|
Swordsman
Swordsmanship or sword fighting refers to the skills and techniques used in combat and training with any type of sword. The term is modern, and as such was mainly used to refer to smallsword fencing, but by extension it can also be applied to any martial art involving the use of a sword. The formation of the English word "swordsman" is parallel to the Latin word ''gladiator'', a term for the professional fighters who fought against each other and a variety of other foes for the entertainment of spectators in the Roman Empire. The word ''gladiator'' itself comes from the Latin word ''gladius'', which is a type of sword. Europe Classical history The Roman legionaries and other forces of the Roman military, until the 2nd century A.D., used the gladius as a short thrusting sword effectively with the '' scutum'', a type of shield, in battle. According to Vegetius, the Romans mainly used underhanded stabs and thrusts, because one thrust into the gut would kill an enemy faster th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German School Of Swordsmanship
The German school of fencing (') is a system of combat taught in the Holy Roman Empire during the Late Medieval, German Renaissance, and early modern periods. It is described in the contemporary Fechtbücher ("fencing books") written at the time. The geographical center of this tradition was in what is now Southern Germany including Augsburg, Frankfurt, and Nuremberg. During the period in which it was taught, it was known as the ', or the ''"Art of Fighting"''. The German school of fencing focuses primarily on the use of the two-handed longsword; it also describes the use of many other weapons, including polearms, medieval daggers, messers (with or without a buckler), and the staff, as well as describing mounted combat and unarmed grappling ('' ringen''). Most authors of writings on the system are, or claim to be, in the tradition of the 14th-century master Johannes Liechtenauer. The earliest surviving treatise on Liechtenauer's system is a manuscript dated to possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fechtbuch
Martial arts manuals are instructions, with or without illustrations, specifically designed to be learnt from a book. Many books detailing specific techniques of martial arts are often erroneously called manuals but were written as treatises. Prose descriptions of martial arts techniques appear late within the history of literature, due to the inherent difficulties of describing a technique rather than just demonstrating it. The earliest extant manuscript on armed combat (as opposed to unarmed wrestling) is Royal Armouries Ms. I.33 ("I.33"), written in Franconia around 1300. Not within the scope of this article are books on military strategy such as Sun Tzu's ''The Art of War'' (before 100 BCE) or Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus' '' De Re Militari'' (4th century), or military technology, such as '' De rebus bellicis'' (4th to 5th century). Predecessors Some early testimonies of historical martial arts consist of series of images only. The earliest example is a fresco in tomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region. Historically, the sword developed in the Bronze Age, evolving from the dagger; the Bronze Age sword, earliest specimens date to about 1600 BC. The later Iron Age sword remained fairly short and without a crossguard. The spatha, as it developed in the Late Roman army, became the predecessor of the European sword of the Middle Ages, at first adopted as the Migration Period sword, and only in the High Middle Ages, developed into the classical Knightly sword, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fencing
Fencing is a combat sport that features sword fighting. It consists of three primary disciplines: Foil (fencing), foil, épée, and Sabre (fencing), sabre (also spelled ''saber''), each with its own blade and set of rules. Most competitive fencers specialise in one of these disciplines. The modern sport gained prominence near the end of the 19th century, evolving from historical European swordsmanship. The Italian school of swordsmanship, Italian school altered the Historical European martial arts, historical European martial art of classical fencing, and the French school of fencing, French school later refined that system. Scoring points in a fencing competition is done by making contact with the opponent with one's sword. The 1904 Olympic Games featured a fourth discipline of fencing known as singlestick, but it was dropped after that year and is not a part of modern fencing. Competitive fencing was one of the first sports to be featured in the Olympics and, along with Athl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martial Art
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defence; military and law enforcement applications; competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; and the preservation of a nation's intangible cultural heritage. The concept of martial arts was originally associated with East Asian tradition, but subsequently the term has been applied to practices that originated outside that region. Etymology "Martial arts" is a direct English translation of the Sino-Japanese word (, ). Literally, it refers to "武 martial" and "芸 arts". The term ''martial arts'' was popularized by mainstream popular culture during the 1960s to 1970s, notably by Hong Kong martial arts films (most famously those of Bruce Lee) during the so-called " chopsocky" wave of the early 1970s. According to John Clements, the term ''martial arts'' itself is derived from an older Latin term meaning "arts of Mars", the Roman god of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Liechtenauer
Johannes Liechtenauer (also ''Lichtnauer'', ''Hans Lichtenawer'') was a German Late Middle Ages, German fencing master who had a great level of influence on the German school of swordsmanship, German fencing tradition in the 14th century. Biography Liechtenauer seems to have been active during the mid-to-late 14th century in Germany, 14th century. The only extant biographical note on Liechtenauer is found in Nürnberger Handschrift GNM 3227a, GNM Hs. 3227a (dated c. 1400), which states that "Master Liechtenauer learnt and mastered [the art of the sword] in a thorough and rightful way, but he did not invent it or make it up himself, as it is stated before. Instead, he travelled across and visited many lands for the sake of this rightful and true art, as he wanted to study and know it." His German family names, surname indicates he was from a place called ''Liechtenau'' (modern ''Lichtenau''). There are several places with this name. Massmann (1844) mentions five candidate locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladiator
A gladiator ( , ) was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their lives and their legal and social standing by appearing in the arena. Most were despised as slaves, schooled under harsh conditions, socially marginalized, and segregated even in death. Irrespective of their origin, gladiators offered spectators an example of Rome's martial ethics and, in fighting or dying well, they could inspire admiration and popular acclaim. They were celebrated in high and low art, and their value as entertainers was commemorated in precious and commonplace objects throughout the Roman world. The origin of gladiatorial combat is open to debate. There is evidence of it in funeral rites during the Punic Wars of the 3rd century BC, and thereafter it rapidly became an essential feature of politics and social life in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
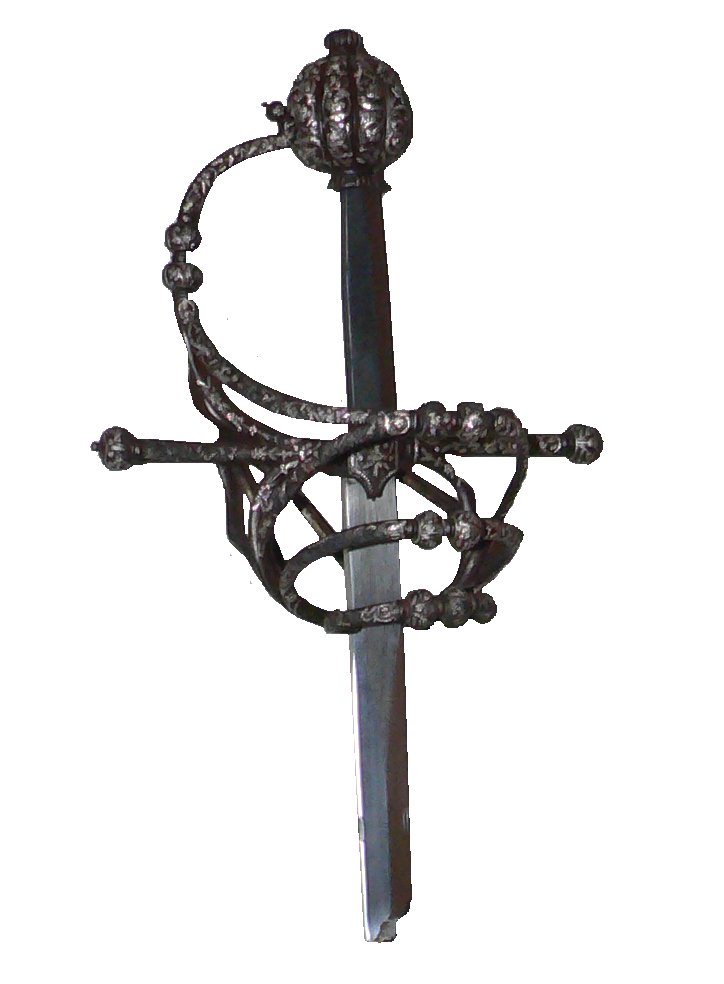
Hilt
The hilt (rarely called a haft or shaft) is the handle of a knife, dagger, sword, or bayonet, consisting of a guard, grip, and pommel. The guard may contain a crossguard or quillons. A tassel or sword knot may be attached to the guard or pommel. Pommel The pommel ( Anglo-Norman "little apple") is an enlarged fitting at the top of the handle. They were originally developed to prevent the sword from slipping from the hand. From around the 11th century in Europe, they became heavy enough to be a counterweight to the blade. This gave the sword a point of balance not too far from the hilt, allowing a more fluid fighting style. Depending on sword design and swordsmanship style, the pommel may also be used to strike the opponent (e.g. using the Mordhau technique). Pommels have appeared in a wide variety of shapes, including oblate spheroids, crescents, disks, wheels, and animal or bird heads. They are often engraved or inlayed with various designs and occasionally gilt and moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity. The concept of a knighthood may have been inspired by the ancient Greek '' hippeis'' (ἱππεῖς) and Roman ''equites''. In the Early Middle Ages in Western Christian Europe, knighthoods were conferred upon mounted warriors. During the High Middle Ages, a knighthood was considered a class of petty nobility. By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect courtly Christian warrior. Often, a knight was a vassal who served as an elite fighter or a bodyguard for a lord, with payment in the form of land holdings. The lords trusted the knights, who were skilled in battle on horseback. In the Middle Ages, a knighthood was closely linked with horsemanship (and especially the joust) from its orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Von Danzig (fencer)
Cod. 44 A 8 also known as MS 1449, Bibliotheca dell'Academica Nazionale dei Lincei e Corsiniana, is a Fechtbuch compiled by Peter von Danzig in 1452. Danzig was a 15th-century German fencing master. He was counted among the 17 members of the "society of Johannes Liechtenauer". The book reports teachings of Johannes Liechtenauer, Andres Lignitzer, Martin Hundfeld and Ott Jud, as well as original material by Peter von Danzig. Andres Lignitzer (Andreas Liegnitzer, Andrew of Liegnitz) was a late 14th- or early 15th-century German fencing master. His teachings are preserved by the mid-15th-century masters Peter von Danzig and Paulus Kal. Paulus Kal names him together with his brother Jacob as being members of the " Liechtenauer society". He may be identical with ''Andres Jud'' ("Andres the Jew") named in 3227a. An English translation of the treatise was published by Tobler (2010). See also * Historical European Martial Arts * German school of swordsmanship The German school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladius
''Gladius'' () is a Latin word properly referring to the type of sword that was used by Ancient Rome, ancient Roman foot soldiers starting from the 3rd century BC and until the 3rd century AD. Linguistically, within Latin, the word also came to mean "sword", regardless of the type used. Early ancient Roman swords were similar to those of the Greeks, called ''xiphos, xiphe'' (, : ''xiphos''). From the 3rd century BC, however, the Roman Republic, Romans adopted a weapon based on the sword of the Celtiberians of Hispania in service to Carthage during the Punic Wars, known in Latin as the ''gladius hispaniensis'', meaning "Hispania, Hispanic-type sword". The Romans improved the weapon and modified it depending on how their battle units waged war, and created over time new types of "''gladii''" such as the ''Mainz gladius'' and the ''Pompeii gladius''. Finally, in the third century AD the heavy Roman infantry replaced the ''gladius'' with the ''spatha'' (already common among Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund Ringeck
Sigmund Schining ein Ringeck (Sigmund ain Ringeck, Sigmund Amring, Sigmund Einring, Sigmund Schining) was a German fencing master. While the meaning of the surname "Schining" is uncertain, the suffix "ain Ringeck" may indicate that he came from the Rhineland region of south-western Germany. He is named in the text of his treatise as ''Schirmaister'' to one Duke Albrecht, Count Palatine of Rhine and Duke of Bavaria. Other than this, the only thing that can be determined about his life is that his renown as a master was sufficient for Paulus Kal to include him on his memorial to the deceased masters of the Society of Liechtenauer in 1470. Ringeck seems to have authored one of the few complete glosses of the epitome of the grand master Johannes Liechtenauer, making him one of the most important German fencing masters of the 15th century. The identity of Ringeck's patron remains unclear, as four men named Albrecht held the title during the fifteenth century. If it is Albrecht I, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |