|
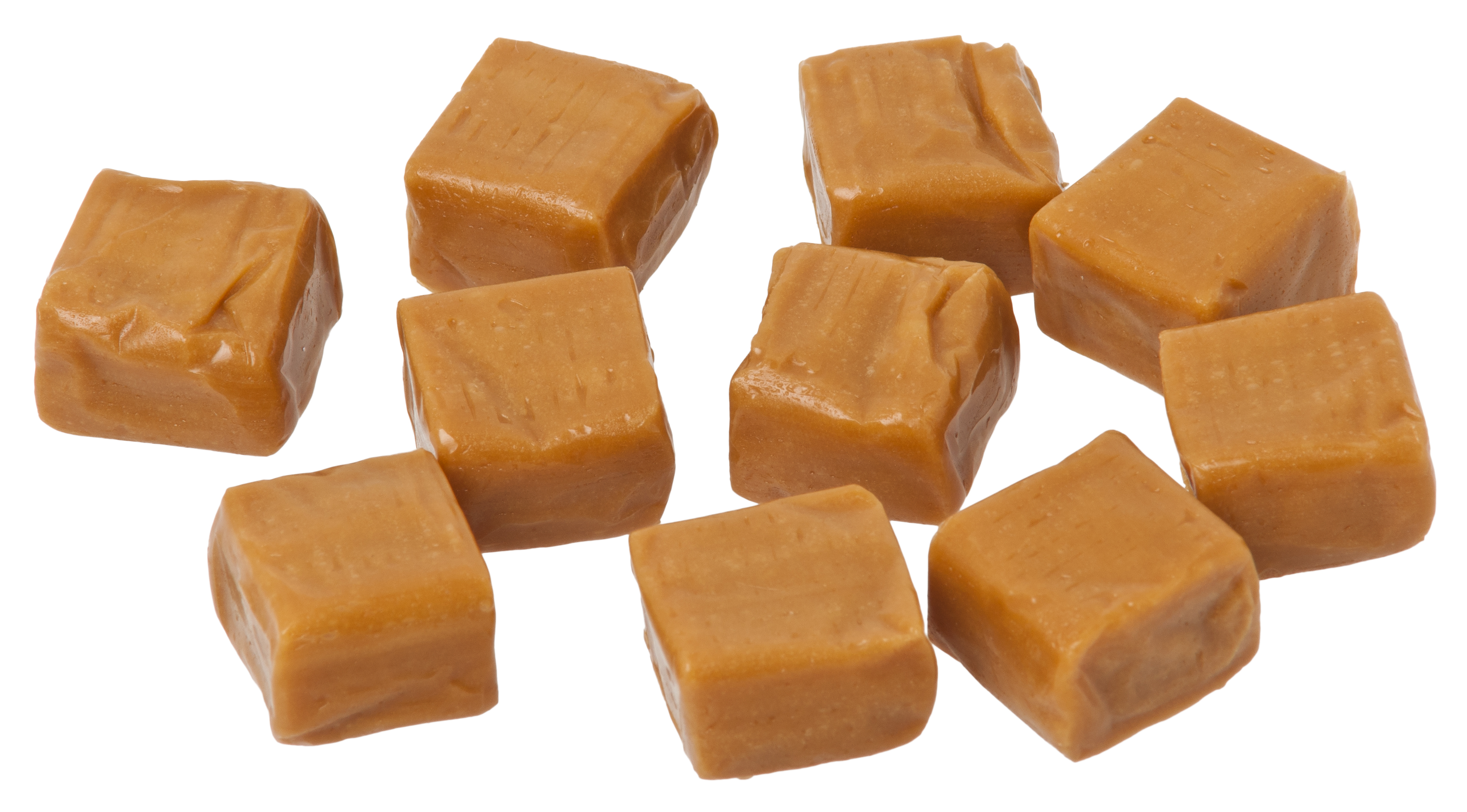
Sugar Candy
Sugar candy is any candy whose primary ingredient is sugar. The main types of sugar candies are hard candies, fondants, Caramel, caramels, jellies, and Nougat, nougats. In British English, this broad category of sugar candies is called ''sweets'', and the name ''candy'' or ''sugar-candy'' is used only for hard candies that are nearly solid sugar. Sugar candy is a sub-type of candy, which includes sugar candies as well as Chocolate, chocolates, chewing gum and other sweet foods. Candy, in turn, is a sub-type of confectionery, which also includes sweet pastries and sometimes ice cream. History The oldest sugar candies are presumed to have been made where the sugar cane plant was domesticated. Sugar cane probably originated in Papua New Guinea, and from there was taken to Southeast Asia and other Pacific Islands, and ultimately to India and China. From India, sugar spread to the Arab states and eventually to Europe. Traditional uses Sugar candy is often used to sweeten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Candy
A hard candy (American English), or boiled sweet (British English), is a sugar candy prepared from one or more sugar-based syrups that is heated to a temperature of 160 °C (320 °F) to make candy. Among the many hard candy varieties are stick candy such as the candy cane, lollipops, rock, aniseed twists, and '' bêtises de Cambrai''. Most hard candy is nearly 100% sugar by weight, with a tiny amount of other ingredients for color or flavor, and negligible water content in the final product. Recipes for hard candy may use syrups of sucrose, glucose, fructose or other sugars. Sugar-free versions have also been created. Creation Recipes for hard candy use a sugar syrup, such as sucrose, glucose or fructose. This is heated to a particular temperature, at which point the candy maker removes it from the heat source and may add citric acid, food dye, and some flavouring, such as a plant extract, essential oil, or flavourant. The syrup concoction, which is now ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tong Sui
''Tong sui'' (; ) or ''tim tong'' is a general term for any sweet soup served as a dessert typically at the end of a meal in Chinese cuisine. ''Tong sui'' originated in the Lingnan region of China, including Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong, Macau, and some parts of other provinces in China. Therefore, in the narrow sense, the term tong sui is used to refer to soupy desserts from Lingnan, while occasionally it is also used in the broad sense, referring to any soupy dessert in Chinese-speaking regions. A large variety of tong sui can be found in specialty stores dedicated to these desserts, called tong sui stores. Today, they have gained prominence in other parts of China and overseas. People can find tong sui stores in various parts of Canada, Australia, and the United States, showcasing the global appeal of these treats. History The origin of Tong sui is hard to track, and its development in different regions also varied. One main theory is that the climate in Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caramel
Caramel ( or ) is a range of food ingredients made by heating sugars to high temperatures. It is used as a flavoring in puddings and desserts, as a filling in bonbons or candy bars, as a topping for ice cream and custard, and as a colorant commonly used in drinks. The process of caramelization primarily consists of heating sugars slowly to around . As the sugar heats, the molecules break down and re-form into compounds with a characteristic colour and flavour. A variety of sweets, desserts, toppings, and confections are made with caramel, including tres leches cake, brittles, nougats, pralines, flan, crème brûlée, crème caramel, and caramel apples. Ice creams are sometimes flavored with or contain swirls of caramel. Etymology The English word comes from French ', borrowed from Spanish (18th century), itself possibly from Portuguese '. Most likely that comes from Late Latin ' 'sugar cane', a diminutive of 'reed, cane', itself from Greek . Less likely, it com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Candies
A hard candy (American English), or boiled sweet (British English), is a sugar candy prepared from one or more sugar-based syrups that is heated to a temperature of 160 °C (320 °F) to make candy. Among the many hard candy varieties are stick candy such as the candy cane, lollipops, rock, aniseed twists, and '' bêtises de Cambrai''. Most hard candy is nearly 100% sugar by weight, with a tiny amount of other ingredients for color or flavor, and negligible water content in the final product. Recipes for hard candy may use syrups of sucrose, glucose, fructose or other sugars. Sugar-free versions have also been created. Creation Recipes for hard candy use a sugar syrup, such as sucrose, glucose or fructose. This is heated to a particular temperature, at which point the candy maker removes it from the heat source and may add citric acid, food dye, and some flavouring, such as a plant extract, essential oil, or flavourant. The syrup concoction, which is now very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fondant Candy
Fondant is a mixture of sugar and water used as a confection, filling, or icing. Sometimes gelatin and glycerine are used as softeners or stabilizers. There are numerous varieties of fondant, with the most basic being poured fondant. Others include fondant icing, chocolate fondant, and honey fondant. Poured fondant ''Poured fondant'' is a creamy confection used as a filling or coating for cakes, pastries, and candies or sweets. In its simplest form, it is sugar and water. Sometimes it is stabilized with gelatin and glycerine. It is cooked to the soft-ball stage, cooled slightly, and stirred or beaten to incorporate air, until it is an opaque mass with a creamy consistency. Sometimes lemon or vanilla is added to the mixture for taste. Other flavorings are used as well, as are various colorings. An example of its use is the Cadbury Creme Egg, the filling of which is inverted sugar syrup, produced by processing fondant with invertase. Fondant fancies are a type of cake typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fudge
''Fudge'' is a generic role-playing game system for use in freeform role-playing games. The name "''FUDGE''" was once an acronym for ''Freeform Universal Donated'' (later, ''Do-it-yourself'') ''Gaming Engine'' and, though the acronym has since been dropped, that phrase remains a good summation of the game's design goals. ''Fudge'' has been nominated for an Origins Award for ''Best Role-Playing Game System'' for the '' Deryni Adventure Game''. Rather than being a rigidly pre-defined set of rules like ''d20 System'' or ''GURPS'', ''Fudge'' offers a customizable toolkit for building the users' own specialized role-playing game system. Such things as what attributes and skills will define characters are left to be determined by the Game Master and players, and several different optional systems for resolving actions and conflicts are offered. ''Fudge'' is not tied to any particular genre or setting and world builders are encouraged to invent appropriate attributes and rules tailored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallization
Crystallization is a process that leads to solids with highly organized Atom, atoms or Molecule, molecules, i.e. a crystal. The ordered nature of a crystalline solid can be contrasted with amorphous solids in which atoms or molecules lack regular organization. Crystallization can occur by various routes including Precipitation (chemistry), precipitation from solution, freezing of a liquid, or Deposition (phase transition), deposition from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal can depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, cooling rate, or Solution (chemistry), solute concentration. Crystallization occurs in two major steps. The first is nucleation, the appearance of a crystalline phase from either a Supercooling, supercooled liquid or a supersaturation, supersaturated solvent. The second step is known as crystal growth, which is the increase in the size of particles and leads to a crystal state. An important feature of this step is that loose particles fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
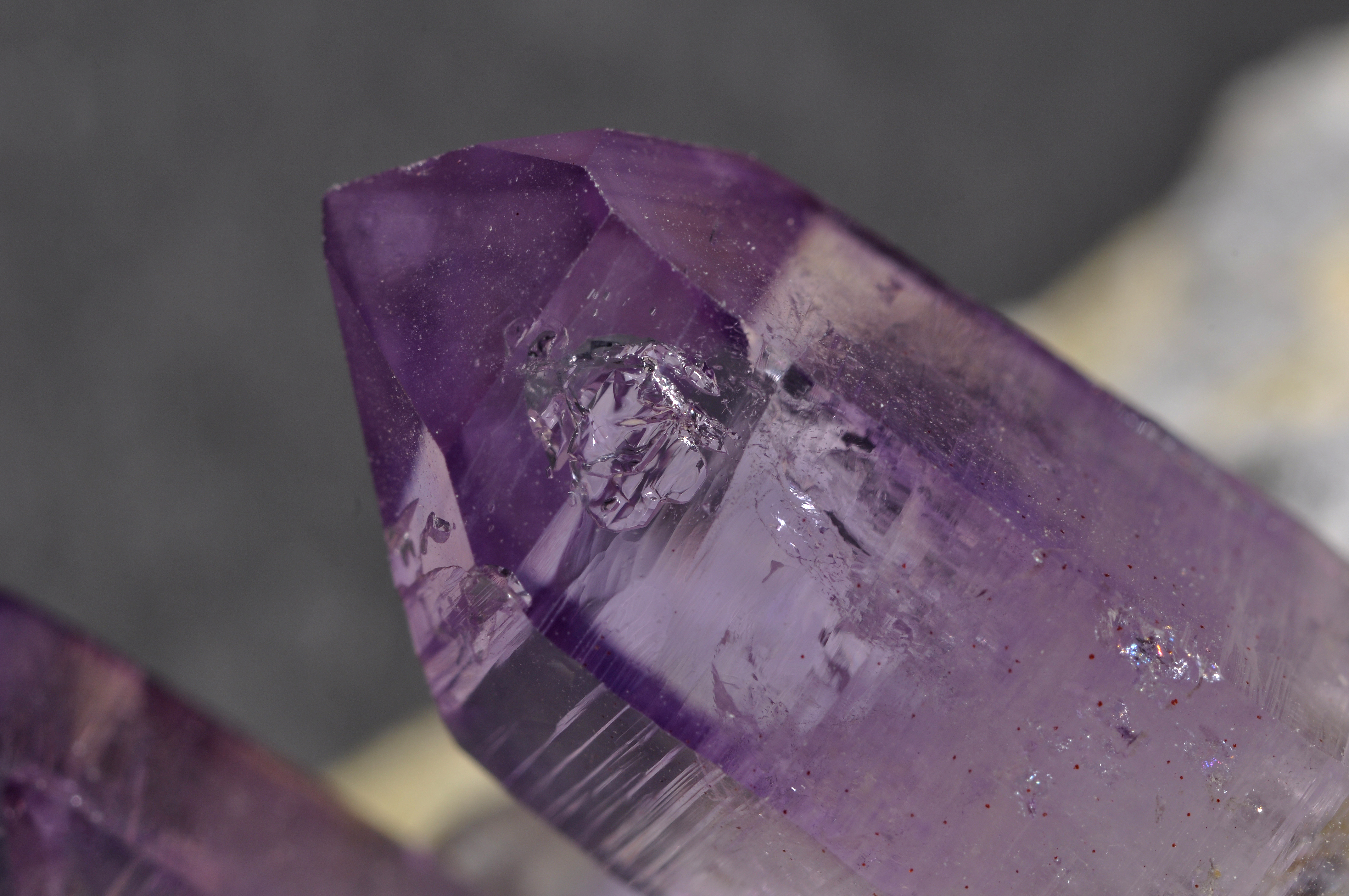
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is a characteristic of a crystal. The terms "glass" and "glassy solid" are sometimes used synonymously with amorphous solid; however, these terms refer specifically to amorphous materials that undergo a glass transition. Examples of amorphous solids include glasses, metallic glasses, and certain types of plastics and polymers. Etymology The term "Amorphous" comes from the Greek language, Greek ''a'' ("without"), and ''morphé'' ("shape, form"). Structure Amorphous materials have an internal structure of molecular-scale structural blocks that can be similar to the basic structural units in the crystalline phase of the same compound. Unlike in crystalline materials, however, no long-range regularity exists: amorphous materials cannot be described by the repetition of a finite unit cell. Statistical measures, such as the atomic density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third categor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
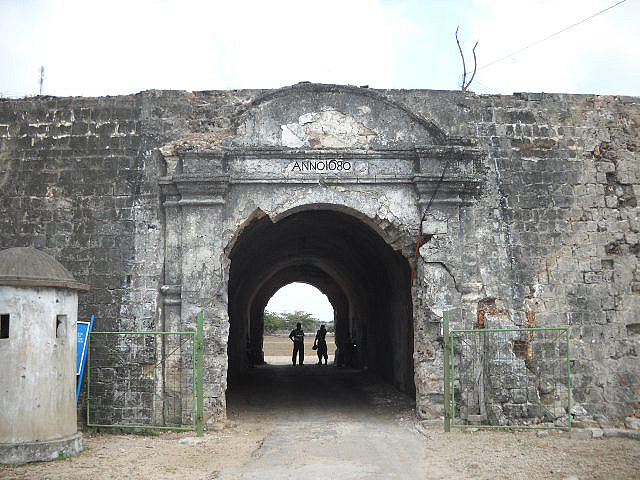
Jaffna
Jaffna (, ; , ) is the capital city of the Northern Province, Sri Lanka, Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jaffna District located on a Jaffna Peninsula, peninsula of the same name. With a population of 88,138 in 2012, Jaffna is Sri Lanka's 12th List of cities in Sri Lanka, most populous city. Jaffna is approximately from Kandarodai which served as an Marketplace, emporium in the Jaffna peninsula from classical antiquity. Jaffna's suburb Nallur, Jaffna, Nallur served as the capital of the four-century-long medieval Tamil Jaffna Kingdom. Prior to the Sri Lankan civil war, Sri Lankan Civil War, it was Sri Lanka's second most populous city after Colombo. The 1980s insurgent uprising led to extensive damage, expulsion of part of the population, and military occupation. Since the end of civil war in 2009, refugees and internally displaced people began returning to homes, while government and private sector reconstruction started taking plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |