|
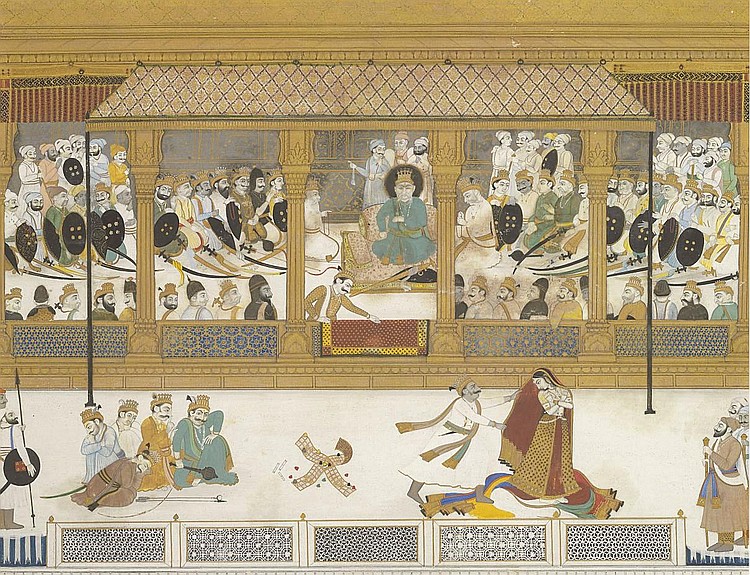
Sudakshina
Sudakshina () is a king of the Kamboja (caste) featured in the Hindu epic Mahabharata. Legend On the 14th day of the Kurukshetra War, Arjuna, with his charioteer Krishna, attempts to reach Jayadratha. Drona and Duryodhana arrange warriors in Arjuna's path, trying to impede his progress until sunset. Sudakshina rallies a fleeing Kaurava akshauhini, challenging Arjuna. He throws a spear at Arjuna; the spear connects and Arjuna swoons in his seat, dripping blood. The Kaurava army begins to cheer, thinking that Arjuna is dead. However, Arjuna quickly recovers and angrily invokes the Indrastra, which multiplies into many arrows and decimates the Kaurava forces. Sudakshina falls to one of these arrows. See also * Srindra Varmana * Chandravarma * Kamatha *Kurukshetra War The Kurukshetra War (), also called the Mahabharata War, is a war described in the Hindu Indian epic poetry, epic poem ''Mahabharata'', arising from a dynastic struggle between two groups of cousins, the Kaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prapaksha Kamboja
The fourth prince of the Kambojas referenced in the Mahābhārata is the younger brother of the prince Sudakshina Kamboja. In the epic, this prince is simply addressed as Kamboja, but according to Pandit Bhagavadatta Sharma, the real name of the prince was Parpakash Kamboja (Bharata ka Itihaas, p 161). Prince Kamboja had also participated with distinction in the Kurukshetra war The Kurukshetra War (), also called the Mahabharata War, is a war described in the Hindu Indian epic poetry, epic poem ''Mahabharata'', arising from a dynastic struggle between two groups of cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandavas, for the thr ... and had fought duels on Kaurava's behalf. After Sudakshina fell on the fourteenth day of the war, the young prince took over the supreme command of the Kamboja division.Some Kshatriya Tribes, p 246, Dr. B. C. Law. See also * Chandravarma Kamboja * Kamatha Kamboja * Sudakshina Kamboja References {{reflist Characters in the Mahabharata Ancient peoples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arjuna
Arjuna (, , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [ɐɾd͡ʒun̪ə]) is one of the central characters of the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the third of the five Pandava brothers, and is widely regarded as the most important and renowned among them. He is the son of Indra, the king of the Deva (Hinduism), gods, and Kunti, wife of King Pandu of Kuru kingdom, Kuru dynasty—making him a Demigod, divine-born hero. Arjuna is famed for his extraordinary prowess in archery and mastery over Astra (weapon), celestial weapons. Throughout the epic, Arjuna sustains a close friendship with his maternal cousin, Krishna, who serves as his spiritual guide. Arjuna is celebrated for numerous heroic exploits throughout the epic. From childhood, he emerges as an excellent pupil, studying under the warrior-sage Drona. In his youth, Arjuna wins the hand of Draupadi, the princess of the Pañcāla, Panchalas, by excelling in a formidable archery competition. Soon after, he goes on a journey during a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indrastra
Indrastra () is the astra (celestial weapon) of the Hindu deity Indra. The astra is featured in Hindu texts such as the Ramayana and the Mahabharata. Literature Mahabharata In the Mahabharata, Indra offers the Indrastra to Arjuna. On the fourteenth day of the Kurukshetra War, when Arjuna wanted to kill King Jayadratha, Drona and Duryodhana sent their men to stop Arjuna. One of these was King Sudakshina, who threw his spear at Arjuna, striking him and causing his blood to flow. Even as the Kauravas believed him to be dead, Arjuna launched the Indrastra, killing King Sudakshina and a large part of his army. On the seventeenth day of the war, Arjuna shot his Indrastra on the Samsaptakas, killing many of them. Ramayana In the Ramayana, Lakshmana employs the Indrastra to kill Indrajita, the son of Ravana. See also * Brahmastra * Narayanastra * Pashupatastra The ''Pashupatastra'' (IAST: Pāśupatāstra, Sanskrit: पाशुपतास्त्र; the Pashupati, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandravarma
The ''Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India composed by Veda Vyasa. At its heart lies the epic struggle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The central characters include the five Pandava brothers—Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—along with their wife Draupadi. On the opposing side, the hundred Kaurava brothers are led by the elder brother, Duryodhana. However, the ''Mahabharata'' is richly populated with other notable figures including Krishna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Kunti, Dushasana, Kripa, Dhritrashtra, Gandhari (Mahabharata), Gandhari, Shakuni, Ashwatthama, Balarama, Subhadra, Vyasa, Abhimanyu, Pandu, Satyavati and Amba (Mahabharata), Amba. The ''Mahabharata'' manuscripts exist in numerous versions, wherein the specifics and details of major characters and episodes vary, often significantly. Except for the sections containing the ''Bhagavad Gita'' which is remarkably consistent between the numerous manuscripts, the rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characters In The Mahabharata
The '' Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India composed by Veda Vyasa. At its heart lies the epic struggle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The central characters include the five Pandava brothers— Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—along with their wife Draupadi. On the opposing side, the hundred Kaurava brothers are led by the elder brother, Duryodhana. However, the ''Mahabharata'' is richly populated with other notable figures including Krishna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Kunti, Dushasana, Kripa, Dhritrashtra, Gandhari, Shakuni, Ashwatthama, Balarama, Subhadra, Vyasa, Abhimanyu, Pandu, Satyavati and Amba. The ''Mahabharata'' manuscripts exist in numerous versions, wherein the specifics and details of major characters and episodes vary, often significantly. Except for the sections containing the ''Bhagavad Gita'' which is remarkably consistent between the numerous manuscripts, the rest of the epic exists in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurukshetra War
The Kurukshetra War (), also called the Mahabharata War, is a war described in the Hindu Indian epic poetry, epic poem ''Mahabharata'', arising from a dynastic struggle between two groups of cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandavas, for the throne of Hastinapura. The war is used as the context for the dialogues of the ''Bhagavad Gita. Background The ''Mahābhārata'' is an account of the life and deeds of several generations of a ruling dynasty called the Kuru (Hindu mythology), Kuru clan. Central to the epic is an account of a war that took place between two rival families belonging to this clan. Kurukshetra (literally "Kshetram, Region of the Kurus"), also known as Dharmakshetra (the "Region of Dharma"), was the battleground on which the Kurukshetra War was fought. The first ''Mahābhārata'' says that this site was chosen because a sin committed on land was forgiven because of the land's sanctity. The events of the war make up more than a quarter of the ''Mahabharata''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srindra Varmana Kamboj
Srindra Varmana according to the ''Skanda Purana'' was a king of the Kamboja kingdom.Studies in Skanda Purana, 1978, p 59, A. B. L. Awasthi. He is said to have installed the image of Varahadeva in his capital and made a gold throne for it.Studies in Skanda Purana, 1978, p 1, A. B. L. Awasthi. See also * Chandravarma Kamboja * Kamatha Kamboja *Sudakshina Kamboja Sudakshina () is a king of the Kamboja (caste) featured in the Hindu epic Mahabharata. Legend On the 14th day of the Kurukshetra War, Arjuna, with his charioteer Krishna, attempts to reach Jayadratha. Drona and Duryodhana arrange warriors in ... References Kambojas {{Hindu-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamatha
Kamatha is a Kamboja king mentioned in the Mahābhārata as one of the principal Kshatriyas taking part in the battle. References See also *Srindra Varmana Kamboj *Chandravarma *Sudakshina Sudakshina () is a king of the Kamboja (caste) featured in the Hindu epic Mahabharata. Legend On the 14th day of the Kurukshetra War, Arjuna, with his charioteer Krishna, attempts to reach Jayadratha. Drona and Duryodhana arrange warriors in ... Characters in the Mahabharata Kambojas {{Asia-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurukshetra War
The Kurukshetra War (), also called the Mahabharata War, is a war described in the Hindu Indian epic poetry, epic poem ''Mahabharata'', arising from a dynastic struggle between two groups of cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandavas, for the throne of Hastinapura. The war is used as the context for the dialogues of the ''Bhagavad Gita. Background The ''Mahābhārata'' is an account of the life and deeds of several generations of a ruling dynasty called the Kuru (Hindu mythology), Kuru clan. Central to the epic is an account of a war that took place between two rival families belonging to this clan. Kurukshetra (literally "Kshetram, Region of the Kurus"), also known as Dharmakshetra (the "Region of Dharma"), was the battleground on which the Kurukshetra War was fought. The first ''Mahābhārata'' says that this site was chosen because a sin committed on land was forgiven because of the land's sanctity. The events of the war make up more than a quarter of the ''Mahabharata''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kambojas
The Kambojas were a southeastern Iranian peoples, Iranian people who inhabited the northeastern most part of the territory populated by Iranian tribes, which bordered the Indian subcontinent, Indian lands. They only appear in Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan inscriptions and literature, being first attested during the later part of the Vedic period. They spoke a language similar to Younger Avestan, whose words are considered to have been incorporated in the Aramao-Iranian version of the Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription erected by the Maurya Empire, Maurya emperor Ashoka (). They were adherents of Zoroastrianism, as demonstrated by their beliefs that insects, snakes, worms, frogs, and other small animals had to be killed, a practice mentioned in the Avestan Vendidad. Etymology ''Kamboja-'' (later form ''Kāmboja-'') was the name of their territory and identical to the Old Iranian name of ''*Kambauǰa-'', whose meaning is uncertain. A long-standing theory is the one propose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kurukshetra War, a war of succession between two groups of princely cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandava, Pāṇḍavas. It also contains Hindu philosophy, philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the ''Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha (sage), Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an Ramopakhyana, abbreviated version of the ''Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyasa, Vy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is widely revered among Hindu divinities. Krishna's birthday is celebrated every year by Hindus on Krishna Janmashtami according to the lunisolar calendar, lunisolar Hindu calendar, which falls in late August or early September of the Gregorian calendar. The anecdotes and narratives of Krishna's life are generally titled as ''Krishna Līlā''. He is a central figure in the ''Mahabharata'', the ''Bhagavata Purana'', the ''Brahma Vaivarta Purana,'' and the ''Bhagavad Gita'', and is mentioned in many Hindu philosophy, Hindu philosophical, Hindu theology, theological, and Hindu mythology, mythological texts. They portray him in various perspectives: as a god-child, a prankster, a model lover, a divine hero, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |