|
Stretch Receptor
Stretch receptors are mechanoreceptors responsive to distention of various organs and muscles, and are neurologically linked to the Medulla oblongata, medulla in the brain stem via Afferent nerve fiber, afferent nerve fibers. Examples include stretch receptors in the arm and leg muscles and tendons, in the heart, in the colon wall, and in the lungs. Stretch receptors are also found around the carotid artery, where they monitor blood pressure and stimulate the release of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin, ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland. Types include: * Golgi organ * Muscle spindle, sensory receptors within the belly of a muscle, which primarily detect changes in the length of this muscle * Pulmonary stretch receptors, mechanoreceptors found in the lungs * Chordotonal organ, in insects See also * Stretch sensor * Carotid sinus * Aortic arch * Mechanoreceptor {{biology-stub Sensory receptors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanoreceptors
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are located on sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, are sent to the central nervous system. Vertebrate mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stimuli that result from physical interaction, including pressure and vibration. They are located in the skin, like other cutaneous receptors. They are all innervated by Aβ fibers, except the mechanorecepting free nerve endings, which are innervated by Aδ fibers. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors can be categorized by what kind of sensation they perceive, by the rate of adaptation, and by morphology. Furthermore, each has a different receptive field. By sensation * The Slowly Adapting type 1 (SA1) mechanoreceptor, with the Merkel corpuscle end-organ (also known as Merkel discs) detect sustaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiovascular center, the respiratory center, vomiting and vasomotor centers, responsible for the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary brain vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afferent Nerve Fiber
Afferent nerve fibers are axons (nerve fibers) of sensory neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Many afferent projections ''arrive'' at a particular brain region. In the peripheral nervous system, afferent nerve fibers are part of the sensory nervous system and arise from outside of the central nervous system. Sensory and mixed nerves contain afferent fibers. Structure Afferent neurons are pseudounipolar neurons that have a single process leaving the cell body dividing into two branches: the long one towards the sensory organ, and the short one toward the central nervous system (e.g. spinal cord). These cells do have sensory afferent dendrites, similar to those typically inherent in neurons. They have a smooth and rounded cell body located in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. Just outside the spinal cord, thousands of afferent neuronal cell bodies are aggregated in a swelling in the dorsal root known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Artery , an artery on each side of the head and neck supplying blood to the brain
{{SIA ...
Carotid artery may refer to: * Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery * External carotid artery, an artery on each side of the head and neck supplying blood to the face, scalp, skull, neck and meninges * Internal carotid artery The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasopressin
Mammalian vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the ''AVP'' gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity ( hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Organ
The Golgi tendon organ (GTO) (also called Golgi organ, tendon organ, neurotendinous organ or neurotendinous spindle) is a proprioceptor – a type of sensory receptor that senses changes in muscle tension. It lies at the interface between a muscle and its tendon known as the musculotendinous junction also known as the myotendinous junction. It provides the sensory component of the Golgi tendon reflex. The Golgi tendon organ is one of several eponymous terms named after the Italian physician Camillo Golgi. Structure The body of the Golgi tendon organ is made up of braided strands of collagen (intrafusal fasciculi) that are less compact than elsewhere in the tendon and are encapsulated. The capsule is connected in series (along a single path) with a group of muscle fibers () at one end, and merge into the tendon proper at the other. Each capsule is about long, has a diameter of about , and is perforated by one or more afferent type Ib sensory nerve fibers ( Aɑ fiber), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Spindle
Muscle spindles are stretch receptors within the body of a skeletal muscle that primarily detect changes in the length of the muscle. They convey length information to the central nervous system via afferent nerve fibers. This information can be processed by the brain as proprioception. The responses of muscle spindles to changes in length also play an important role in regulating the contraction of muscles, for example, by activating motor neurons via the stretch reflex to resist muscle stretch. The muscle spindle has both sensory and motor components. * Sensory information conveyed by primary type Ia sensory fibers which spiral around muscle fibres within the spindle, and secondary type II sensory fibers * Activation of muscle fibres within the spindle by up to a dozen gamma motor neurons and to a lesser extent by one or two beta motor neurons ''.'' Structure Muscle spindles are found within the belly of a skeletal muscle. Muscle spindles are fusiform (spindle-shaped), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Stretch Receptors
Pulmonary stretch receptors are mechanoreceptors found in the lungs. When the lung expands, the receptors initiate the Hering-Breuer reflex, which reduces the respiratory rate. This signal is transmitted by vagus nerve. Increased firing from the stretch receptors also increases production of pulmonary surfactant. Intercostal muscles and thoracic diaphragm receive impulses from the respiratory center, stretch receptors in the lungs send impulses to the respiratory center giving information about the state of the lungs. See also * Stretch receptor Stretch receptors are mechanoreceptors responsive to distention of various organs and muscles, and are neurologically linked to the Medulla oblongata, medulla in the brain stem via Afferent nerve fiber, afferent nerve fibers. Examples include stre ... External links * Reference Respiratory physiology Sensory receptors {{Respiratory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordotonal Organ
Chordotonal organs are stretch receptor organs found only in insects and crustaceans. They are located at most joints and are made up of clusters of scolopidia that either directly or indirectly connect two joints and sense their movements relative to one another. They can have both Exteroception, extero- and Proprioception, proprioceptive functions, for example sensing auditory stimuli or leg movement. The word was coined by Vitus Graber in 1882, though he interpreted them as being stretched between two points like a string, sensing vibrations through resonance. Structure Chordotonal organs can be composed of a single Scolopidia, scolopidium with only a single sensory, bipolar neuron (such as the Tympanal organ, tympanal ear of a notodontid moth), or up to several thousand scolopidia, each equipped with up to four sensory neurons (as in the mosquito Johnston's organ). The bipolar sensory neurons each have an apical dendritic structure with a cilium densely packed with microtubu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretch Sensor
A stretch sensor is a sensor which can be used to measure deformation and stretching forces such as tension or bending. They are usually made from a material that is itself soft and stretchable. Most stretch sensors fall into one of three categories. The first type consists of an electrical conductor for which the electrical resistance changes (usually increases) substantially when the sensor is deformed. The second type consists of a capacitor for which the capacitance changes under deformation. Known properties of the sensor can then be used to deduce the deformation from the resistance/capacitance. Both the rheostatic and capacitive types often take the form of a cord, tape, or mesh. The third type of sensor uses high performance piezoelectric systems in soft, flexible/stretchable formats for measuring signals using the capability of piezoelectric materials to interconvert mechanical and electrical forms of energy. Applications Wearable stretch sensors can be used for tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Sinus
In human anatomy, the carotid sinus is a dilated area at the base of the internal carotid artery just superior to the bifurcation of the internal carotid and external carotid at the level of the superior border of thyroid cartilage. The carotid sinus extends from the bifurcation to the "true" internal carotid artery. The carotid sinuses are sensitive to pressure changes in the arterial blood at this level. They are two out of the four baroreception sites in humans and most mammals. Structure The carotid sinus is the reflex area of the carotid artery, consisting of baroreceptors which monitor blood pressure. Function The carotid sinus contains numerous baroreceptors which function as a "sampling area" for many homeostatic mechanisms for maintaining blood pressure. The carotid sinus baroreceptors are innervated by the carotid sinus nerve, which is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX). The neurons which innervate the carotid sinus centrally project to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
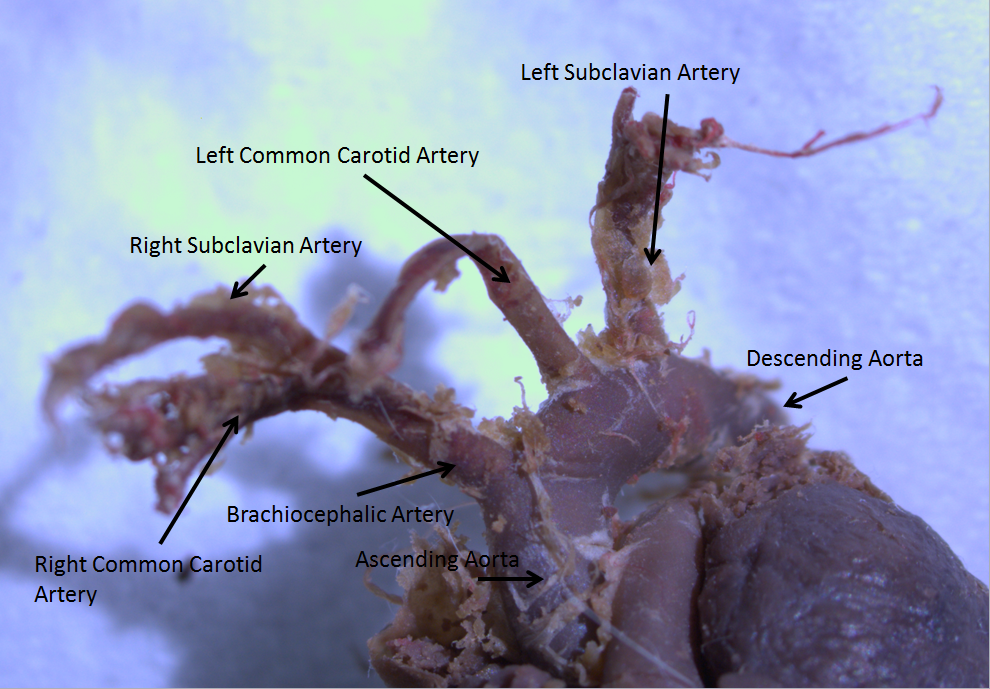
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea. Structure The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second/third sternocostal articulation of the right side, behind the ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary trunk. The right atrial appendage overlaps it. The first few centimeters of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk lies in the same pericardial sheath and runs at first upward, arches over the pulmonary trunk, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus to lie behind the right second coastal cartilage. The right lung and sternum lies anterior to the aorta at this point. The aorta then passes posteriorly and to the left, anterior to the trachea, and arches over left main bronchus and left pulmonary artery, and reaches to the left side of the T4 vertebral body. Apart from T4 vertebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |