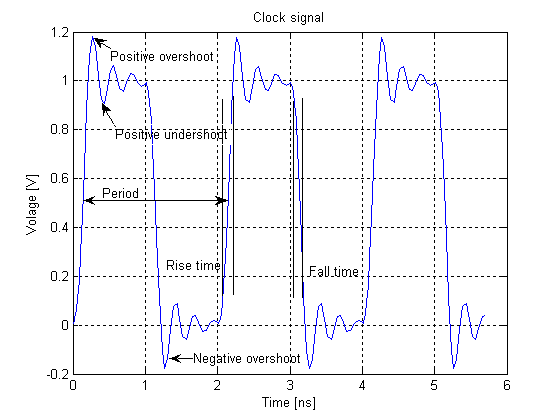
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Synchronization
Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillation, oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic potential, post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic scale, macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalography, electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time can apply to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or frequency of anything from microseconds to several seconds (as with the riff in a rock music song); to several minutes or hours, or, at the most extreme, even over many years. The Oxford English Dictionary defines rhythm as ''"The measured flow of words or phrases in verse, forming various patterns of sound as determined by the relation of long and short or stressed and unstressed syllables in a metrical foot or line; an instance of this"''. Rhythm is related to and distinguished from pulse, meter, and beats: In the performance arts, rhythm is the timing of events on a human scale; of musical sounds and silences that occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms, such as Text (literary theory), writing, Sound, audio, images, animations, or video, into a single presentation. This is in contrast to traditional mass media, such as printed material or audio recordings, which only feature one form of media content. Popular examples of multimedia include video podcasts, audio slideshows, and animated videos. Creating multimedia content involves the application of the principles of effective interactive communication. The five main building blocks of multimedia are text, image, audio, video, and animation. Multimedia encompasses various types of content, each serving different purposes: * Text - Fundamental to multimedia, providing context and information. * Audio - Includes music, sound effects, and voiceovers that enhance the experience. Recent developments include spatial audio and advanced sound design. * Ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lip Sync
Lip sync or lip synch (pronounced , like the word ''sink'', despite the Hard and soft C, spelling of the participial forms ''synced'' and ''syncing''), short for lip synchronization, is a technical term for matching a Speech, speaking or singing person's lip movements with sung or spoken vocals. Audio for lip syncing is generated through the sound reinforcement system in a live performance or via television, computer, cinema Loudspeaker, speakers, or other forms of Audio signal, audio output. The term can refer to any of a number of different techniques and processes, in the context of live performances and audiovisual recordings. In Filmmaking, film production, lip syncing is often part of the post-production phase. Dubbing foreign-language films and making Animation, animated characters appear to speak both require elaborate lip syncing. Many video games make extensive use of lip-synced sound files to create an immersive environment in which on-screen characters appear to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logy, -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of Adversary (cryptography), adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing Communication protocol, protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (confidentiality, data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, Smart card#EMV, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, password, computer passwords, and military communications. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronization (computer Science)
In computer science, synchronization is the task of coordinating multiple processes to join up or handshake at a certain point, in order to reach an agreement or commit to a certain sequence of action. Motivation The need for synchronization does not arise merely in multi-processor systems but for any kind of concurrent processes; even in single processor systems. Mentioned below are some of the main needs for synchronization: '' Forks and Joins:'' When a job arrives at a fork point, it is split into N sub-jobs which are then serviced by n tasks. After being serviced, each sub-job waits until all other sub-jobs are done processing. Then, they are joined again and leave the system. Thus, parallel programming requires synchronization as all the parallel processes wait for several other processes to occur. '' Producer-Consumer:'' In a producer-consumer relationship, the consumer process is dependent on the producer process until the necessary data has been produced. ''Exclusiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race Condition
A race condition or race hazard is the condition of an electronics, software, or other system where the system's substantive behavior is dependent on the sequence or timing of other uncontrollable events, leading to unexpected or inconsistent results. It becomes a bug when one or more of the possible behaviors is undesirable. The term ''race condition'' was already in use by 1954, for example in David A. Huffman's doctoral thesis "The synthesis of sequential switching circuits". Race conditions can occur especially in logic circuits or multithreaded or distributed software programs. Using mutual exclusion can prevent race conditions in distributed software systems. In electronics A typical example of a race condition may occur when a logic gate combines signals that have traveled along different paths from the same source. The inputs to the gate can change at slightly different times in response to a change in the source signal. The output may, for a brief period, chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (computing)
In computing, a process is the Instance (computer science), instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many thread (computing), threads. There are many different process models, some of which are light weight, but almost all processes (even entire virtual machines) are rooted in an operating system (OS) process which comprises the program code, assigned system resources, physical and logical access permissions, and data structures to initiate, control and coordinate execution activity. Depending on the OS, a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions Concurrency (computer science), concurrently. While a computer program is a passive collection of Instruction set, instructions typically stored in a file on disk, a process is the execution of those instructions after being loaded from the disk into memory. Several processes may be associated with the same program; for example, opening up several instances of the same progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thread (computing)
In computer science, a thread of execution is the smallest sequence of programmed instructions that can be managed independently by a scheduler, which is typically a part of the operating system. In many cases, a thread is a component of a process. The multiple threads of a given process may be executed concurrently (via multithreading capabilities), sharing resources such as memory, while different processes do not share these resources. In particular, the threads of a process share its executable code and the values of its dynamically allocated variables and non- thread-local global variables at any given time. The implementation of threads and processes differs between operating systems. History Threads made an early appearance under the name of "tasks" in IBM's batch processing operating system, OS/360, in 1967. It provided users with three available configurations of the OS/360 control system, of which Multiprogramming with a Variable Number of Tasks (MVT) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |