|
Subthalamus
The subthalamus or ventral thalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a subcortical nucleus of the basal ganglia. Structure The subthalamus is located ventral to the thalamus, medial to the internal capsule and lateral to the hypothalamus. It is a region formed by several grey matter nuclei and their associated white matter structures, namely: *The subthalamic nucleus, whose neurons contain glutamate and have excitatory effects over neurons of globus pallidus and substantia nigra * Zona incerta, located between fields of Forel H1 and H2. It is continuous with the thalamic reticular nucleus and receives input from the precentral cortex. * Subthalamic fasciculus, formed by fibers that connect the globus pallidus with the subthalamic nucleus * Fields of Forel * Ansa lenticularis During development the subthalamus is continuous with the hypothalamus, but is separated by whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fields Of Forel
The fields of Forel is a complex region in the posterior subthalamus, consisting of a concentrated collection of bundles of fibers. The tracts formed include the thalamic fasciculus that includes the ansa lenticularis and lenticular fasciculus, cerebellothalamic tracts, and pallidothalamic tracts. Other included fibers connect to other brain regions. These tracts are described in regions known as ''H fields''. H fields *Field H1, is the thalamic fasciculus, a horizontal white matter tract composed of the ansa lenticularis, lenticular fasciculus, and cerebellothalamic tracts between the subthalamus and the thalamus. These fibers are projections to the ventral anterior and ventral lateral thalamus from the basal ganglia (globus pallidus) and the cerebellum. H1 is separated from H2 by the zona incerta. *Field H2 (synonymous with lenticular fasciculus) is also made up of projections from the pallidum to the thalamus, but these course the subthalamic nucleus (dorsal). *Field H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
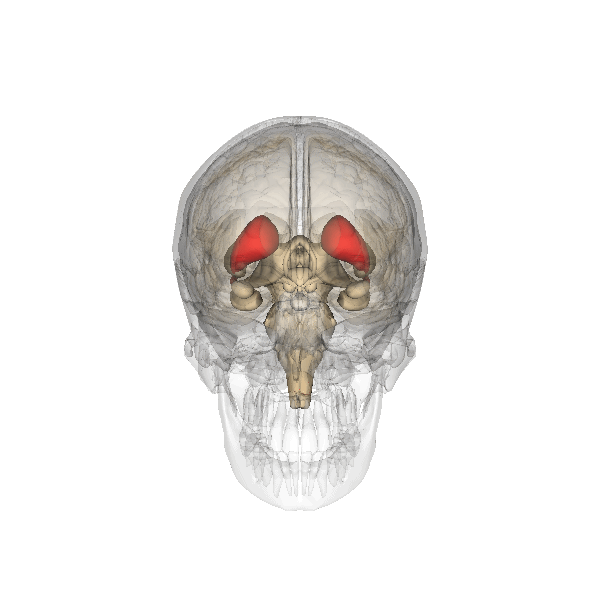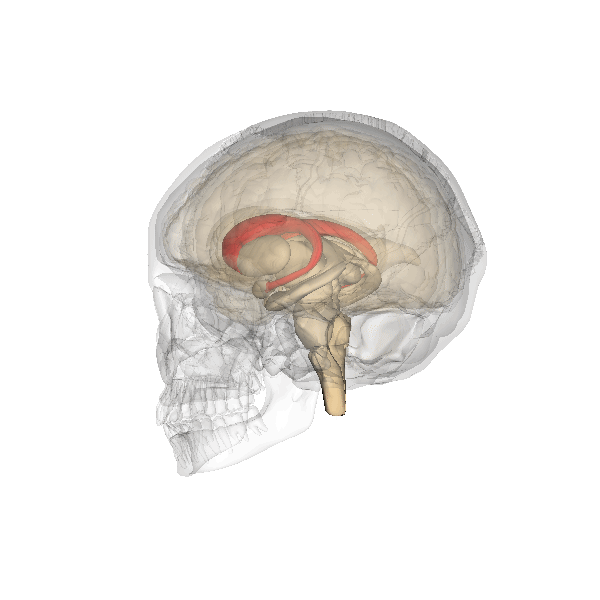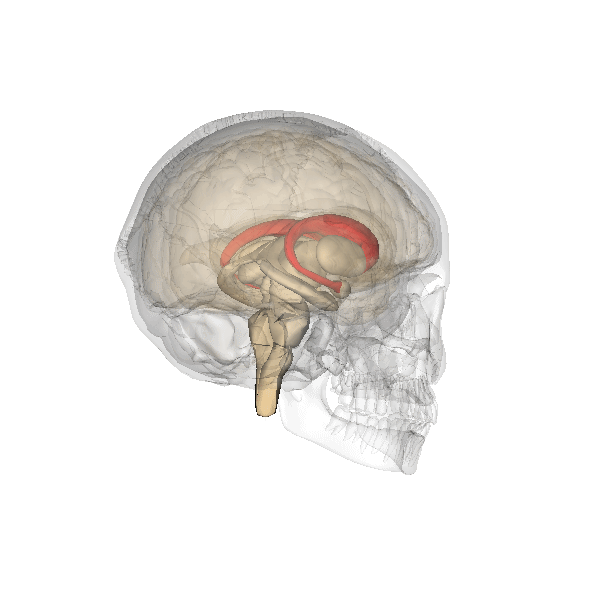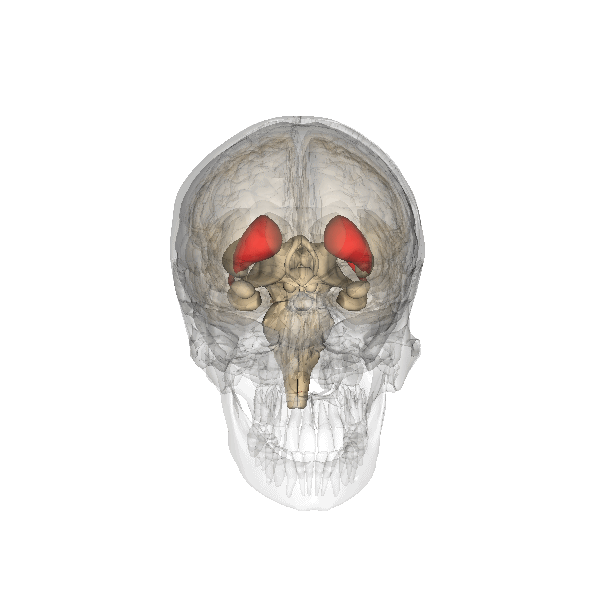
Zona Incerta
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated small Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus that separates the larger subthalamic nucleus from the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord. Its function is unknown, though several potential functions related to "limbic–motor integration" have been proposed, such as controlling visceral activity and pain; gating sensory input and synchronizing cortical and subcortical brain rhythms. Its dysfunction may play a role in central pain syndrome. It has also been identified as a promising deep brain stimulation therapy target for treating Parkinson's disease. Its existence was first described by Auguste Forel in 1877 as a "region of which nothing certain can be said". A hundred and thirty years later in 2007, Nadia Urbain and Martin Deschênes of Université Laval noted that the "zona incerta is among the least studied regions of the brain; its name does not even appear in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the Basal (anatomy), basal part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is about the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus has the function of regulating certain metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls thermoregulation, body temperature, hunger (physiology), hunger, important aspects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diencephalon
In the human brain, the diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as the tweenbrain in older literature. It consists of structures that are on either side of the third ventricle, including the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the epithalamus and the subthalamus. The diencephalon is one of the main brain vesicle, vesicles of the brain formed during human embryonic development, embryonic development. During the third week of development a neural tube is created from the ectoderm, one of the three primary germ layers, and forms three main vesicles: the prosencephalon, the Midbrain, mesencephalon and the Hindbrain, rhombencephalon. The prosencephalon gradually divides into the telencephalon (the cerebrum) and the diencephalon. Structure The diencephalon consists of the following structures: * Thalamus * Hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subthalamic Fasciculus
The subthalamic fasciculus is a bi-directional nerve tract that interconnects the lateral globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus as part of the indirect pathway. The pallidal efferents are GABAergic, but also contain enkephalin. Its fibers interweave perpendicularly among the fibers of the internal capsule The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way nerve tract, tract, carrying afferent nerve fiber, ascending and efferent nerve fiber, descending axon, fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situate .... References External links * http://isc.temple.edu/neuroanatomy/lab/atlas/dan1/ * https://web.archive.org/web/20071126015854/http://www.sci.uidaho.edu/med532/subthalamus.htm Basal ganglia connections Subthalamus {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Nucleus
The red nucleus or nucleus ruber is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. The red nucleus is pale pink, which is believed to be due to the presence of iron in at least two different forms: hemoglobin and ferritin. The structure is located in the midbrain tegmentum next to the substantia nigra and comprises caudal magnocellular and rostral parvocellular components. The red nucleus and substantia nigra are subcortical centers of the extrapyramidal motor system. Function In a vertebrate without a significant corticospinal tract, gait is mainly controlled by the red nucleus. However, in primates, where the corticospinal tract is dominant, the rubrospinal tract may be regarded as vestigial in motor function. Therefore, the red nucleus is less important in primates than in many other mammals. Nevertheless, the crawling of babies is controlled by the red nucleus, as is arm swinging in typical walking. The red nucleus may play an additional role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telencephalon
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal, it lies either in front or on top of the brainstem. In humans, the cerebrum is the largest and best-developed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a subcortical nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus with a rounded structure, in the basal ganglia nuclear group. It is located at the base of the forebrain and above the midbrain. The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. Through various pathways, the putamen is connected to the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, the claustrum, and the thalamus, in addition to many regions of the cerebral cortex. A primary function of the putamen is to regulate movements at various stages such as in preparation and execution; and to influence various types of learning. It employs GABA, acetylcholine, and enkephalin to perform its functions. The putamen also plays a role in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease. History The word "putamen" is from Latin, referring to that which "falls off in pruning", from "putare", meaning "to prune, to think, or to consider". Most MRI research was focused broadly on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostral and caudal, Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while Rostral and caudal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is part of the basal ganglia in the human brain. Although the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes because of its relation to Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease, it also plays important roles in nonmotor functions, such as procedural learning, associative learning, and inhibitory control of action. The caudate is also one of the brain structures that compose the reward system, and it functions as part of the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Structure Along with the putamen, the caudate forms the dorsal striatum, which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white-matter tract, the internal capsule, so it is sometimes also described as two structures—the medial dorsal striatum (the caudate) and the lateral dorsal striatum (the putamen). In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |