|
Sudetes
The Sudetes ( ), also known as the Sudeten Mountains or Sudetic Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince of the Bohemian Massif province in Central Europe, shared by the Czech Republic, Poland and Germany. They consist mainly of mountain ranges and are the highest part of the Bohemian Massif. They stretch from the Saxon capital of Dresden in the northwest across to the region of Lower Silesia in Poland and to the city of Ostrava in the Czech Republic in the east. Geographically the Sudetes are a '' Mittelgebirge'' with some characteristics typical of high mountains. Its plateaus and subtle summit relief makes the Sudetes more akin to mountains of Northern Europe than to the Alps. In the east of the Sudetes, the Moravian Gate and Ostrava Basin separates from the Carpathian Mountains. The Sudetes' highest mountain is Sněžka () at , which is also the highest mountain of the Czech Republic, Bohemia, Silesia, and Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It lies in the Giant Mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship (, ) in southwestern Poland, is one of the 16 Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeships (provinces) into which Poland is divided. It covers an area of and has a total population of 2,899,986. It is one of the wealthiest provinces in Poland, as natural resources such as copper, Lignite, brown coal and rock materials are widely present. Its capital and largest city is Wrocław, situated on the Oder, Oder River. The voivodeship is host to several spa towns, many castles and palaces, and the Giant Mountains, with several ski resorts. For this reason, tourism is a large part of this region's economy. History In the past 1,200 years, the region has been part of Great Moravia, the Medieval Kingdom of Poland, the Crown of Bohemia, Kingdom of Hungary, Habsburg monarchy (Austria), Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire, and modern Poland after 1945. Silesian tribes settled the lands at the end of the first millennium after the Migration Period. In the 9th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karkonosze National Park
Giant Mountains National Park () is a National Park in the Giant Mountains in the Sudetes in southwestern Poland, along the border with the Czech Republic. The national park is located in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in the highest part of the Sudetes. It was created in 1959, covering an area of 55.10 km2. Today it is slightly larger at , of which 17.18 km2 is strictly protected. The majority of the park area, around 33.80 km2, consists of forests. In 1992 Karkonosze National Park, together with the neighbouring Czech Krkonoše National Park, became part of the Krkonoše/Karkonosze Transboundary Biosphere Reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme. (SeeUNESCO brochure in PDF). Also, 40 hectares of peat bogs were designated a Ramsar international wetland site. Geography The Giant Mountains are the highest range of the much broader Sudetes mountains stretching horizontally from south-western Poland along the northern border of the Czech Republic to eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
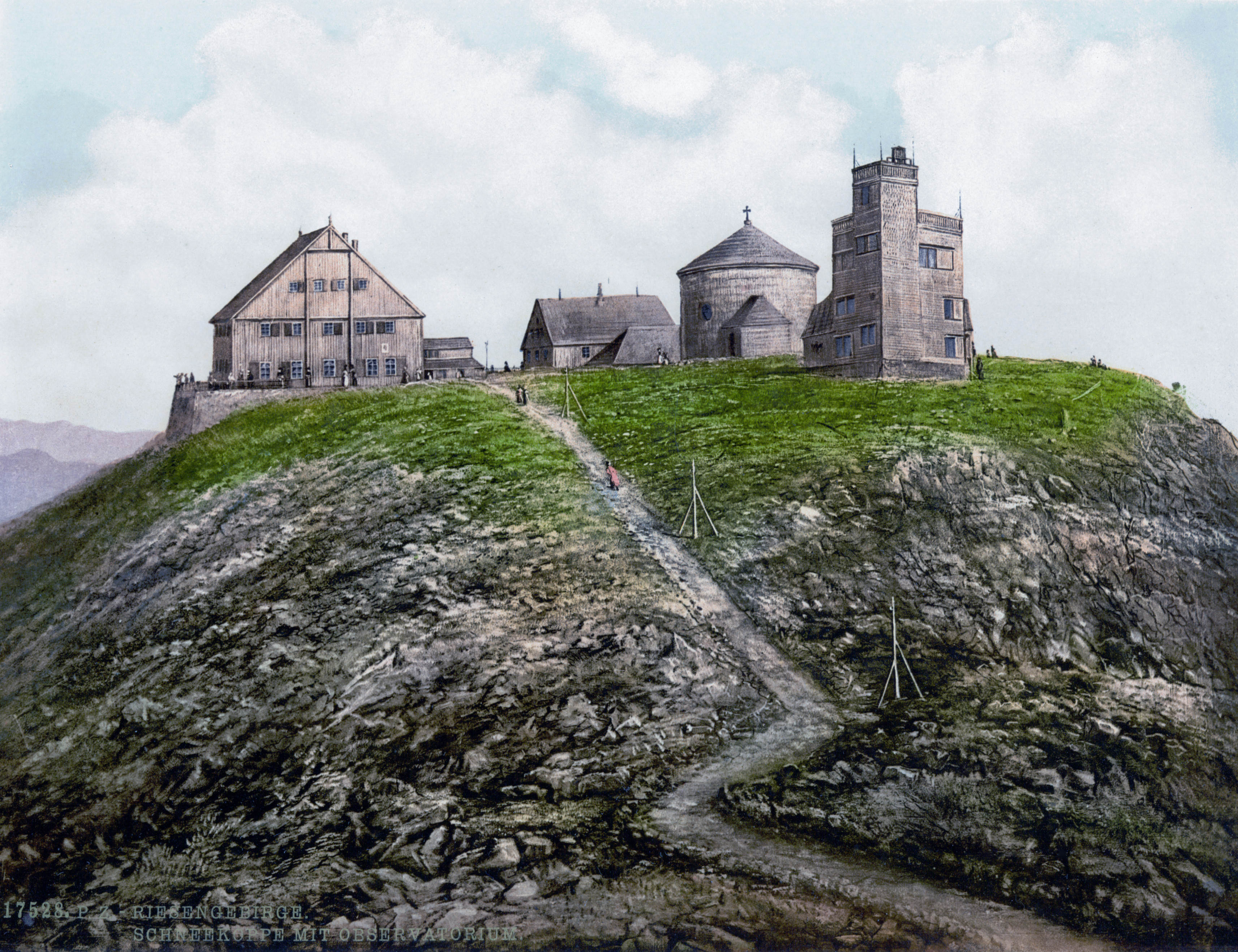
Śnieżne Kotły
Śnieżne Kotły (, , , literally ''Snowy Pits'', ''Snowy Cirque'', ''Snowy Cwm'') are two glacial cirques situated in Poland in the Sudetes in the Karkonosze National Park. They are a unique example of the alpine landscape in the area and have been a nature reserve since 1933. Description The walls of both cirques are about high and contain small tarn lakes. They were formed during the last phase of the glacial period and consist predominantly of granite. However, in two exposed places basalt was found (apparently of volcanic origin), which is quite rare in this part of Central Europe. Some rare species of arctic and alpine plants appear in the cold and dark parts of the cirques: Pulsatilla alpina, Gentiana asclepiadea, Aconitum napellus, and the only place in the Sudetes where Micranthes nivalis appears. etrieved 2009-12-26/ref> At the top of the larger cirque, at the Łabski Szczyt, there is a radio and television tower. Hiking and climbing It is possible to climb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mittelgebirge
A ''Mittelgebirge'' (; German: ''Mittel'', "middle or mid"; ''Gebirge'', "mountains or mountainous area") is a type of relatively low mountain range or highland area typical of the geography of central Europe, especially central and southern Germany; it refers to something between rolling low hill country or ''Hügelland'' and a proper mountain range ( or ''Hochgebirge'') like the High Alps. Characteristics The term is not precise, but typically refers to topography where the peaks rise at least to above the surrounding terrain (as opposed to above sea level). The summits usually do not reach the tree line and were not glaciated after the last glacial period. In contrast, ''Hochgebirge'' is used to refer to mountain ranges rising above approximately to . The delineation corresponds with the differentation between Montane and Alpine level according to altitudinal zonation. ''Mittelgebirge'' ranges In the plural, ''die Mittelgebirge'' (as opposed to the singular, ''das Mittelgeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemian Massif
The Bohemian Massif ( or ''Český masiv'', or ''Böhmisches Massiv'') is a geomorphological province in Central Europe. It is a large massif stretching over most of the Czech Republic, eastern Germany, southern Poland and northern Austria. The massif encompasses a number of mittelgebirges and consists of crystalline rocks, which are older than the Permian (more than 300 million years old) and therefore deformed during the Variscan Orogeny. Parts of the Sudetes within the Bohemian Massif, Giant Mountains in particular, stand out from the ordinary mittelgebirge pattern by having up to four distinct levels of altitudinal zonation, glacial cirques, small periglacial landforms and an elevation significantly above the timber line. Geomorphological divisions The Bohemian Massif is a province within the Hercynian Forest subsystem. It borders with four provinces: Western Carpathians on the east, Eastern Alps on the south, North European Plain on the north, and Central Upla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Orogeny
The Alpine orogeny, sometimes referred to as the Alpide orogeny, is an orogenic phase in the Late Mesozoic and the current Cenozoic which has formed the mountain ranges of the Alpide belt. Cause The Alpine orogeny was caused by the African continent, the Arabian Peninsula, the Indian subcontinent, and the Cimmerian plate colliding with Eurasia in the north. Convergent movements between the African, Arabian and Indian plates from the south, and the Eurasian plate and the Anatolian sub-plate from the north – as well as many smaller (micro)plates – had already begun during the early Cretaceous, but the major phases of mountain building began during the Paleocene to the Eocene. The process continues currently in some of the Alpide mountain ranges. The Alpine orogeny is considered one of the three major phases of orogeny in Europe that define the geology of that continent, along with the Caledonian orogeny that formed the Old Red Sandstone Continent when the continents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sněžka
Sněžka () or Śnieżka (, ) is a mountain on the border between the Czech Republic and Poland, the most prominent point of the Silesian Ridge in the Giant Mountains. At , its summit is the highest point in the Czech Republic, in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in the Giant Mountains and in the entire Sudetes. History Sněžka was one of the first European mountains visited by many tourists. This was mainly due to the relatively minor technical difficulties of the ascent and the fact that since the sixteenth century, many resort visitors flocked to the nearby Cieplice Śląskie-Zdrój, Bad Warmbrunn (today: Cieplice Śląskie-Zdrój) and the highly visible Sněžka, visually dominant over all Giant Mountains was for them an important attraction. The first historical account of an ascent to the peak is in 1456, by an unknown Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant searching for precious stones. The first settlements on the mountain soon appeared, being primarily mining communiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian Gate
The Moravian Gate (, , , ) is a geomorphological feature in the Moravian region of the Czech Republic and the Upper Silesia region in Poland. It is formed by the depression between the Carpathian Mountains in the east and the Sudetes in the west. The drainage divide between the upper Oder river and the Baltic Sea in the north and the Bečva River of the Danube basin runs through it. Geography It stretches from Moravia towards Czech Silesia north-eastward in the length of about and is bordered by the confluence of the Olza and the Odra ( Oder) rivers in the north. Its crest is located between the villages of Olšovec and Bělotín at . Its average altitude is . Because of its low altitude, the Moravian Gate has since ancient times been a natural pass between the Sudetes ( Oderské vrchy range) in the northwest and the Western Carpathians ( Moravian-Silesian Beskids) in the southeast. Here ran the most important trade routes, such as the Amber Road from the Baltic to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Saxony, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Dresden Basin, Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
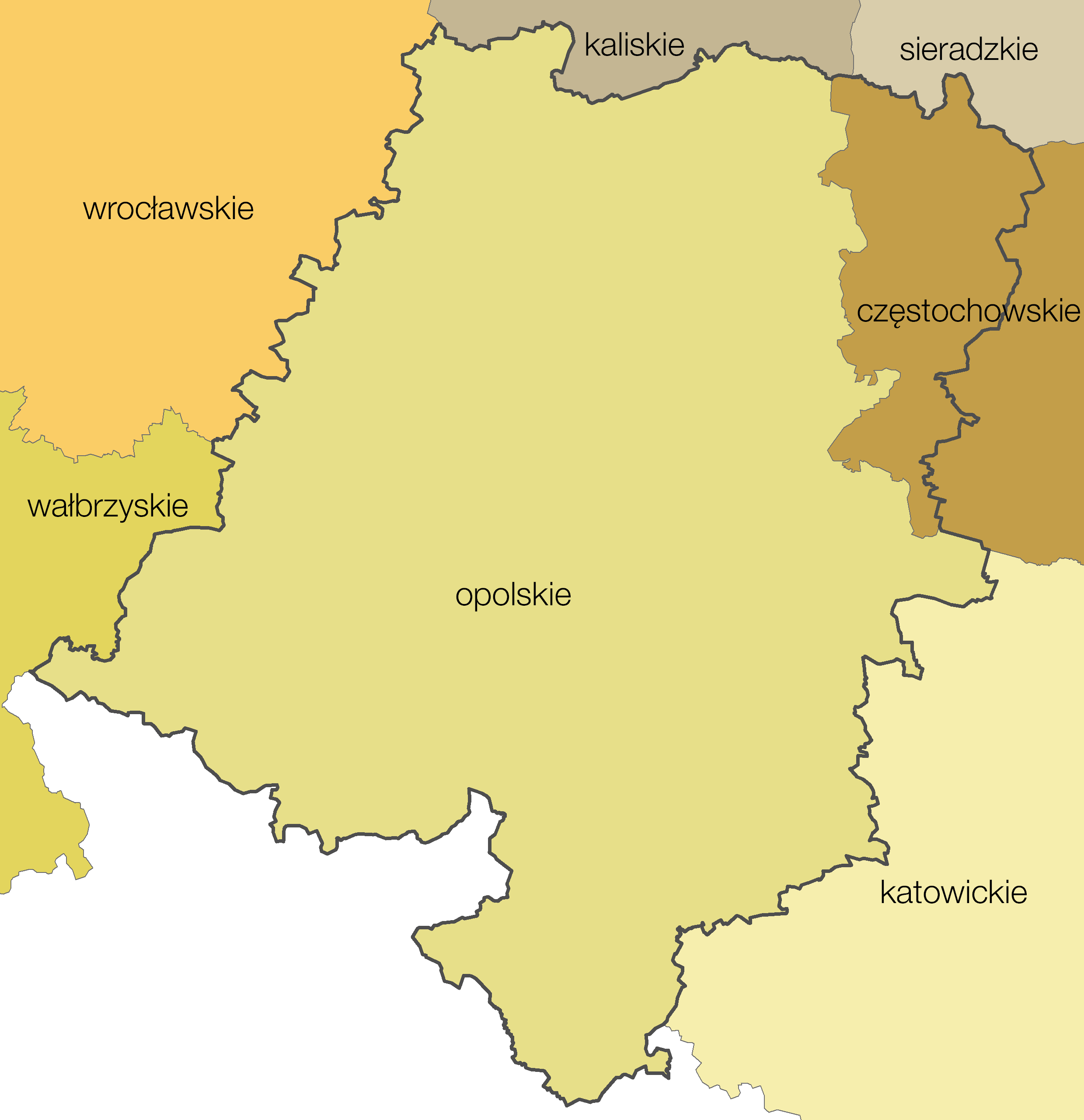
Opole Voivodeship
Opole Voivodeship ( , , ), is the smallest and least populated voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Silesia. A relatively large Germans, German minority lives in the voivodeship, and the German language is co-official in 28 communes. Opole Voivodeship is bordered by Lower Silesian Voivodeship to the west, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Greater Poland and Łódź Voivodeships to the north, Silesian Voivodeship to the east, and the Czech Republic (Olomouc Region and Moravian-Silesian Region) to the south. Opole Province's geographic location, economic potential, and its population's level of education make it an attractive business partner for other Polish regions (especially Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Lower Silesian and Silesian Voivodeships) and for foreign investors. Formed in 1997, the Euroregion Praděd, Praděd/Pradziad Euroregion with its headquarter in Prud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of with a mostly temperate Humid continental climate, continental and oceanic climate. The capital and largest city is Prague; other major cities and urban areas include Brno, Ostrava, Plzeň and Liberec. The Duchy of Bohemia was founded in the late 9th century under Great Moravia. It was formally recognized as an Imperial Estate of the Holy Roman Empire in 1002 and became Kingdom of Bohemia, a kingdom in 1198. Following the Battle of Mohács in 1526, all of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were gradually integrated into the Habsburg monarchy. Nearly a hundred years later, the Protestantism, Protestant Bohemian Revolt led to the Thirty Years' War. After the Battle of White ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |