|
Styli
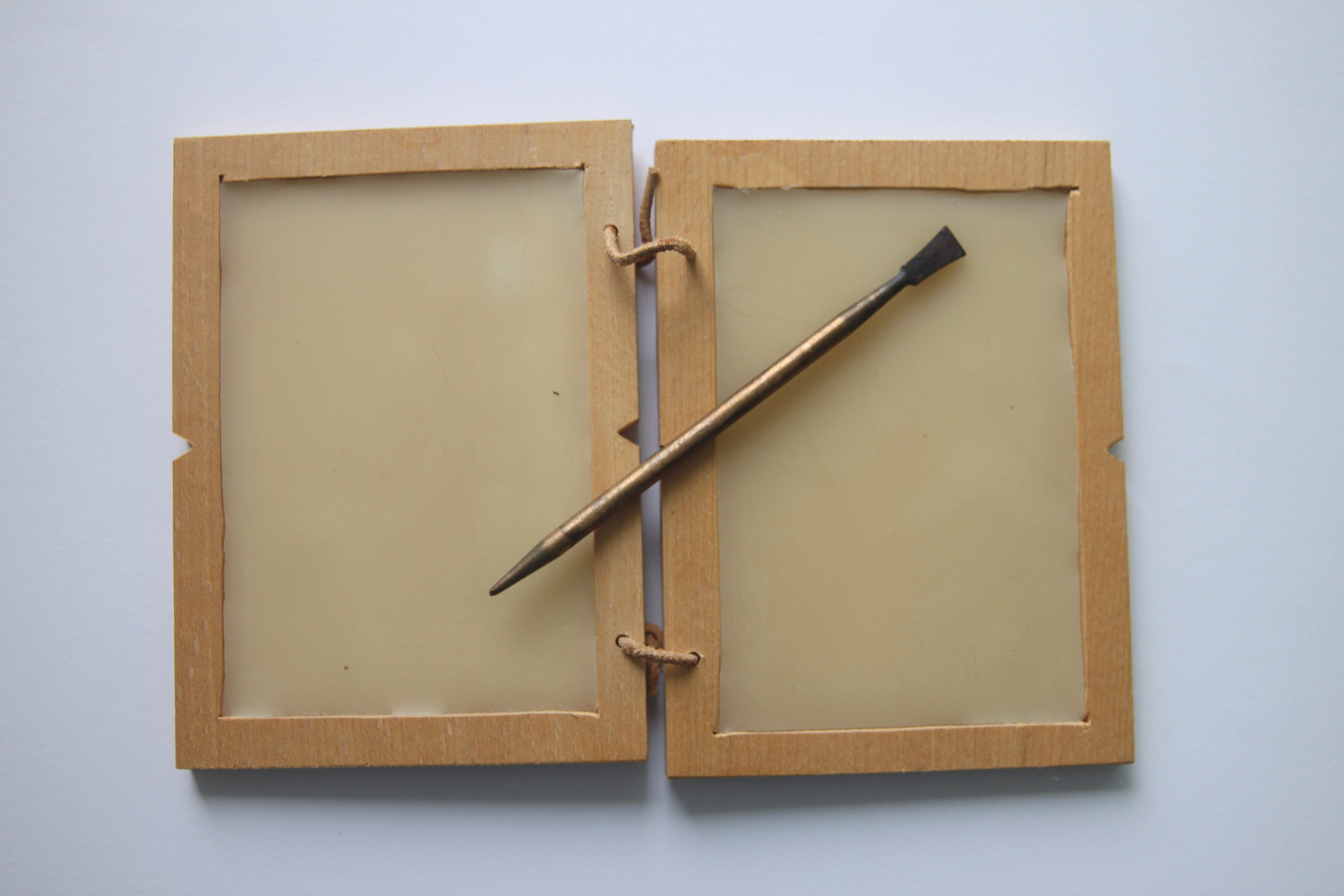
A stylus is a writing utensil or tool for scribing or marking into softer materials. Different styluses were used to write in cuneiform by pressing into wet clay, and to scribe or carve into a wax tablet. Very hard styluses are also used to engrave metal, and the slate and stylus system is used to punch out dots to write in Braille. Styluses are held in the hand and thus are usually a narrow elongated shape, similar to a modern ballpoint pen. Many styluses are heavily curved to be held more easily. The word ''stylus'' is also used to describe computer styluses used to assist in navigating or providing more precision when using touchscreens. Etymology ''Stylus'' comes from the Latin —the spelling ''stylus'' arose from an erroneous connection with Greek (), 'pillar'.''Oxford Latin Dictionary'', s.v. "stilus" (2012). The Latin word had several meanings, including "a long, sharply pointed piece of metal; the stem of a plant; a pointed instrument for incising letters; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchscreen
A touchscreen (or touch screen) is a type of electronic visual display, display that can detect touch input from a user. It consists of both an input device (a touch panel) and an output device (a visual display). The touch panel is typically layered on the top of the electronic visual display of a device. Touchscreens are commonly found in smartphones, tablet computer, tablets, laptops, and other electronic devices. The display is often an Liquid-crystal display, LCD, AMOLED or OLED display. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special Stylus (computing), stylus or one or more fingers. Some touchscreens use ordinary or specially coated gloves to work, while others may only work using a special stylus or pen. The user can use the touchscreen to react to what is displayed and, if the software allows, to control how it is displayed; for example, Zooming user interface, zooming to inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing Style
In literature, writing style is the manner of expressing thought in language characteristic of an individual, period, school, or nation. Thus, style is a term that may refer, at one and the same time, to singular aspects of an individual's writing habits or a particular document and to aspects that go well-beyond the individual writer. Beyond the essential elements of spelling, grammar, and punctuation, writing style is the choice of words, sentence structure, and paragraph structure, used to convey the meaning effectively. The former are referred to as ''rules'', ''elements'', ''essentials'', ''mechanics'', or ''handbook''; the latter are referred to as ''style'', or ''rhetoric''. The rules are about ''what'' a writer does; style is about ''how'' the writer does it. While following the rules drawn from established English usage, a writer has great flexibility in how to express a concept. Some have suggested that the point of writing style is to: * express the message to the reade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leather-hard
In pottery, leather-hard is the condition of a clay or clay body when it has been partially dried to a consistency similar to leather of the same thickness as the clay. At this stage, the clay object has approximately 15% moisture content. The clay is still visibly damp (normally a darkish grey, if it began whiteish) but has dried enough to be able to be handled without deformation. The body is able to be gouged or incised without breaking. The leather-hard stage is the easiest place to add on extension material that cannot be dried with the rest of the pot without causing some issues to occur. For instance, in some cases when handles are added before the base and sides have been dried, the handle can dry before the sides do and cause cracking, as the weight of the dried portion is no longer at the same equivalence with the wet side. The same goes for other additions to the pot that will not dry at the same rate as the rest of the pot. These include bases that are not the same sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylus
A stylus is a writing utensil or tool for scribing or marking into softer materials. Different styluses were used to write in cuneiform by pressing into wet clay, and to scribe or carve into a wax tablet. Very hard styluses are also used to Engraving, engrave metal, and the slate and stylus system is used to punch out dots to write in Braille. Styluses are held in the hand and thus are usually a narrow elongated shape, similar to a modern ballpoint pen. Many styluses are heavily curved to be held more easily. The word ''stylus'' is also used to describe Stylus (computing), computer styluses used to assist in navigating or providing more precision when using touchscreens. Etymology ''Stylus'' comes from the Latin —the spelling ''stylus'' arose from an erroneous connection with Greek (), 'pillar'.''Oxford Latin Dictionary'', s.v. "stilus" (2012). The Latin word had several meanings, including "a long, sharply pointed piece of metal; the stem of a plant; a pointed instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform scripts are marked by and named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions (Latin: ) which form their Grapheme, signs. Cuneiform is the History of writing#Inventions of writing, earliest known writing system and was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian language, Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform Text corpus, corpora are Eblaite language, Eblaite, Elamit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design on a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a Burin (engraving), burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or Glass engraving, glass are engraved, or may provide an Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio printing plate, of copper or another metal, for printing images on paper as prints or illustrations; these images are also called "engravings". Engraving is one of the oldest and most important techniques in printmaking. Wood engravings, a form of relief printing and stone engravings, such as petroglyphs, are not covered in this article. Engraving was a historically important method of producing images on paper in artistic printmaking, in mapmaking, and also for commercial reproductions and illustrations for books and magazines. It has long been replaced by various photographic processes in its commercial applications and, partly because of the difficulty of learning the techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slate And Stylus
The slate and stylus are tools used by blind people to write text that they can read without assistance.Alpha Chi Omega (1908) Invented by Charles Barbier as the tool for writing letters that could be read by touch, the slate and stylus allow for a quick, easy, convenient and constant method of making embossed printing for Braille character encoding. Prior methods of making raised printing for the blind required a movable type printing press. Design The basic design of the slate consists of two pieces of metal, plastic, or wood fastened together with a hinge at one side.Harry Houdini Collection (1888) The back part of the slate is solid with slight depressions spaced in braille cells of six dots each. The depressions are approximately deep and about in diameter. The horizontal and vertical spacing between dots within a cell is approximately , while the distance between adjacent cells is about . The front of the slate consists of rectangular windows that fit over the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing Utensil
A writing implement or writing instrument is an object used to produce writing. Writing consists of different figures, lines, and or forms. Most of these items can be also used for other functions such as painting, drawing and technical drawing, but writing instruments generally have the ordinary requirement to create a smooth, controllable line. Another writing implement employed by a smaller population is the stylus used in conjunction with the slate for punching out the dots in Braille. Autonomous An autonomous writing implement is one that cannot "run out"—the only way to render it useless is to destroy it. Without pigment The oldest known examples were created by incising a flat surface with a rigid tool rather than applying pigment with a secondary object, e.g., Chinese jiaguwen carved into turtle shells. However, this may simply represent the relative durability of such artifacts rather than truly representing the evolution of techniques, as the meaningful application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphrátēs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform 𒌓𒄒𒉣; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in general, the word can be used for any low-lying and seasonally waterlogged terrain. In Europe and in agricultural literature low-lying meadows that require draining and embanked polderlands are also referred to as marshes or marshland. Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and the marsh is sometimes called a carr. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat. Marshes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
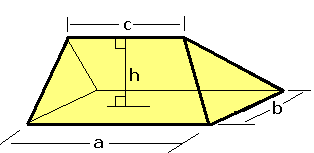
Wedge (geometry)
In solid geometry, a wedge is a polyhedron defined by two triangles and three trapezoid faces. A wedge has five faces, nine edges, and six vertices. Properties A wedge is a polyhedron of a rectangular base, with the faces are two Isosceles triangle, isosceles triangles and two trapezoids that meet at the top of an edge.. A prismatoid is defined as a polyhedron where its vertices lie on two parallel planes, with its lateral faces are triangles, Trapezoid, trapezoids, and Parallelogram, parallelograms; the wedge is an example of prismatoid because of its top edge is parallel to the rectangular base. The volume of a wedge is V = bh \left(\frac+\frac\right), where the base rectangle is a by b , c is the Apex (geometry), apex edge length parallel to a , and h is the height from the base rectangle to the apex edge. Examples In some special cases, the wedge is the right prism if all edges connecting triangles are equal in length, and the triangular faces are perpendicula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table With Was And Stylus Roman Times
Table may refer to: * Table (database), how the table data arrangement is used within the databases * Table (furniture), a piece of furniture with a flat surface and one or more legs * Table (information), a data arrangement with rows and columns * Table (landform), a flat area of land * Table (parliamentary procedure) * Table (sports), a ranking of the teams in a sports league * Tables (board game) * Mathematical table * Tables of the skull, a term for the flat bones * Table, surface of the sound board (music) of a string instrument * ''Al-Ma'ida'', the fifth ''surah'' of the Qur'an, occasionally translated as “The Table” * Calligra Tables, a spreadsheet application * Water table See also * Spreadsheet, a computer application * Table cut, a type of diamond cut * The Table (other) * Table Mountain (other) * Table Rock (other) * Tabler (other) * Tablet (other) * * * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |