|
Stylomastoid Foramen
The stylomastoid foramen is a foramen between the styloid and mastoid processes of the temporal bone of the skull. It is the termination of the facial canal, and transmits the facial nerve, and stylomastoid artery. Facial nerve inflammation in the stylomastoid foramen may cause Bell's palsy. Structure The stylomastoid foramen is between the styloid and mastoid processes of the temporal bone. The average distance between the opening of the stylomastoid foramen and the styloid process is around 0.7 mm or 0.8 mm in adults, but may decrease to around 0.2 mm during aging. The stylomastoid foramen transmits the facial nerve, and the stylomastoid artery. These 2 structures lie directly next to each other. Clinical significance Bell's palsy can result from inflammation of the facial nerve The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Of Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, inferior area of the human skull, skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the Calvaria (skull), calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone *Sphenoid bone *Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus *Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull *Foramen cecum (frontal bone), Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum *Foramen magnum *Foramen ovale (skull), Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture *Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve) and anterior to cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve). The facial nerve also supplies preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to several head and neck ganglia. The facial and intermediate nerves can be collectively referred to as the nervus intermediofacialis. The path of the facial nerve can be divided into six segments: # intracranial (cisternal) segment (from brainstem pons to internal auditory canal) # meatal (canalicular) segment (with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
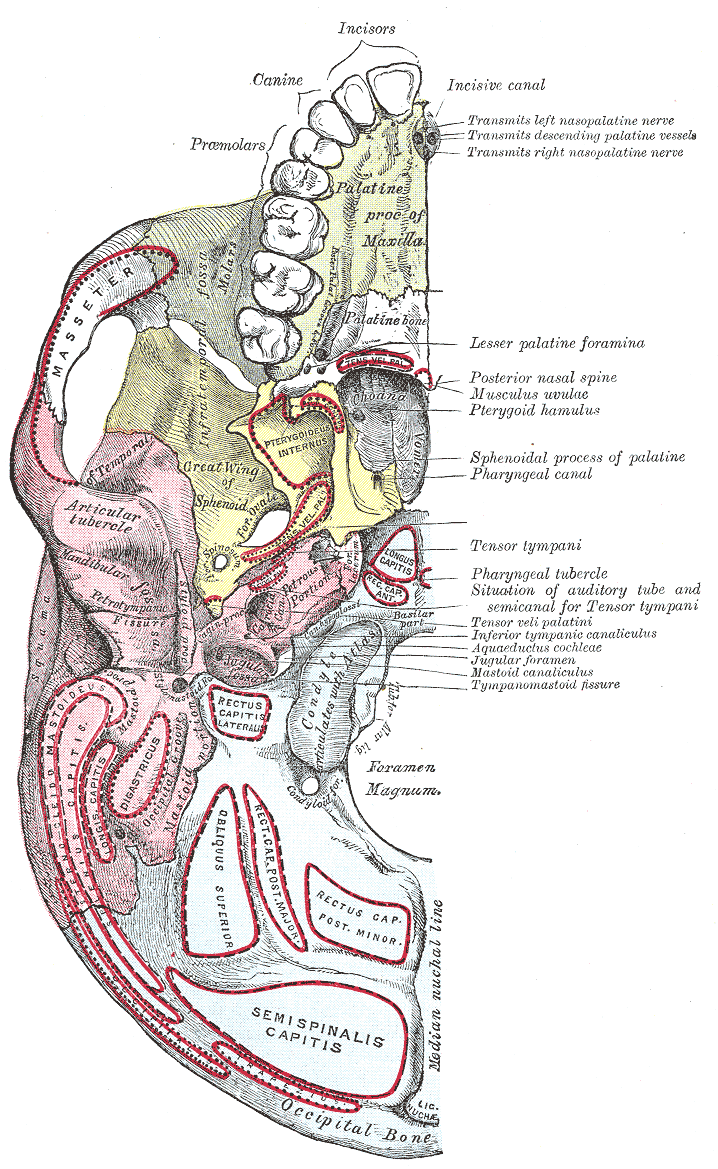
Foramina Of The Skull
This article lists Foramen, foramina that occur in the human body. __TOC__ Skull The human skull has numerous openings (foramen, foramina), through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. These foramina vary in size and number, with age. Gray193.png , Base of skull, Base of the skull, upper surface Gray187.png , Base of the skull, inferior surface, attachment of muscles marked in red Spine Within the vertebral column (spine) of vertebrates, including the Human vertebral column, human spine, each bone has an opening at both its top and bottom to allow nerves, arteries, veins, etc. to pass through. Other * Apical foramen, the opening at the tip of the root of a tooth * Foramen ovale (heart), an opening between the venous and arterial sides of the fetal heart * Foramen transversarium, one of a pair of openings in each cervical vertebra, in which the vertebral artery travels * Greater sciatic foramen, a major foramen of the pelvis * Interv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiology (journal)
''Radiology'' is a monthly, peer reviewed, medical journal, owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America. The editor is Linda Moy, MD. The focus of ''Radiology'' is imaging research articles in radiology and medical imaging. Publishing formats Publishing formats are original research articles (3000 words), research letters (600 words), technical developments (2000), invited perspectives (2500) review articles (4500), special report, invited editorial, statements and guidelines (3000), Images in Radiology, Radiology Diagnosis Please, and letter to the editor. Abstracting and indexing According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Radiology'' has a 2023 impact factor of 12.1. In addition, the journal is indexed in the following databases: * ''Science Citation Index'' * '' SciSearch'' * ''Chemical Abstracts'' * ''Current Contents/Clinical Medicine'' * ''Current Contents/Life Sciences'' * ''BIOSIS Previews'' * ''Computer & Control Abstracts'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical And Radiologic Anatomy
''Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal that publishes original research and review articles on the bases of medical, surgical and radiologic anatomy. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', it has a current impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 1.2, ranking it 13th out of 20 journals in the category "Anatomy & Morphology". It ranked 116th out of 135 categorized under "Surgery". References {{Reflist External links Journal website Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Academic journals established in 1978 English-language journals Anatomy journals Quarterly journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell's Palsy
Bell's palsy is a type of facial paralysis that results in a temporary inability to control the facial muscles on the affected side of the face. In most cases, the weakness is temporary and significantly improves over weeks. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe. They may include muscle twitching, weakness, or total loss of the ability to move one or, in rare cases, both sides of the face. Other symptoms include drooping of the eyebrow, a change in taste, and pain around the ear. Typically symptoms come on over 48 hours. Bell's palsy can trigger an increased sensitivity to sound known as hyperacusis. The cause of Bell's palsy is unknown and it can occur at any age. Risk factors include diabetes, a recent upper respiratory tract infection, and pregnancy. It results from a dysfunction of cranial nerve VII (the facial nerve). Many believe that this is due to a viral infection that results in swelling. Diagnosis is based on a person's appearance and ruling out other possible caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylomastoid Artery
The stylomastoid artery enters the stylomastoid foramen and supplies the tympanic cavity, the tympanic antrum and mastoid cells, and the semicircular canals. It is a branch of the posterior auricular artery, and thus part of the external carotid arterial system. In the young subject, a branch from this vessel forms, with the anterior tympanic artery from the internal maxillary, a vascular circle, which surrounds the tympanic membrane, and from which delicate vessels ramify on that membrane. It anastomoses with the superficial petrosal branch of the middle meningeal artery The middle meningeal artery (') is typically the third branch of the maxillary artery#First portion, first portion of the maxillary artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum t ... by a twig which enters the hiatus canalis facialis. References External links ArcLab Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Canal
The facial canal (also known as the Fallopian canal) is a Z-shaped canal in the temporal bone of the skull. It extends between the internal acoustic meatus and stylomastoid foramen. It transmits the facial nerve (CN VII) (after which it is named). Anatomy The facial canal gives passage to the facial nerve (CN VII) (hence the name). Its proximal opening is at the internal auditory meatus; its distal opening is the stylomastoid foramen. In humans, the canal is approximately 3 cm long, making it the longest bony canal of a nerve in the human body. It is located within the middle ear region. The facial nerve gives rise to three nerves while passing through the canal: the greater petrosal nerve, nerve to stapedius, and the chorda tympani. Structure Horizontal part The proximal portion of the facial canal is termed the horizontal part. It commences at the introitus of facial canal at the distal end of the internal auditory meatus. The horizontal part is further sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Bone
The temporal bone is a paired bone situated at the sides and base of the skull, lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples where four of the cranial bones fuse. Each temple is covered by a temporal muscle. The temporal bones house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone. Structure The temporal bone consists of four parts—the squamous, mastoid, petrous and tympanic parts. The squamous part is the largest and most superiorly positioned relative to the rest of the bone. The zygomatic process is a long, arched process projecting from the lower region of the squamous part and it articulates with the zygomatic bone. Posteroinferior to the squamous is the mastoid part. Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Portion Of The Temporal Bone
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has Foramen, openings for blood vessels. From its borders, the mastoid part articulation (anatomy), articulates with two other bones. Etymology The word "mastoid" is derived from the Greek word for "breast", a reference to the shape of this bone. Surfaces Outer surface Its outer surface is rough and gives attachment to the occipitalis and posterior auricular muscles. It is perforated by numerous foramen, foramina (holes); for example, the mastoid foramen is situated near the posterior border and transmits a vein to the transverse sinus and a small branch of the occipital artery to the dura mater. The position and size of this foramen are very variable; it is not always present; sometimes it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal and the occipital. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styloid Process (temporal)
The temporal styloid process is a slender bony process of the temporal bone extending downward and forward from the undersurface of the temporal bone just below the ear. The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments. Structure The styloid process is a slender and pointed bony process of the temporal bone projecting anteroinferiorly from the inferior surface of the temporal bone just below the ear. Its length normally ranges from just under 3 cm to just over 4 cm. It is usually nearly straight, but may be curved in some individuals. Its ''proximal'' (''tympanohyal'') ''part'' is ensheathed by the tympanic part of the temporal bone ''(vaginal process), whereas'' its ''distal (stylohyal)'' ''part'' gives attachment to several structures. Attachments The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments. It serves as an anchor point for several muscles associated with the tongue and larynx. * stylohyoid ligament * stylomandi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |