|
Supermoon
A supermoon is a full moon or a new moon that nearly coincides with perigee—the closest that the Moon comes to the Earth in its orbit—resulting in a slightly larger-than-usual apparent size of the lunar disk as viewed from Earth. The technical name is a perigee syzygy (of the Earth–Moon–Sun system) or a full (or new) Moon around perigee. Because the term ''supermoon'' is astrological in origin, it has no precise astronomical definition. The association of the Moon with both oceanic and crustal tides has led to claims that the supermoon phenomenon may be associated with increased risk of events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, but no such link has been found. The opposite phenomenon, an apogee syzygy or a full (or new) Moon around apogee, has been called a micromoon. Definitions The name ''supermoon'' was coined by astrologer Richard Nolle in 1979, in '' Dell Horoscope'' magazine arbitrarily defined as: He came up with the name while reading ''Strategi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermoon Comparison
A supermoon is a full moon or a new moon that nearly coincides with perigee—the closest that the Moon comes to the Earth in Orbit of the Moon, its orbit—resulting in a slightly larger-than-usual apparent size of the lunar disk as viewed from Earth. The technical name is a perigee syzygy (of the Earth–Moon–Sun system) or a full (or new) Moon around perigee. Because the term ''supermoon'' is astrological in origin, it has no precise astronomical definition. The association of the Moon with both Tide, oceanic and Earth tide, crustal tides has led to claims that the supermoon phenomenon may be associated with increased risk of events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, but no such link has been found. The opposite phenomenon, an apogee syzygy or a full (or new) Moon around apogee, has been called a micromoon. Definitions The name ''supermoon'' was coined by astrologer Richard Nolle in 1979, in ''Dell Horoscope'' magazine arbitrarily defined as: He came up with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dell Horoscope
''Dell Horoscope'' was a periodic American magazine originally published by Dell Magazines and then sold to Penny Publications covering modern astrology, calling itself "the world's leading astrology magazine". It was in circulation between 1935 and 2020. History The magazine was first published in November 1935 with the title ''Your Daily Horoscope: The Monthly Magazine of Personal Astrology''. Its title changed several times during its existence. The magazine was published in New York City from its start in 1935 to 1985. The publication received attention outside of the astrology community in recent years because of a 1979 article by Richard Nolle defining the concept of a supermoon A supermoon is a full moon or a new moon that nearly coincides with perigee—the closest that the Moon comes to the Earth in its orbit—resulting in a slightly larger-than-usual apparent size of the lunar disk as viewed from Earth. The te .... According to its most recent statement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
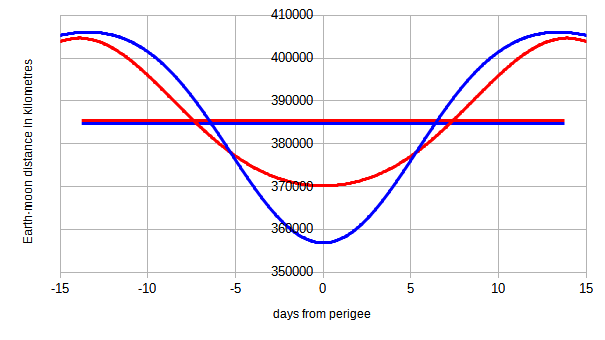
Lunar Distance
The instantaneous Earth–Moon distance, or distance to the Moon, is the distance from the center of Earth to the center of the Moon. In contrast, the Lunar distance (LD or \Delta_), or Earth–Moon characteristic distance, is a unit of measure in astronomy. More technically, it is the semi-major axis of the geocentric lunar orbit. The average lunar distance is approximately , or 1.3 light-seconds. It is roughly 30 times Earth's diameter and a non-stop plane flight traveling that distance would take more than two weeks. Around 389 lunar distances make up an astronomical unit (roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun). Lunar distance is commonly used to express the distance to near-Earth object encounters. Lunar semi-major axis is an important astronomical datum. It has implications for testing gravitational theories such as general relativity and for refining other astronomical values, such as the mass, radius, and rotation of Earth. The measurement is also useful in measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon Distance With Full & New
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It orbits around Earth at an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth's diameter). The Moon rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the largest and most massive satellite in relation to its parent planet, the fifth-largest and fifth-most massive moon overall, and larger and more massive than all known dwarf planets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |