|
Superhard
A superhard material is a material with a hardness value exceeding 40 gigapascals ( GPa) when measured by the Vickers hardness test. They are virtually incompressible solids with high electron density and high bond covalency. As a result of their unique properties, these materials are of great interest in many industrial areas including, but not limited to, abrasives, polishing and cutting tools, disc brakes, and wear-resistant and protective coatings. Diamond is the hardest known material to date, with a Vickers hardness in the range of 70–150 GPa. Diamond demonstrates both high thermal conductivity and electrically insulating properties, and much attention has been put into finding practical applications of this material. However, diamond has several limitations for mass industrial application, including its high cost and oxidation at temperatures above 800 °C. In addition, diamond dissolves in iron and forms iron carbides at high temperatures and therefore is ineffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OsB2
Osmium borides are compounds of osmium and boron. Their most remarkable property is potentially high hardness. It is thought that a combination of high electron density of osmium with the strength of boron-osmium covalent bonds will make osmium borides superhard materials, however this has not been demonstrated yet. For example, OsB2 is hard (hardness comparable to that of sapphire), but not superhard. Synthesis Osmium borides are produced in vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent formation of osmium tetroxide Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the ..., which is a hazardous compound. Synthesis occurs at high temperatures (~1000 °C) from a mixture of MgB2 and OsCl3. Structure Three osmium borides are known: OsB, Os2B3 and OsB2. The first two have hexagonal structure, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregated Diamond Nanorod
Aggregated diamond nanorods, or ADNRs, are a nanocrystalline form of diamond, also known as nanodiamond or hyperdiamond. Discovery Nanodiamond or hyperdiamond was produced by compression of graphite in 2003 by a group of researchers in Japan and in the same work, published in ''Nature'', it was shown to be much harder than bulk diamond. Later it was also produced by compression of fullerene and confirmed to be the hardest and least compressible known material, with an isothermal bulk modulus of 491 gigapascals (GPa), while a conventional diamond has a modulus of 442–446 GPa; these results were inferred from X-ray diffraction data, which also indicated that ADNRs are 0.3% denser than regular diamond. The same group later described ADNRs as "having a hardness and Young's modulus comparable to that of natural diamond, but with 'superior wear resistance'". Hardness A surface (normal to the largest diagonal of a cube) of pure diamond has a hardness value of 167±6 GPa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ReB2
Rhenium diboride (ReB2) is a synthetic superhard material. It was first synthesized in 1962 and re-emerged recently due to hopes of achieving high hardness comparable to that of diamond. The reported ultrahigh hardness has been questioned, although this is a matter of definition as in the initial test rhenium diboride was able to scratch diamond. The production method of this material does not involve high pressures as with other hard synthetic materials, such as cubic boron nitride, which makes production cheap. However, rhenium itself is an expensive metal. The compound is formed from a mixture of rhenium, noted for its resistance to high pressure, and boron, which forms short, strong covalent bonds with rhenium. Synthesis ReB2 can be synthesized by at least three different methods at standard atmospheric pressure: solid-state metathesis, melting in an electric arc, and direct heating of the elements. In the metathesis reaction, rhenium trichloride and magnesium d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPHT
Lab-grown diamond (LGD; also called laboratory-grown, laboratory-created, man-made, artisan-created, artificial, synthetic, or cultured diamond) is diamond that is produced in a controlled technological process (in contrast to naturally formed diamond, which is created through geological processes and obtained by mining). Unlike diamond simulants (imitations of diamond made of superficially-similar non-diamond materials), synthetic diamonds are composed of the same material as naturally formed diamonds – pure carbon crystallized in an isotropic 3D form – and share identical chemical and physical properties. Numerous claims of diamond synthesis were reported between 1879 and 1928; most of these attempts were carefully analyzed but none was confirmed. In the 1940s, systematic research of diamond creation began in the United States, Sweden and the Soviet Union, which culminated in the first reproducible synthesis in 1953. Further research activity yielded the discoveries of HP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
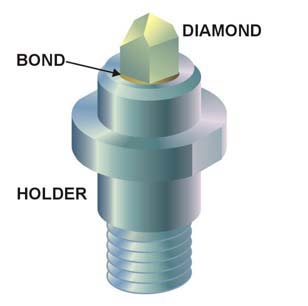
Diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Boron Nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic ( zincblende aka sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN; it is softer than diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite but slightly softer than the cubic form. Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. Structure Boron nitride exists in multiple forms that differ in the arrangement of the boron and nitrogen atoms, giving rise to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohs Scale Of Mineral Hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a Qualitative property, qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch hardness, scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material. The scale was introduced in 1812 by the German geologist and Mineralogy, mineralogist Friedrich Mohs, in his book ''"Versuch einer Elementar-Methode zur naturhistorischen Bestimmung und Erkennung der Fossilien"''; it is one of several definitions of Hardness comparison, hardness in materials science, some of which are more quantitative. The method of comparing hardness by observing which minerals can scratch others is of great antiquity, having been mentioned by Theophrastus in his treatise ''On Stones'', , followed by Pliny the Elder in his ''Natural History (Pliny), Naturalis Historia'', . The Mohs scale is useful for identification of minerals in the field, but is not an accurate predictor of how well materials endure in an industrial s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Materials Research
The ''Annual Review of Materials Research'' is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes review articles about materials science. It has been published by the nonprofit Annual Reviews since 1971, when it was first released under the title the ''Annual Review of Materials Science''. Three people have served as editors, with the current editor David R. Clarke serving in the position since 2001. It has an impact factor of 13.972 as of 2022. History The ''Annual Review of Materials Science'' was first published in 1971 by the nonprofit publisher Annual Reviews, making it their sixteenth journal. Its first editor was Robert Huggins. In 2001, its name was changed to the current form, the ''Annual Review of Materials Research''. The name change was intended "to better reflect the broad appeal that materials research has for so many diverse groups of scientists and not simply those who identify themselves with the academic discipline of materials science." As of 2020, it was published both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Modulus
In materials science, shear modulus or modulus of rigidity, denoted by ''G'', or sometimes ''S'' or ''μ'', is a measure of the elastic shear stiffness of a material and is defined as the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain: :G \ \stackrel\ \frac = \frac = \frac where :\tau_ = F/A \, = shear stress :F is the force which acts :A is the area on which the force acts :\gamma_ = shear strain. In engineering :=\Delta x/l = \tan \theta , elsewhere := \theta :\Delta x is the transverse displacement :l is the initial length of the area. The derived SI unit of shear modulus is the pascal (Pa), although it is usually expressed in gigapascals (GPa) or in thousand pounds per square inch (ksi). Its dimensional form is M1L−1T−2, replacing ''force'' by ''mass'' times ''acceleration''. Explanation The shear modulus is one of several quantities for measuring the stiffness of materials. All of them arise in the generalized Hooke's law: * Young's modulus ''E'' describes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Hardened Steel-vickers Hardness Test
Case or CASE may refer to: Containers * Case (goods), a package of related merchandise * Cartridge case or casing, a firearm cartridge component * Bookcase, a piece of furniture used to store books * Briefcase or attaché case, a narrow box to carry paperwork * Computer case, the enclosure for a PC's main components * Keep case, DVD or CD packaging * Pencil case * Phone case, protective or vanity accessory for mobile phones ** Battery case * Road case or flight case, for fragile equipment in transit * Shipping container or packing case * Suitcase, a large luggage box * Type case, a compartmentalized wooden box for letterpress typesetting Places * Case, Laclede County, Missouri * Case, Warren County, Missouri * Case River, a Kabika tributary in Ontario, Canada * Case Township, Michigan * Case del Conte, Italy People * Case (name), people with the surname (or given name) * Case (singer), American R&B singer-songwriter and producer (Case Woodard) Arts, entertainment, and media * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |